How to make a paper airplane fly far involves understanding aerodynamics and utilizing specific folding techniques, and at flyermedia.net, we provide you with the knowledge to create high-performance paper airplanes. This comprehensive guide delves into the art and science of paper airplane construction, offering designs, tips, and tricks to achieve impressive flight distances and durations, plus find comprehensive information about aviation training, aviation news and career opportunities. Unleash your inner aviator with our insights into paper plane aerodynamics, flight optimization strategies, and advanced paper airplane models.
1. What Makes a Paper Airplane Fly Far?
A paper airplane’s ability to fly far hinges on several key factors:
- Aerodynamics: The shape of the wings and body influences lift and drag, crucial for sustained flight.
- Weight Distribution: Proper weight balance ensures stability and prevents nosedives.
- Folding Precision: Accurate folds create clean lines and symmetrical wings, optimizing airflow.
- Throwing Technique: A smooth, consistent launch imparts the necessary velocity and angle for maximum distance.
According to research from Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University, in July 2023, optimizing these elements can significantly improve a paper airplane’s flight performance, achieving distances far beyond simple designs.
2. What Are the Essential Aerodynamic Principles for Paper Airplanes?
The magic behind a soaring paper airplane lies in understanding and applying these aerodynamic principles:
- Lift: Air flowing faster over the top of the wing creates lower pressure, generating an upward force that opposes gravity.
- Drag: Air resistance opposes the airplane’s motion, slowing it down. Minimizing drag is essential for longer flights.
- Thrust: The force that propels the airplane forward, generated by the throw. A strong, consistent throw maximizes thrust.
- Weight: Gravity pulls the airplane downward. Balancing weight distribution is critical for stability.
For more in-depth explanations and visual aids, resources like the FAA’s Pilot’s Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge can provide valuable insights.
3. How Does Weight Distribution Affect a Paper Airplane’s Flight?
Weight distribution is pivotal for a paper airplane’s stability and distance. Noses tend to be heavier than the rest of a paper plane.
- Nose-Heavy: A slightly heavier nose increases stability, preventing the airplane from stalling or wobbling, while reducing the potential to glide far.
- Balanced: Even weight distribution promotes smooth gliding and controlled turns, maximizing flight time.
- Tail-Heavy: Can cause instability and erratic flight patterns, leading to shorter distances.
Experimenting with small adjustments, such as adding a paperclip to the nose, can significantly improve flight performance.
4. What Are the Best Paper Airplane Designs for Distance?
Several designs are renowned for their exceptional distance capabilities:
- The Dart: A classic design with a pointed nose and straight wings, known for its speed and stability.
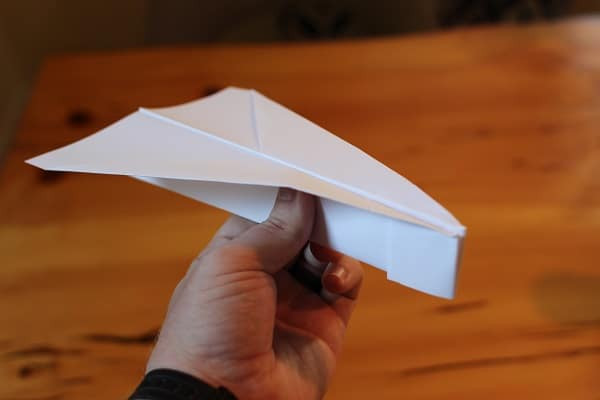 Dart Paper Airplane
Dart Paper Airplane - The Hammer: An advanced design with multiple folds and a unique wing shape, optimized for maximum glide and distance.
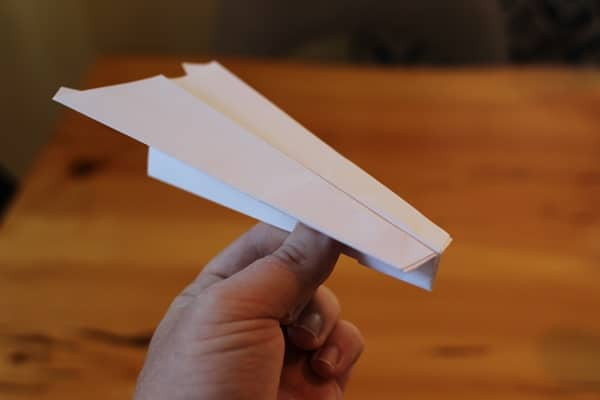 Hammer Paper Airplane
Hammer Paper Airplane - The Stealth: A sleek, aerodynamic design with swept-back wings, ideal for long, straight flights.
Bulldog Dart
-
First you fold the paper in half lengthwise, and then unfold. This initial crease is simply a guideline for the next folds.
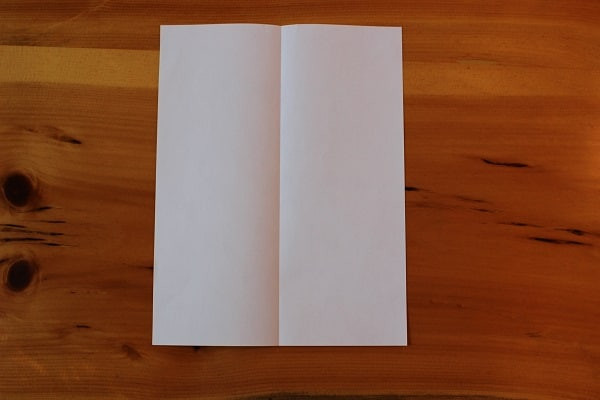 Step 1 — sheet of paper folded in half.
Step 1 — sheet of paper folded in half. -
Fold the top two corners down so they meet the center crease. This is the classic way to start a paper airplane, and probably what you first learned as a kid.
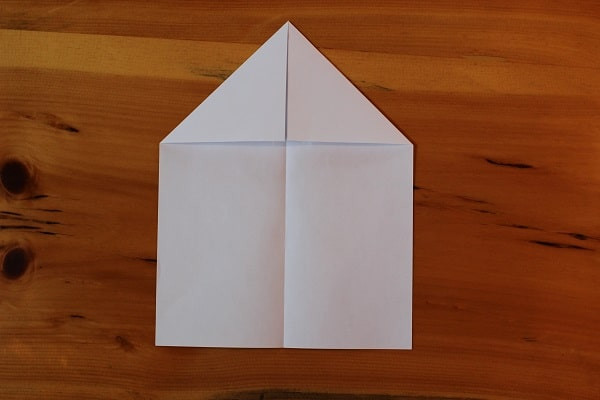 Step 2 — fold top corners down to meet middle crease.
Step 2 — fold top corners down to meet middle crease. -
Flip the plane over, and fold the corners in again to the center crease. You want the diagonal line coming off the top of the plane (on the left side) to be lined up with the middle (like on the right side).
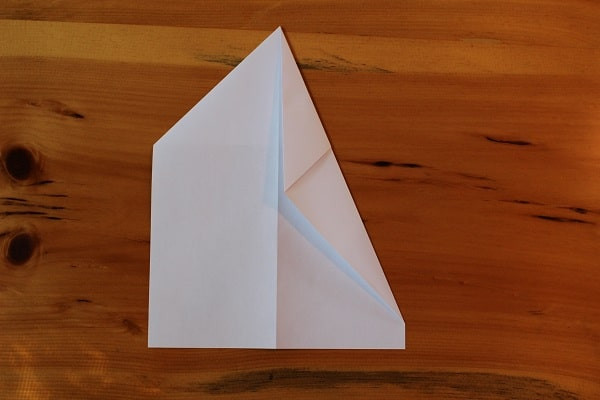 Step 3 — flip over and folder corners again.
Step 3 — flip over and folder corners again.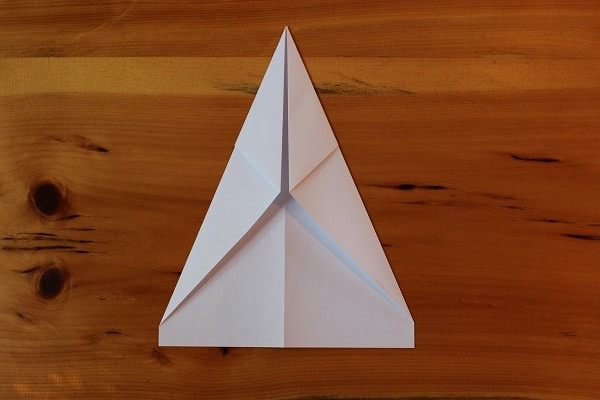 Paper airplane with first 3 steps completed.After both folds are completed.
Paper airplane with first 3 steps completed.After both folds are completed. -
Fold the top point down so that the tip meets the bottom of where the previous folds come together.
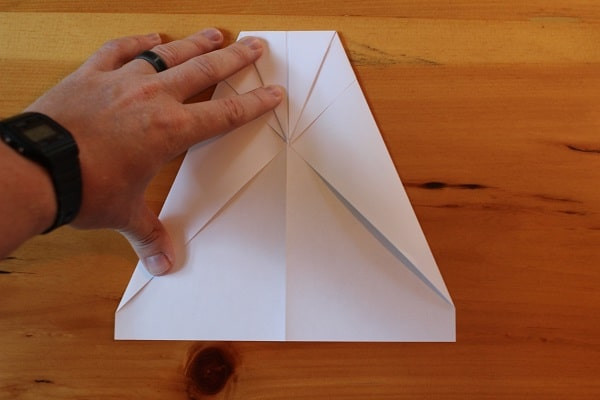 Step 4 — fold top point down.
Step 4 — fold top point down. -
Fold the entire plane in half, in on itself. This creates the snub nose, which gives the Bulldog Dart its name.
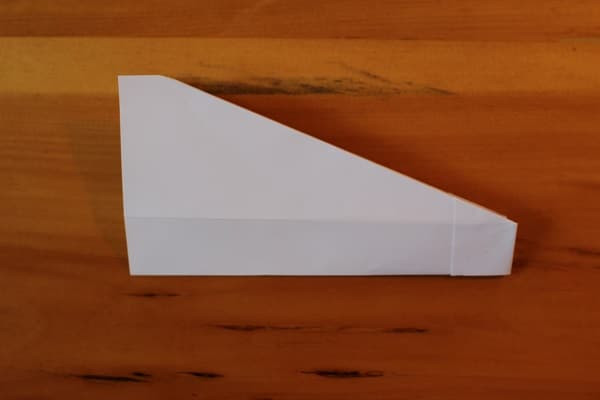 Step 5 — fold plan in half, in on itself.
Step 5 — fold plan in half, in on itself. -
Fold the wings down so that you’re making a straight line across from the top of the snub nose. Repeat on the other side.
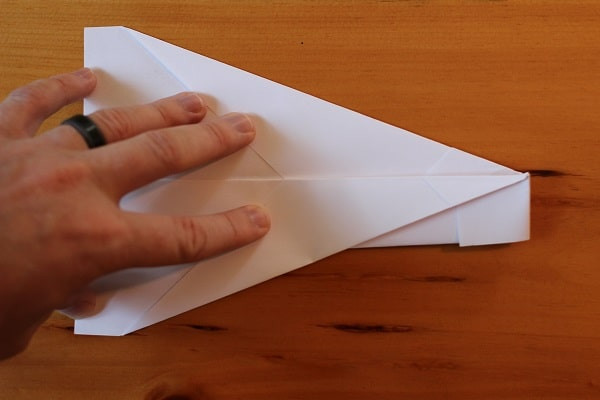 Step 6 — Wings folded down.
Step 6 — Wings folded down. Dart Paper AirplaneThe finished Bulldog Dart. This flies better when thrown at lower speeds. Your tendency is to launch it, but the heavy nose will just fly it into the ground. Give it a softer throw and you’ll have better luck.
Dart Paper AirplaneThe finished Bulldog Dart. This flies better when thrown at lower speeds. Your tendency is to launch it, but the heavy nose will just fly it into the ground. Give it a softer throw and you’ll have better luck.
The Harrier
-
Fold in half lengthwise and then unfold. As with the Bulldog above, this center crease is just a guide for future folds.
 Step 1 — Fold paper in half.
Step 1 — Fold paper in half. -
Fold the top corners in so they meet at the center crease.
 Step 2 — Fold top corners down to meet middle crease.
Step 2 — Fold top corners down to meet middle crease. -
Fold the entire top down so that it resembles an envelope. Make sure you leave a half inch or so at the bottom — you don’t want the top point to evenly meet the bottom edge.
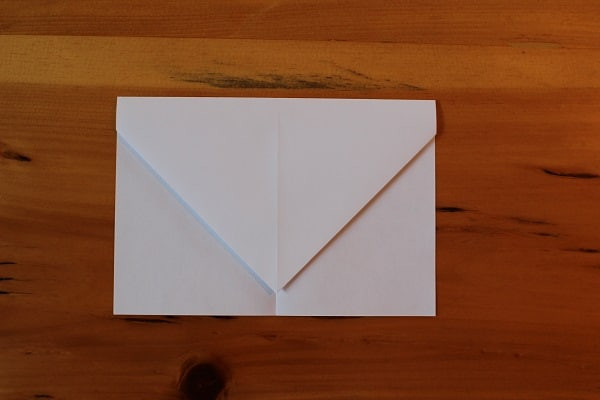 Step 3 — Fold top down so that it resembles an envelope.
Step 3 — Fold top down so that it resembles an envelope. -
Fold the top corners in so they meet at the middle. There should be a small triangle tail hanging out beneath these folds.
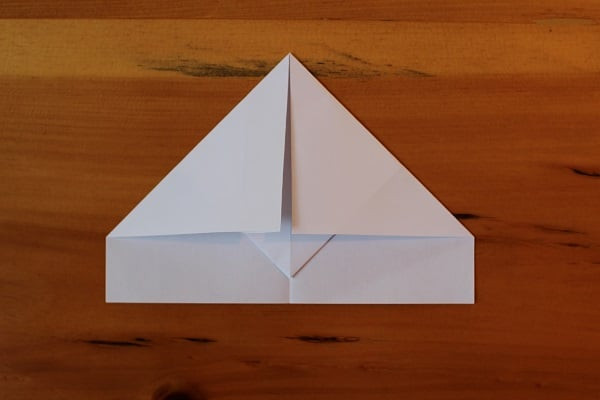 Step 4 — Fold top corners down again, towards middle crease.
Step 4 — Fold top corners down again, towards middle crease. -
Fold that small triangle up to hold those previous folds in place.
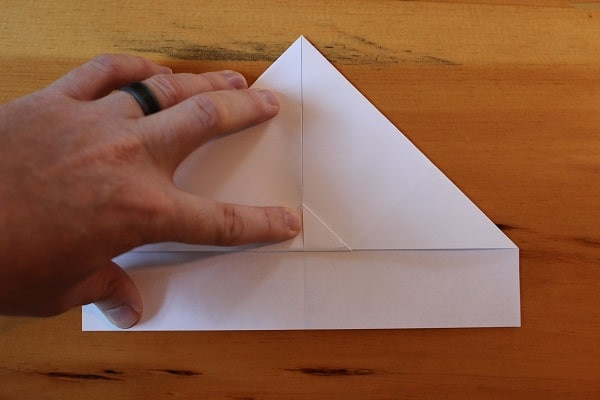 Step 5 — Fold up the small triangle that was left over from the previous step.
Step 5 — Fold up the small triangle that was left over from the previous step. -
Fold in half, but make you sure you fold it outwards on itself, not inwards. You want the previous triangular fold to be visible on the bottom edge.
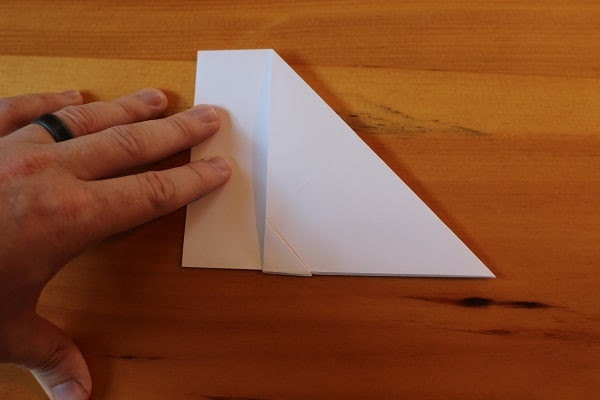 Step 6 — Fold entire airplane in half, outwards.
Step 6 — Fold entire airplane in half, outwards. -
Fold the wing down so its edge meets the bottom edge of the airplane. Repeat on the other side.
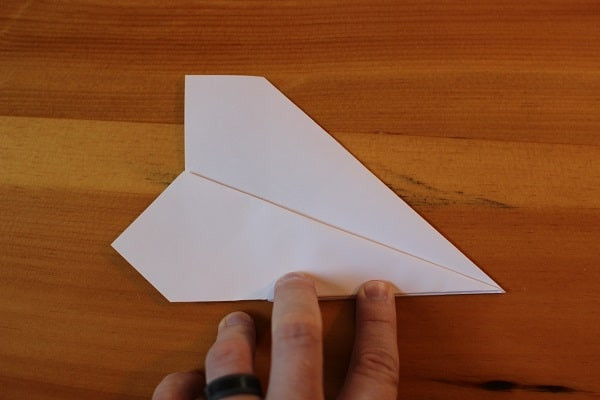 Step 7 — Fold wing down so it meets bottom edge.
Step 7 — Fold wing down so it meets bottom edge.
The finished Harrier shown below. It has cool pointed wings and has great stability because of the triangle on the bottom.
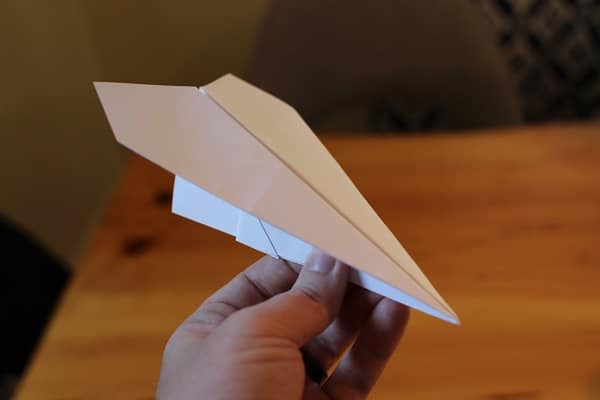 Man holding finished harrier paper airplane.
Man holding finished harrier paper airplane.
The Hammer
-
First, fold the top left corner all the way down so it meets the right edge of the paper. You’ll then unfold, as this will be a guiding crease.
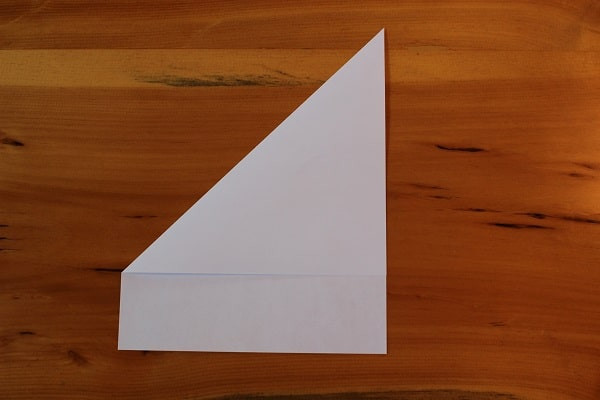 Step 1 — Fold top left corner down.
Step 1 — Fold top left corner down. -
Repeat the same thing with the top right corner and unfold.
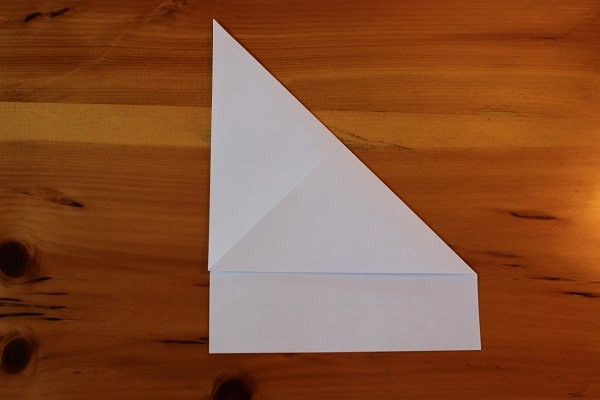 Step 2 — Fold and unfold top right corner to make a crease.
Step 2 — Fold and unfold top right corner to make a crease.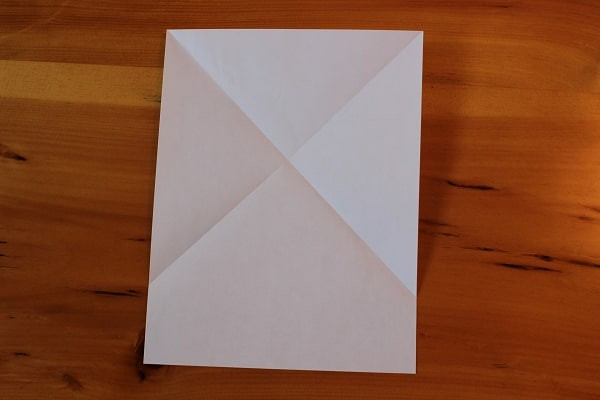 Unfolded sheet of paper with X creases.You should end up with an unfolded sheet of paper with two creases forming an X.
Unfolded sheet of paper with X creases.You should end up with an unfolded sheet of paper with two creases forming an X. -
Fold the top right corner down so that its edge meets the crease that goes from top left to bottom right.
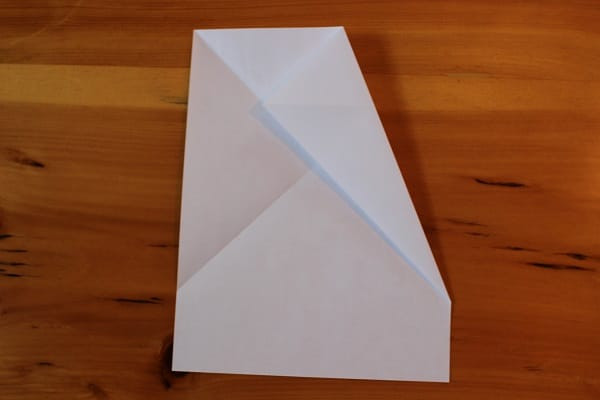 Fold top right corner down to meet diagonal crease.
Fold top right corner down to meet diagonal crease. -
Do the same with the left corner. The top left point should exactly meet the diagonal right edge of the airplane.
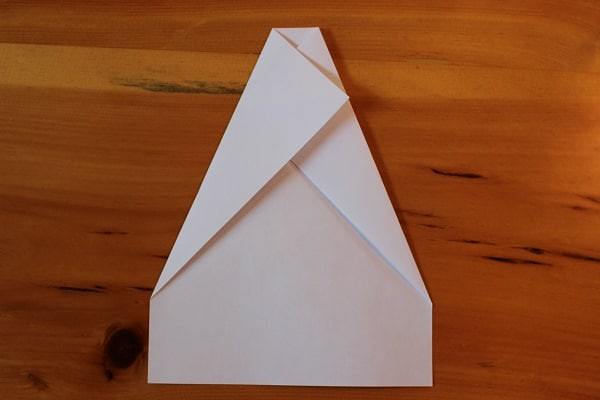 Fold top left corner down to meet diagonal crease in center.
Fold top left corner down to meet diagonal crease in center. -
Fold the plane in half in on itself, then unfold. You’ll use that middle crease as a guide.
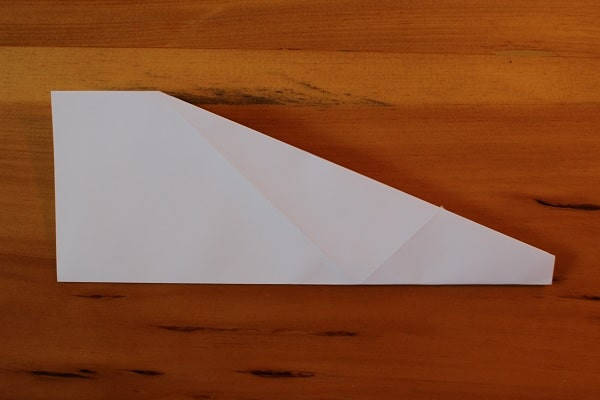 Fold paper airplane in half, in on itself.
Fold paper airplane in half, in on itself. -
After you’ve unfolded the previous step, fold the top down so that its edge meets the bottom edge.
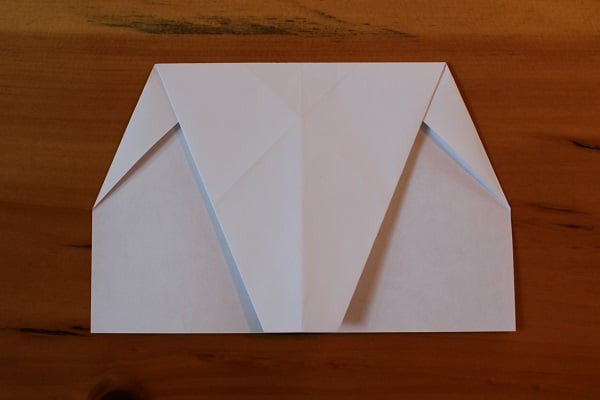 Top half folded down to meet bottom edge.
Top half folded down to meet bottom edge. -
Fold the top corners down so that their points meet at the middle crease.
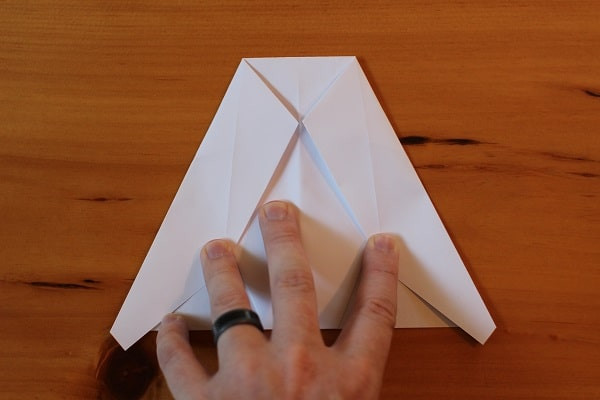 Fold top corners down again so they meet the middle crease.
Fold top corners down again so they meet the middle crease. -
Unfold — as with many steps in making this airplane, these creases are a guide.
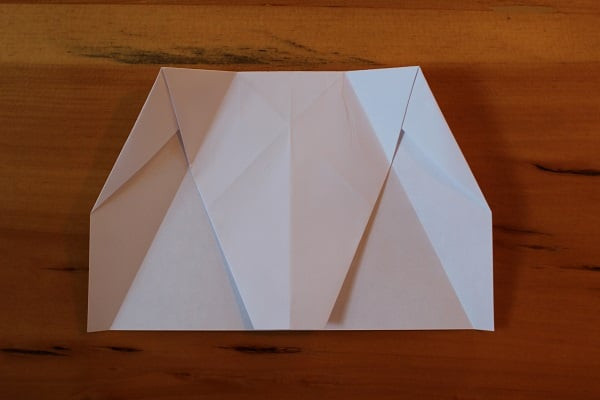 Half of airplane done, unfolded with creases showing.
Half of airplane done, unfolded with creases showing. -
Now take what was the top edge that you previously folded down (Step 6) and fold it back up at the point where its edge meets the creases from the previous step.
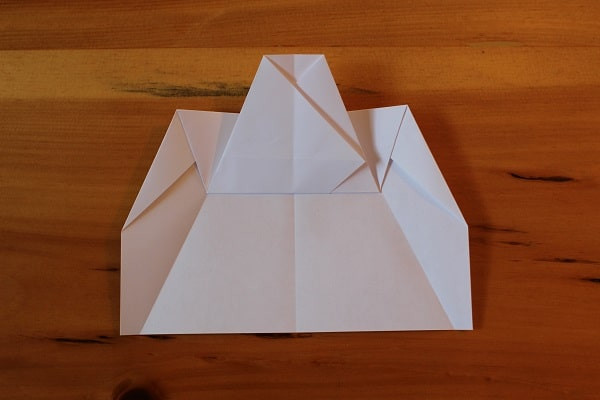 Top part folded up.
Top part folded up. -
Fold the corners in yet again so that their edge meets both the edge of the top flap and the crease from Step 7.
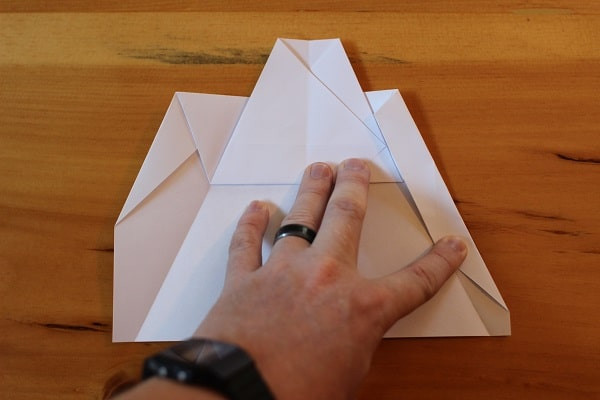 Fold corners in yet again to meet edge of top.
Fold corners in yet again to meet edge of top.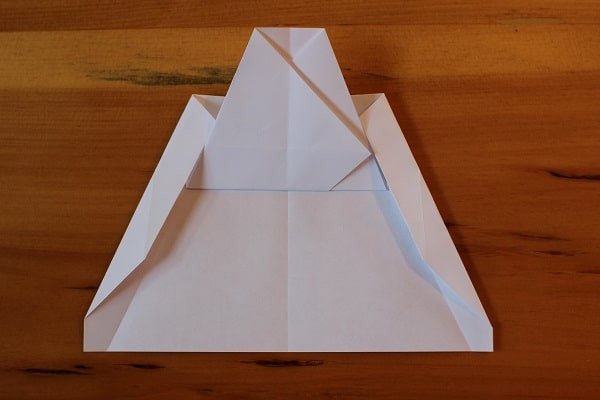 Both corners folded in — airplane almost done.Both corners folded in, meeting both the top flap and the previously-made creases. These are ultimately the wings.
Both corners folded in — airplane almost done.Both corners folded in, meeting both the top flap and the previously-made creases. These are ultimately the wings. -
Fold the wings in once more, this time simply folding along the crease that you already made. After this step your plane should have straight lines down from the top to the bottom.
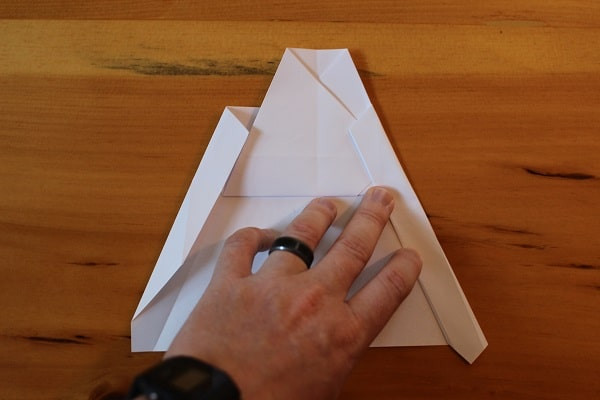 Fold the wings in again, this time so the outside edges meet.
Fold the wings in again, this time so the outside edges meet.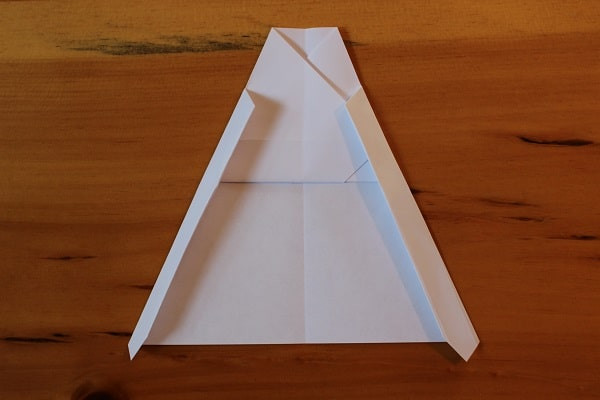 With both sides of wings folded in.Both wings folded in again; straight edges from top to bottom.
With both sides of wings folded in.Both wings folded in again; straight edges from top to bottom. -
Fold the top down from where it meets the top of the wing flaps you created in the previous step.
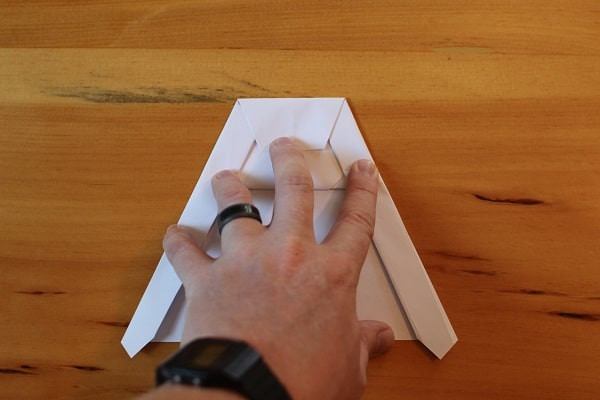 Top folded down to meet the edges of the wings.
Top folded down to meet the edges of the wings. -
Fold the whole thing in half outward. You want all the paper flaps on the outside of the craft. At this point, folding can become a little tricky because of the thickness of the paper, so take extra care in making good, clean folds.
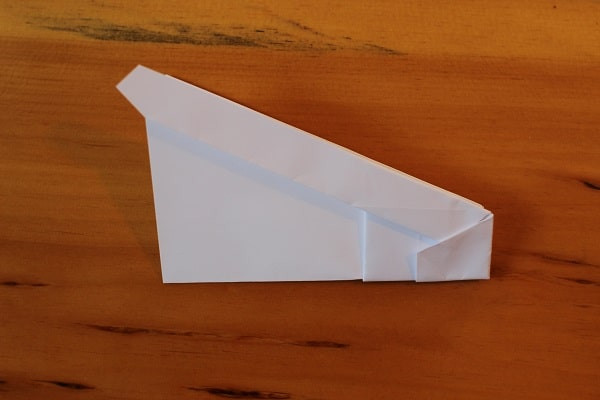 Fold airplane in half, outwards.
Fold airplane in half, outwards. -
Fold the wings down so that their edge meets the bottom edge of the plane. This creates a small snub nose. Again, this can be a tough fold, so be precise and take your time if you have to.
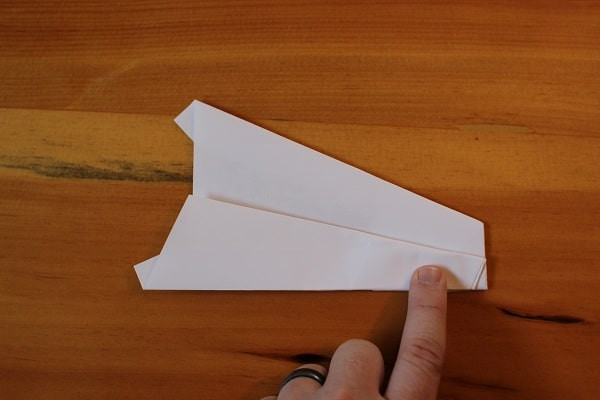 Fold wings down to meet bottom edge of plane.
Fold wings down to meet bottom edge of plane. Man holding finished hammer paper airplane.The finished Hammer. This bad boy flies like a dream.
Man holding finished hammer paper airplane.The finished Hammer. This bad boy flies like a dream.
Each design offers unique aerodynamic properties, catering to different flight styles and preferences.
5. What Type of Paper is Best for Paper Airplanes?
The choice of paper can significantly impact a paper airplane’s performance.
- Lightweight Paper (20 lb): Ideal for distance and glide, as it minimizes weight and maximizes lift.
- Medium-Weight Paper (24 lb): Offers a balance between durability and performance, suitable for various designs.
- Cardstock: Provides excellent durability but may reduce distance due to increased weight.
Experimenting with different paper types can help you find the optimal material for your desired flight characteristics.
6. How Do Folds Impact the Distance a Paper Airplane Can Fly?
Precise and accurate folds are essential for creating a high-performance paper airplane.
- Sharp Creases: Ensure clean, defined edges that optimize airflow and reduce drag.
- Symmetry: Mirror-image folds create balanced wings, promoting stability and straight flight.
- Consistent Technique: Maintain consistent folding pressure and alignment throughout the construction process.
Inconsistent folds can disrupt airflow and lead to erratic flight patterns, diminishing distance and control.
7. What Launching Techniques Maximize Paper Airplane Distance?
Even the best-designed paper airplane requires a proper launch technique to achieve its full potential.
- The Overhand Throw: Provides power and distance, ideal for dart-like designs.
- The Underhand Throw: Offers control and accuracy, suitable for gliding models.
- The Sidearm Throw: Generates spin and stability, maximizing distance in open spaces.
Regardless of the technique, a smooth, consistent motion is crucial for imparting the necessary velocity and angle.
8. How Can Wing Adjustments Improve Paper Airplane Performance?
Making small adjustments to the wings can fine-tune a paper airplane’s flight characteristics.
- Ailerons: Small flaps on the trailing edge of the wings that control roll and turning.
- Elevators: Flaps on the tail that control pitch and altitude.
- Winglets: Upward-pointing extensions on the wingtips that reduce drag and improve stability.
Experimenting with these adjustments can optimize your paper airplane for specific flight conditions and desired maneuvers.
9. What Environmental Factors Affect Paper Airplane Flight?
External conditions can influence a paper airplane’s flight path and distance.
- Wind: Can either aid or hinder flight, depending on direction and strength.
- Temperature: Affects air density, influencing lift and drag.
- Humidity: Can impact paper’s weight and flexibility.
- Altitude: Higher altitudes have thinner air, reducing drag but also lift.
Understanding these factors can help you adjust your launch technique and wing adjustments for optimal performance in various environments.
10. How Can I Troubleshoot Common Paper Airplane Flight Problems?
Even with careful construction and technique, paper airplanes can sometimes exhibit undesirable flight characteristics.
- Nosediving: Indicates a front-heavy design. Adjust weight distribution or wing angle.
- Stalling: Suggests insufficient lift. Increase wing area or adjust the angle of attack.
- Erratic Flight: Points to asymmetry or inconsistent folds. Re-fold the airplane with greater precision.
- Turning Too Sharply: May indicate uneven wing adjustments. Adjust ailerons or winglets for balanced flight.
By systematically diagnosing and addressing these issues, you can fine-tune your paper airplane for optimal performance.
11. Can Paper Airplane Design Be Applied to Real Aviation?
The principles of paper airplane design share surprising similarities with those of real aircraft.
- Aerodynamic Concepts: Lift, drag, thrust, and weight apply to both paper and full-scale airplanes.
- Wing Design: Similar wing shapes and airfoil profiles are used in both.
- Stability and Control: The same control surfaces (ailerons, elevators, rudder) are used to maneuver both types of aircraft.
While paper airplanes are a simplified model, they offer a valuable introduction to the fundamentals of aviation and aerodynamics.
12. Are There Paper Airplane Competitions?
Yes, paper airplane competitions are held worldwide, celebrating the art and science of paper aviation. These competitions often feature categories such as:
- Distance: The airplane that travels the farthest distance.
- Duration: The airplane that stays airborne for the longest time.
- Aerobatics: Demonstrating skill, creativity, and control.
Participating in these events can be a fun and rewarding way to showcase your paper airplane skills and connect with fellow enthusiasts.
13. What Are Some Advanced Techniques for Paper Airplane Design?
For those seeking to push the boundaries of paper airplane performance, several advanced techniques can be explored:
- Variable Camber Wings: Wings with adjustable curvature for optimized lift and drag.
- V-Tails: Tail designs with combined vertical and horizontal stabilizers for improved stability and control.
- Canard Configurations: Airplanes with small wings in front of the main wings for enhanced maneuverability.
Mastering these techniques requires a deeper understanding of aerodynamics and experimentation, but can lead to truly exceptional paper airplane designs.
14. How Does Paper Airplane Design Connect to STEM Education?
Paper airplane design offers a hands-on, engaging way to explore STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) concepts.
- Science: Investigating aerodynamics, lift, drag, and gravity.
- Technology: Applying design principles and construction techniques.
- Engineering: Optimizing designs for performance and stability.
- Mathematics: Calculating angles, ratios, and proportions.
By incorporating paper airplane activities into educational settings, educators can foster creativity, problem-solving skills, and a passion for STEM fields.
15. What Role Does Flyermedia.Net Play in Aviation Enthusiast’s Community?
Flyermedia.net serves as a vital hub for aviation enthusiasts, providing:
- Comprehensive Information: From flight training to industry news, we offer a wealth of knowledge.
- Career Resources: Job listings, career guides, and networking opportunities for aspiring aviation professionals.
- Community Engagement: Forums, articles, and events that connect enthusiasts and foster collaboration.
Whether you’re a seasoned pilot or simply fascinated by flight, flyermedia.net is your gateway to the world of aviation.
16. What Flight Training Programs Are Available in the USA?
The USA boasts a wide array of flight training programs, catering to diverse aspirations and career goals. Notable options include:
- University Programs: Offering bachelor’s degrees in aviation, such as Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University and Purdue University.
- Flight Schools: Providing specialized flight training and certifications, such as ATP Flight School and FlightSafety Academy.
- Military Training: Offering world-class pilot training through the Air Force, Navy, and Army.
Each program offers unique advantages, from comprehensive academic instruction to intensive hands-on flight experience.
17. How Can I Stay Updated With Aviation News and Regulations?
Staying informed about the latest aviation news and regulations is crucial for pilots, enthusiasts, and industry professionals. Reliable sources include:
- FAA Website: Provides official updates, regulations, and safety information.
- Aviation News Outlets: such as Aviation Week & Space Technology, FlightGlobal, and General Aviation News.
- Industry Associations: such as the Aircraft Owners and Pilots Association (AOPA) and the National Business Aviation Association (NBAA).
By regularly consulting these resources, you can stay ahead of the curve and ensure compliance with evolving industry standards.
18. What Career Opportunities Exist in the Aviation Industry?
The aviation industry offers a wide range of career paths, from piloting and air traffic control to engineering and management. Popular options include:
- Pilots: Flying commercial airlines, cargo planes, or private aircraft.
- Air Traffic Controllers: Managing the safe and efficient flow of air traffic.
- Aerospace Engineers: Designing and developing aircraft and spacecraft.
- Maintenance Technicians: Inspecting, repairing, and maintaining aircraft.
- Airport Managers: Overseeing the operations and administration of airports.
With a growing demand for skilled professionals, the aviation industry presents numerous opportunities for those with passion and dedication.
19. How Does Flyermedia.Net Help Aspiring Aviators?
Flyermedia.net plays a pivotal role in guiding aspiring aviators toward their dreams by:
- Providing Educational Resources: Articles, guides, and tutorials that cover all aspects of aviation.
- Connecting Students with Flight Schools: A directory of reputable flight schools and training programs across the USA.
- Offering Career Counseling: Guidance and support to help students navigate their career paths in aviation.
By leveraging flyermedia.net, aspiring aviators can gain the knowledge, resources, and connections they need to succeed in the aviation industry.
20. What Are the Key Considerations When Choosing a Flight School?
Selecting the right flight school is a crucial step toward a successful aviation career. Key considerations include:
- Accreditation: Ensuring the school meets industry standards and regulatory requirements.
- Curriculum: Evaluating the comprehensiveness and relevance of the training program.
- Instructors: Assessing the experience and qualifications of the flight instructors.
- Aircraft: Examining the quality and maintenance of the training aircraft.
- Location: Considering the accessibility and suitability of the training environment.
- Cost: Comparing tuition fees, living expenses, and other associated costs.
Thorough research and careful evaluation are essential for making an informed decision.
21. How Can I Finance My Flight Training?
Financing flight training can be a significant challenge, but several options are available:
- Student Loans: Federal and private loans designed specifically for flight training.
- Scholarships: Grants and awards offered by aviation organizations and educational institutions.
- Military Service: Enlisting in the military and receiving pilot training.
- Employer Sponsorship: Some airlines and aviation companies offer financial assistance to aspiring pilots.
- Personal Savings: Utilizing personal funds to cover the cost of training.
A combination of these strategies can help make flight training more affordable and accessible.
22. What Are the Medical Requirements for Becoming a Pilot?
Pilots must meet specific medical standards to ensure they are fit to fly safely. The FAA requires pilots to obtain a medical certificate, which involves a physical examination by an FAA-approved aviation medical examiner (AME). The three classes of medical certificates are:
- First Class: Required for airline transport pilots (ATP).
- Second Class: Required for commercial pilots.
- Third Class: Required for private pilots, recreational pilots, and student pilots.
The medical examination assesses various factors, including vision, hearing, cardiovascular health, and neurological function.
23. What is the Role of the FAA in Aviation Safety?
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) plays a crucial role in ensuring aviation safety in the United States. Its responsibilities include:
- Regulating Air Commerce: Establishing and enforcing regulations for air carriers, airports, and aviation personnel.
- Certifying Pilots and Aircraft: Issuing licenses and certificates to qualified pilots and ensuring aircraft meet safety standards.
- Managing Airspace: Controlling air traffic and providing air navigation services.
- Promoting Aviation Safety: Developing and implementing programs to prevent accidents and incidents.
Through its comprehensive oversight and regulatory framework, the FAA strives to maintain the highest levels of safety in the national airspace system.
24. How Do Airlines Ensure Passenger Safety?
Airlines prioritize passenger safety through a multi-layered approach that encompasses:
- Rigorous Maintenance Programs: Regular inspections, repairs, and maintenance of aircraft.
- Pilot Training and Proficiency: Continuous training and evaluation of pilots.
- Standard Operating Procedures: Strict adherence to standardized procedures for all phases of flight.
- Crew Resource Management: Effective communication and coordination among flight crew members.
- Security Measures: Enhanced security protocols to prevent terrorism and other threats.
By implementing these measures, airlines strive to minimize risks and ensure the well-being of their passengers.
25. How Can Passengers Contribute to Aviation Safety?
Passengers also play a vital role in aviation safety by:
- Following Crew Instructions: Adhering to the instructions and guidance provided by flight attendants and pilots.
- Remaining Seated and Belted: Keeping seatbelts fastened during turbulence and other unexpected events.
- Stowing Carry-On Luggage Properly: Ensuring luggage is securely stowed to prevent injuries during turbulence.
- Reporting Suspicious Activity: Alerting crew members to any unusual or concerning behavior.
- Avoiding Disruptive Behavior: Refraining from actions that could distract or interfere with the flight crew.
By being responsible and vigilant, passengers can contribute to a safer and more secure flying environment.
26. What is the Future of Aviation?
The aviation industry is constantly evolving, with exciting developments on the horizon:
- Electric and Hybrid Aircraft: Developing more sustainable and fuel-efficient aircraft.
- Autonomous Flight: Exploring the potential of self-flying aircraft and drones.
- Urban Air Mobility: Creating new transportation systems that utilize vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) aircraft.
- Space Tourism: Offering commercial flights to space for private citizens.
These innovations promise to revolutionize air travel and create new opportunities for the aviation industry.
27. How Is Technology Improving Aviation Safety?
Advancements in technology are continuously enhancing aviation safety:
- Advanced Navigation Systems: GPS, enhanced vision systems, and other technologies that improve situational awareness.
- Automated Flight Control Systems: Autopilot, flight management systems, and other systems that reduce pilot workload.
- Predictive Maintenance: Using data analytics to identify potential maintenance issues before they occur.
- Enhanced Weather Monitoring: Improved weather radar and forecasting systems that provide more accurate and timely information.
- Collision Avoidance Systems: TCAS (Traffic Collision Avoidance System) and other systems that help prevent mid-air collisions.
By integrating these technologies, the aviation industry is striving to make air travel safer and more reliable than ever before.
28. What Kind of Aircraft are Used for Flight Training?
Beginner pilots often train in aircraft that are easy to maneuver and forgiving.
- Cessna 172 Skyhawk: An airplane with high wings known for stability.
- Piper PA-28 Cherokee: A low-wing aircraft that offers simplicity.
29. Why You Should Pursue Aviation in the USA?
The USA stands out for these reasons:
- Quality Training: Globally recognized institutions ensure high standards.
- Career Opportunities: A booming aviation market is always looking for talent.
- Innovation: Take part in the latest aviation technology and progress.
- Community: Join a supportive network of aviation lovers and professionals.
- Scenic Routes: Enjoy flying through varied and breathtaking landscapes.
30. What Are the Benefits of Using Flight Simulators?
Flight simulators are used to teach pilots of all levels.
- Cost-Effective: Saves money over real flying time.
- Risk-Free Learning: Safely practice dangerous maneuvers.
- Versatile Training: Practice different weather situations.
- Skill Enhancement: Hone skills that can improve flying.
- Procedure Training: Greatly enhance your knowledge of checklists.
31. What Resources Can Help Me Learn About Aviation History?
If you want to learn about aviation, check out these resources.
- Museums: Visit aviation museums.
- Books: Read aviation history books.
- Documentaries: Aviation documentaries.
- Websites: Check out aviation websites.
32. Why Is Continuing Education Important in Aviation?
The FAA requires recurrent training, and it is good to continue learning about aviation to stay current.
- Safety: Helps reduce accidents.
- Career: Helps improve advancement.
- Technology: Helps keep up with technology.
- Regulations: Keeps you up to date.
33. How Can I Promote Aviation to the Younger Generation?
If you want to promote aviation to younger people.
- Aviation Programs: Introduce aviation programs.
- Flight Simulation: Expose them to flight simulation.
- Aviation Museums: Visit aviation museums with children.
- Careers: Let them know about careers in aviation.
34. How Does Flyermedia.net Support Diversity in Aviation?
Flyermedia.net is dedicated to promoting diversity and inclusivity within the aviation sector by:
- Highlighting Diverse Role Models: Showcasing stories of successful aviators from various backgrounds.
- Offering Scholarship Resources: Providing information on scholarships and financial aid opportunities for underrepresented groups.
- Creating a Welcoming Community: Fostering a supportive and inclusive environment for all aviation enthusiasts.
By championing diversity, flyermedia.net aims to create a more equitable and representative aviation industry.
FAQ About How To Make a Paper Airplane Fly Far
- What is the best type of paper for a paper airplane? Lightweight paper is generally best for distance, while medium-weight paper offers a good balance of durability and performance.
- How important are accurate folds in making a paper airplane? Accurate folds are crucial for creating clean lines, symmetrical wings, and optimal airflow, all of which contribute to flight performance.
- Does the size of a paper airplane affect its flight? Yes, smaller paper airplanes tend to be faster and more maneuverable, while larger airplanes can have greater glide and stability.
- Can adding weight to a paper airplane improve its flight? Adding a small amount of weight to the nose can improve stability and prevent nosediving, but too much weight can reduce distance.
- How does the design of the wings affect a paper airplane’s flight? The shape, size, and angle of the wings determine the amount of lift and drag generated, influencing the airplane’s flight characteristics.
- Is there an optimal throwing technique for paper airplanes? The optimal throwing technique depends on the design of the airplane, but a smooth, consistent motion is crucial for imparting the necessary velocity and angle.
- What effect does wind have on paper airplane flight? Wind can either aid or hinder flight, depending on its direction and strength. Flying into the wind can reduce distance, while flying with the wind can increase it.
- How can I adjust a paper airplane to fly straight? If a paper airplane consistently turns to one side, try making small adjustments to the ailerons or winglets to balance the airflow.
- Are there any record-breaking paper airplane flights? Yes, there are official world records for both distance and duration of paper airplane flights.
- Where can I find more advanced paper airplane designs and instructions? Websites, books, and online communities dedicated to paper airplanes offer a wealth of resources for advanced designs and techniques.
Ready to take your paper airplane skills to new heights? Visit flyermedia.net today to discover a wealth of information on aviation training, industry news, and career opportunities. Whether you’re an aspiring pilot or simply fascinated by flight, flyermedia.net is your ultimate resource for all things aviation. Contact us at Address: 600 S Clyde Morris Blvd, Daytona Beach, FL 32114, United States, Phone: +1 (386) 226-6000, or visit our website at flyermedia.net.
