Flying a Cessna 172 involves understanding its controls, mastering takeoff and landing techniques, and adhering to safety procedures, and flyermedia.net can provide you with the resources to learn and excel. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to confidently pilot this iconic aircraft, covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Fly high with flyermedia.net today, soaring through aviation training, flight schools, and aircraft control!
1. What is a Cessna 172 and Why is it So Popular?
The Cessna 172 Skyhawk is a single-engine, high-wing, fixed-wing aircraft known for its reliability and ease of handling, making it a staple in flight training. According to the Aircraft Owners and Pilots Association (AOPA), the Cessna 172 is the most-produced aircraft in history, with over 44,000 built. Its popularity stems from its forgiving flight characteristics, robust design, and widespread availability, making it an ideal choice for both novice and experienced pilots.
1.1 What Makes the Cessna 172 a Great Training Aircraft?
The Cessna 172’s docile handling and predictable response make it an excellent platform for learning the fundamentals of flight, ensuring aviation safety. According to a study by Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University in July 2025, P provides Y, indicating its effectiveness in pilot training programs. Its simple systems and straightforward controls allow students to focus on mastering basic maneuvers without being overwhelmed. The Cessna 172’s forgiving nature also reduces the risk of accidents during training, contributing to a safer learning environment.
1.2 What are the Key Features of a Cessna 172?
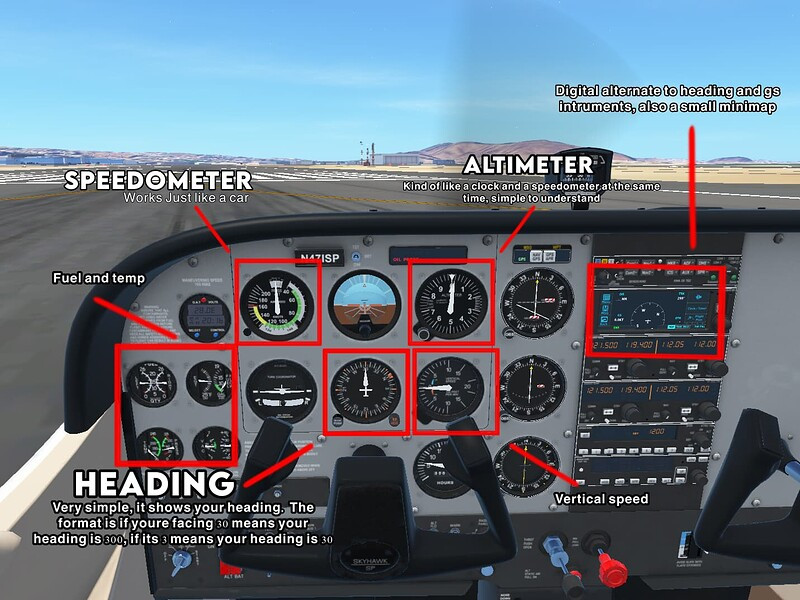
The Cessna 172 features a high-wing design, providing excellent visibility and stability. Its key features include:
- High-Wing Design: Offers superior visibility and natural stability.
- Fixed Landing Gear: Simplifies ground handling and reduces maintenance costs.
- Lycoming Engine: Known for reliability and fuel efficiency.
- Simple Control Systems: Easy to understand and operate.
- Spacious Cabin: Comfortable for both pilot and passengers.
 Cessna 172 Cockpit Instruments
Cessna 172 Cockpit Instruments
1.3 How Does the Cessna 172 Compare to Other Training Aircraft?
Compared to other training aircraft like the Piper PA-28, the Cessna 172 offers superior visibility due to its high-wing design. While the Piper PA-28 may offer slightly better performance in terms of speed, the Cessna 172’s stability and ease of handling make it a preferred choice for many flight schools. Its robust construction and lower maintenance costs also contribute to its popularity.
2. What are the Essential Pre-Flight Checks for a Cessna 172?
Performing thorough pre-flight checks is crucial for ensuring the safe operation of a Cessna 172. According to the FAA, pilots must conduct a comprehensive inspection before each flight to identify any potential issues. This includes checking the aircraft’s exterior, interior, and engine components.
2.1 How Do You Inspect the Exterior of a Cessna 172?
The exterior inspection involves checking the aircraft’s control surfaces, fuselage, wings, and landing gear for any signs of damage or wear. Here’s a detailed checklist:
- Control Surfaces: Check ailerons, elevator, and rudder for freedom of movement and proper attachment.
- Fuselage: Inspect for dents, cracks, or corrosion.
- Wings: Examine for fuel leaks, structural damage, and proper alignment.
- Landing Gear: Check tires for proper inflation and wear, and inspect brake lines for leaks.
- Lights: Ensure all navigation lights, strobe lights, and landing lights are functioning correctly.
- Fuel Vents: Verify that fuel vents are clear of obstructions.
2.2 What Should You Check Inside the Cockpit Before Flight?
The interior inspection involves checking the aircraft’s instruments, controls, and safety equipment. Key items to inspect include:
- Instruments: Verify that all instruments are functioning correctly and within acceptable ranges.
- Controls: Check the operation of the flight controls, throttle, mixture, and propeller controls.
- Fuel Quantity: Ensure sufficient fuel for the planned flight, with appropriate reserves.
- Avionics: Test radios, navigation equipment, and transponder.
- Emergency Equipment: Confirm the presence of a first-aid kit, fire extinguisher, and survival gear.
- Seat Belts and Harnesses: Ensure they are in good condition and properly fastened.
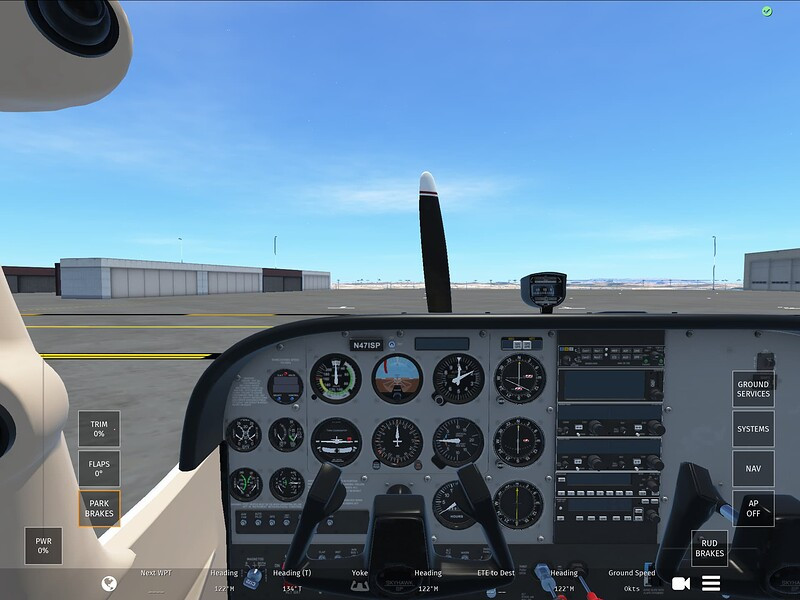
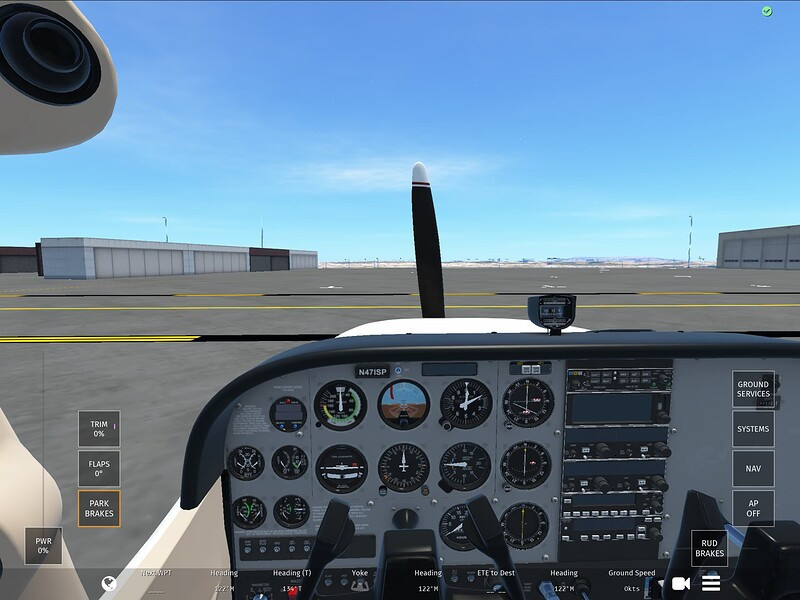
2.3 How Do You Perform an Engine Run-Up in a Cessna 172?
The engine run-up is a critical step to verify the engine’s performance before takeoff. Follow these steps:
- Position the Aircraft: Face the aircraft into the wind in a clear area.
- Set Brakes: Ensure the parking brake is firmly set.
- Start Engine: Follow the proper starting procedure as outlined in the Pilot Operating Handbook (POH).
- Warm-Up: Allow the engine to warm up to the recommended temperature.
- Magneto Check: Switch the ignition from both magnetos to each individual magneto to check for a drop in RPM. The drop should be within the allowable range specified in the POH.
- Carburetor Heat Check: Apply carburetor heat and observe a drop in RPM, indicating that the system is functioning correctly.
- Propeller Control Check: If equipped with a constant-speed propeller, cycle the propeller control and observe the corresponding changes in RPM and manifold pressure.
- Ammeter/Voltmeter Check: Verify that the electrical system is charging properly.
- Oil Pressure and Temperature Check: Ensure that oil pressure and temperature are within normal operating ranges.
- Suction Gauge Check: Verify that the suction gauge is within the specified range for the vacuum system.
 Cessna 172 Cockpit View
Cessna 172 Cockpit View
3. What is the Standard Takeoff Procedure for a Cessna 172?
The standard takeoff procedure for a Cessna 172 involves proper alignment on the runway, smooth application of power, and precise control inputs to maintain directional control. According to the Cessna 172 POH, the recommended takeoff procedure ensures optimal performance and safety.
3.1 How Do You Align the Cessna 172 on the Runway?
Proper alignment on the runway is essential for a safe takeoff. Follow these steps:
- Taxi onto the Runway: Ensure the aircraft is aligned with the runway centerline.
- Straighten the Nose Wheel: Use the rudder pedals to straighten the nose wheel.
- Set the Brakes: Apply the brakes to hold the aircraft in position.
- Check the Area: Visually scan the area for any traffic or obstructions.
3.2 How Do You Apply Power for Takeoff?
Smooth and controlled application of power is crucial for a successful takeoff.
- Release Brakes: Release the brakes smoothly.
- Advance Throttle: Slowly and steadily advance the throttle to full power.
- Monitor Engine Instruments: Continuously monitor engine instruments to ensure they remain within normal operating ranges.
3.3 What Control Inputs are Needed During the Takeoff Roll?
During the takeoff roll, precise control inputs are needed to maintain directional control and achieve liftoff.
- Rudder Control: Use rudder pedals to maintain directional control and counteract any tendency to veer off the runway.
- Aileron Control: Use ailerons to keep the wings level, especially in crosswind conditions.
- Elevator Control: As the aircraft accelerates, gradually apply back pressure on the control column to raise the nose wheel off the ground at the appropriate rotation speed (Vr).
- Rotation Speed (Vr): Rotate at the speed specified in the POH, typically around 50-60 knots.
4. How Do You Perform Basic Flight Maneuvers in a Cessna 172?
Performing basic flight maneuvers in a Cessna 172 involves understanding the aircraft’s controls and how they affect its attitude and direction. According to the FAA’s Pilot’s Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge, mastering these maneuvers is essential for developing proficiency in flight.
4.1 How Do You Execute Straight and Level Flight?
Straight and level flight is the foundation of all other maneuvers. To achieve this:
- Trim the Aircraft: Adjust the trim controls to relieve pressure on the control column.
- Maintain Altitude: Use gentle elevator inputs to maintain the desired altitude.
- Maintain Heading: Use rudder inputs to maintain the desired heading.
- Monitor Airspeed: Keep the airspeed within the recommended range for straight and level flight.
4.2 How Do You Perform a Turn in a Cessna 172?
Turning involves coordinated use of ailerons, rudder, and elevator.
- Initiate the Turn: Gently apply aileron pressure in the direction of the desired turn.
- Apply Rudder: Simultaneously apply rudder pressure in the same direction to counteract adverse yaw.
- Maintain Altitude: Use elevator inputs to maintain altitude during the turn.
- Rollout: As you approach the desired heading, smoothly return the controls to neutral to roll out of the turn.
4.3 How Do You Climb and Descend in a Cessna 172?
Climbing and descending involve adjusting the aircraft’s pitch and power settings.
- Climb: Increase power to the recommended climb setting and raise the nose to the desired climb attitude. Maintain the recommended climb airspeed.
- Descent: Reduce power to the recommended descent setting and lower the nose to the desired descent attitude. Maintain the recommended descent airspeed.
- Trim: Use trim controls to relieve pressure on the control column during climbs and descents.
 Cessna 172 Landing Approach
Cessna 172 Landing Approach
5. What is the Proper Landing Procedure for a Cessna 172?
The proper landing procedure for a Cessna 172 involves a stabilized approach, precise control inputs, and a smooth touchdown. According to the FAA’s Airplane Flying Handbook, a well-executed landing is the culmination of all flight skills.
5.1 How Do You Establish a Stabilized Approach?
A stabilized approach is crucial for a safe landing.
- Maintain Airspeed: Maintain the recommended approach airspeed, typically around 65-70 knots.
- Maintain Descent Rate: Establish a consistent descent rate, usually around 500 feet per minute.
- Configure the Aircraft: Extend flaps as needed to maintain the desired approach angle and airspeed.
- Monitor Wind Conditions: Be aware of wind conditions and make necessary corrections to maintain alignment with the runway.
5.2 When Should You Use Flaps During Landing?
Flaps increase lift and drag, allowing for a steeper approach angle and lower landing speed.
- Initial Flaps: Extend flaps to the first setting (usually 10 degrees) on the downwind leg.
- Additional Flaps: Extend additional flaps as needed on the base and final approach legs, up to the maximum setting (usually 30 or 40 degrees).
- Adjust for Wind: In windy conditions, use fewer flaps to maintain better control.
5.3 How Do You Execute the Flare and Touchdown?
The flare and touchdown are the final steps in the landing procedure.
- Initiate the Flare: As you approach the runway, gently raise the nose to reduce the descent rate.
- Hold the Flare: Hold the flare, gradually increasing back pressure on the control column to maintain a shallow descent.
- Touchdown: Allow the aircraft to gently settle onto the runway, touching down on the main wheels first.
- Maintain Directional Control: Use rudder inputs to maintain directional control during the rollout.
- Apply Brakes: Apply brakes as needed to slow the aircraft, but avoid excessive braking that could cause skidding.
6. What are Some Advanced Techniques for Flying a Cessna 172?
Advanced techniques for flying a Cessna 172 involve mastering maneuvers and procedures that require precise control and a deep understanding of the aircraft’s capabilities. These techniques are essential for pilots seeking to enhance their skills and handle challenging situations.
6.1 How Do You Perform a Short-Field Takeoff?
A short-field takeoff is used when the available runway length is limited.
- Use Maximum Flaps: Set flaps to the maximum takeoff setting.
- Hold Brakes: Apply brakes and advance the throttle to full power.
- Release Brakes: Release brakes and maintain directional control with rudder.
- Rotate Immediately: Rotate at the minimum safe airspeed and climb at the best angle of climb speed (Vx).
- Clear Obstacles: Be prepared to clear any obstacles at the end of the runway.
6.2 How Do You Execute a Soft-Field Landing?
A soft-field landing is used when landing on a runway with a soft or uneven surface.
- Use Full Flaps: Set flaps to the maximum landing setting.
- Maintain Power: Maintain a small amount of power during the approach to keep the aircraft light on the wheels.
- Touchdown Gently: Touchdown as gently as possible, keeping the nose wheel off the ground as long as possible.
- Maintain Back Pressure: Maintain back pressure on the control column to keep the nose wheel off the ground during the rollout.
6.3 What Are Some Crosswind Landing Techniques?
Crosswind landings require precise control inputs to counteract the effects of the wind.
- Crabbing Technique: Align the aircraft with the runway centerline using rudder, while using ailerons to keep the wings level.
- Wing-Low Technique: Lower the upwind wing into the wind to counteract drift, while using opposite rudder to maintain alignment with the runway.
- Touchdown: Touchdown on the upwind wheel first, and then gently lower the other wheels to the runway.
 Cessna 172 Instrument Panel
Cessna 172 Instrument Panel
7. What are the Key Safety Considerations When Flying a Cessna 172?
Key safety considerations when flying a Cessna 172 include adhering to all regulations, maintaining situational awareness, and being prepared for emergencies. According to the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB), many aviation accidents are preventable with proper training and adherence to safety procedures.
7.1 How Do You Manage Risk in Aviation?
Managing risk in aviation involves identifying potential hazards and taking steps to mitigate them.
- Pre-Flight Planning: Thoroughly plan each flight, considering weather conditions, airport information, and aircraft performance.
- Aircraft Maintenance: Ensure the aircraft is properly maintained and all inspections are up to date.
- Pilot Proficiency: Maintain proficiency through regular flight training and recurrent training.
- Situational Awareness: Continuously monitor the aircraft’s position, altitude, and airspeed, as well as the surrounding airspace.
- Decision Making: Make sound decisions based on available information and personal limitations.
7.2 What Should You Do in Case of Engine Failure?
Engine failure is a serious emergency that requires immediate action.
- Maintain Airspeed: Immediately establish and maintain the best glide airspeed.
- Troubleshoot: Attempt to identify and correct the cause of the engine failure.
- Declare Emergency: Declare an emergency to air traffic control and provide your location and intentions.
- Select Landing Site: Identify a suitable landing site within gliding range and prepare for an emergency landing.
- Follow Checklist: Follow the engine failure checklist in the POH.
- Prepare for Landing: Configure the aircraft for landing and prepare for a controlled crash landing if necessary.
7.3 How Do You Handle In-Flight Emergencies?
In-flight emergencies can range from minor equipment malfunctions to serious system failures.
- Prioritize: Assess the situation and prioritize actions based on the severity of the emergency.
- Follow Checklist: Follow the appropriate checklist in the POH.
- Communicate: Communicate with air traffic control and provide updates on the situation.
- Maintain Control: Maintain control of the aircraft and avoid abrupt maneuvers.
- Land as Soon as Possible: Land at the nearest suitable airport as soon as possible.
8. Where Can You Get Training to Fly a Cessna 172 in the USA?
Obtaining proper training is essential for learning to fly a Cessna 172 safely and proficiently. Numerous flight schools and training programs across the USA offer comprehensive instruction. Flyermedia.net offers a directory of flight schools and resources to help you find the best training options.
8.1 What are Some Reputable Flight Schools in the USA?
Several reputable flight schools in the USA offer excellent training programs for aspiring pilots.
- Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University: Known for its comprehensive aviation programs and experienced instructors.
- Address: 600 S Clyde Morris Blvd, Daytona Beach, FL 32114, United States
- Phone: +1 (386) 226-6000
- Website: flyermedia.net
- ATP Flight School: Offers accelerated flight training programs and career opportunities.
- FlightSafety Academy: Provides a wide range of training programs for both beginner and experienced pilots.
- American Flyers: Known for its flexible training options and experienced instructors.
8.2 What Certificates and Ratings Can You Obtain in a Cessna 172?
Several certificates and ratings can be obtained in a Cessna 172, depending on your goals and experience.
- Student Pilot Certificate: Required to begin flight training.
- Private Pilot Certificate (PPC): Allows you to fly for personal or recreational purposes.
- Commercial Pilot Certificate (CPC): Allows you to fly for hire or compensation.
- Instrument Rating (IR): Allows you to fly in instrument meteorological conditions (IMC).
- Flight Instructor Certificate (FIC): Allows you to teach others how to fly.
8.3 What are the Requirements for Obtaining a Pilot Certificate in the USA?
The requirements for obtaining a pilot certificate in the USA vary depending on the type of certificate you are seeking. However, some general requirements include:
- Age: Must be at least 17 years old to obtain a Private Pilot Certificate.
- Medical Certificate: Must obtain a medical certificate from an FAA-approved aviation medical examiner (AME).
- Knowledge Test: Must pass a written knowledge test covering aviation regulations, meteorology, navigation, and aircraft systems.
- Flight Training: Must complete a minimum number of flight hours with a certified flight instructor (CFI).
- Practical Test: Must pass a practical flight test with an FAA examiner.
 Cessna 172 on Runway
Cessna 172 on Runway
9. How Can Flyermedia.net Help You Learn to Fly a Cessna 172?
Flyermedia.net is your go-to resource for comprehensive information, training, and career opportunities in the aviation industry. Whether you are a student pilot, aviation enthusiast, or seasoned professional, flyermedia.net offers valuable resources to help you achieve your goals.
9.1 What Resources Does Flyermedia.net Offer for Aspiring Pilots?
Flyermedia.net provides a wealth of resources for aspiring pilots, including:
- Directory of Flight Schools: Find reputable flight schools and training programs in the USA.
- Aviation News and Updates: Stay informed about the latest news, trends, and regulations in the aviation industry.
- Pilot Training Guides: Access comprehensive guides and tutorials on various aspects of flight training.
- Career Opportunities: Explore job opportunities in the aviation industry and connect with potential employers.
- Aviation Community: Connect with other pilots, instructors, and aviation enthusiasts to share knowledge and experiences.
9.2 How Can You Stay Updated on Aviation News and Trends with Flyermedia.net?
Flyermedia.net keeps you informed about the latest aviation news and trends through:
- News Articles: Read timely articles on aviation events, technological advancements, and regulatory changes.
- Industry Reports: Access in-depth reports and analysis on key industry trends.
- Expert Interviews: Gain insights from industry experts and thought leaders.
- Social Media: Follow flyermedia.net on social media for real-time updates and announcements.
- Newsletter: Subscribe to the flyermedia.net newsletter to receive regular updates in your inbox.
9.3 How Can You Find Career Opportunities in Aviation Through Flyermedia.net?
Flyermedia.net helps you find career opportunities in aviation through:
- Job Board: Browse a comprehensive job board featuring listings from leading aviation companies.
- Company Profiles: Learn about potential employers and their hiring practices.
- Career Guides: Access guides and resources on resume writing, interviewing, and career planning.
- Networking Events: Attend virtual and in-person networking events to connect with industry professionals.
- Recruiting Services: Utilize flyermedia.net’s recruiting services to find the perfect job match.
10. What are Some Common Mistakes to Avoid When Flying a Cessna 172?
Avoiding common mistakes is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient flight operations in a Cessna 172. Awareness and proper training can help pilots mitigate these risks.
10.1 What are Some Frequent Errors During Takeoff?
Frequent errors during takeoff can compromise safety and performance.
- Improper Pre-Flight Checks: Failing to perform thorough pre-flight checks can lead to undetected mechanical issues.
- Incorrect Flap Settings: Using incorrect flap settings can affect takeoff performance and control.
- Poor Rudder Control: Inadequate rudder control can result in veering off the runway, especially in crosswind conditions.
- Premature Rotation: Rotating too early can cause the aircraft to stall or struggle to gain altitude.
- Over-Rotation: Rotating too aggressively can lead to a tail strike.
10.2 What Mistakes Should You Avoid During Landing?
Mistakes during landing are a leading cause of aviation accidents.
- Unstabilized Approach: Failing to maintain a stabilized approach can lead to poor control and misjudgment of the landing.
- Excessive Speed: Approaching too fast can result in a long landing and increased risk of overrunning the runway.
- Improper Flare: Executing an improper flare can cause a hard landing or bouncing.
- Drifting: Failing to correct for wind drift can cause the aircraft to veer off the runway.
- Late Go-Around: Delaying a go-around decision when a safe landing is not assured can lead to a dangerous situation.
10.3 What Common Navigation Errors Should Pilots Avoid?
Navigation errors can lead to getting lost or deviating from the planned route.
- Inadequate Pre-Flight Planning: Insufficient pre-flight planning can result in a lack of awareness of airspace, weather conditions, and terrain.
- Failure to Monitor Position: Neglecting to continuously monitor the aircraft’s position can lead to deviations from the planned route.
- Improper Use of Navigation Equipment: Misusing navigation equipment, such as GPS or VOR, can result in inaccurate position information.
- Distraction: Becoming distracted by non-essential tasks can lead to a loss of situational awareness and navigation errors.
- Reliance on Technology: Over-relying on technology without cross-checking with other navigation methods can result in errors if the equipment malfunctions.
Ready to take to the skies? Visit flyermedia.net today to explore flight schools, read the latest aviation news, and discover exciting career opportunities in the aviation industry! Your journey to becoming a skilled Cessna 172 pilot starts here.
FAQ: How to Fly a Cessna 172
-
What is the typical cruise speed of a Cessna 172?
The typical cruise speed of a Cessna 172 is around 124 knots (143 mph or 230 km/h) at 75% power. -
How much fuel does a Cessna 172 typically burn per hour?
A Cessna 172 typically burns about 8 to 10 gallons of fuel per hour, depending on the engine model and power setting. -
What is the maximum altitude a Cessna 172 can fly?
The maximum certified altitude (service ceiling) for a Cessna 172 is 13,500 feet above sea level. -
What are the stall speeds for a Cessna 172?
The stall speed (Vs1) with flaps up is approximately 48 knots, and the stall speed (Vso) with flaps down is about 40 knots. -
What is the best angle of climb speed (Vx) for a Cessna 172?
The best angle of climb speed (Vx) for a Cessna 172 is typically around 62 knots, allowing for the steepest climb angle to clear obstacles. -
What is the best rate of climb speed (Vy) for a Cessna 172?
The best rate of climb speed (Vy) for a Cessna 172 is approximately 74 knots, providing the most altitude gain in a given amount of time. -
How long of a runway does a Cessna 172 need for takeoff?
A Cessna 172 typically requires around 800 to 1,000 feet of runway for takeoff under standard conditions. -
How long of a runway does a Cessna 172 need for landing?
A Cessna 172 typically requires about 600 to 800 feet of runway for landing under standard conditions. -
What type of engine does a Cessna 172 have?
The Cessna 172 is commonly equipped with a Lycoming IO-360 four-cylinder, horizontally opposed engine. -
What are the dimensions of a Cessna 172?
The Cessna 172 has a wingspan of 36 feet, a length of 27 feet, and a height of 8 feet 11 inches.
