Ever wondered how a tiny fly can so easily dodge your swatting attempts? How Does A Fly See the world differently than us? This article from flyermedia.net delves into the fascinating world of insect vision, exploring the science behind their incredible agility and perception. Discover the secrets of their compound eyes, rapid processing, and unique neural adaptations, providing you with insights into the aviation industry. Ready to explore the captivating details about fly sight?
1. What Are the Key Components of a Fly’s Eye?
A fly’s eye is a compound eye. Instead of a single lens like a human eye, a fly’s eye is composed of hundreds to thousands of individual lenses called facets. Each facet captures a small part of the visual field, and the fly’s brain combines these individual images to create a mosaic-like view of the world. These components enable them to perceive the world in a unique way. This mosaic vision helps flies to detect even the slightest movement, crucial for survival and navigating the aerial world.
1.1. How Do Facets Contribute to Fly Vision?
Facets act as individual pixels. Each facet focuses light onto a cluster of photoreceptors, which are light-sensitive cells. These photoreceptors convert light into electrical signals that are sent to the brain for processing. This pixelated vision is low-resolution compared to human vision, but it excels at detecting fast movements.
1.2. What Role Do Photoreceptors Play in Fly Vision?
Photoreceptors are crucial for light detection. They transform light into electrical signals, which are then transmitted to the fly’s brain for processing. The speed at which these photoreceptors can process light directly impacts how quickly the fly perceives motion.
2. How Does a Fly’s Vision Differ from Human Vision?
A fly’s vision differs greatly. While humans have high-resolution vision with a wide field of view, flies have low-resolution, mosaic-like vision that is exceptionally sensitive to motion. Humans discern a maximum of about 60 discrete flashes of light per second, while some flies can see up to 250 flashes per second. This makes them highly adept at detecting fast movements.
2.1. What Are the Advantages of Compound Eyes?
Compound eyes provide advantages in motion detection. This is particularly useful for detecting predators and prey. The mosaic-like vision also offers a wide field of view, allowing flies to see in almost all directions at once.
2.2. How Does Resolution Affect Fly Vision?
Flies have low-resolution vision compared to humans. However, they compensate with their ability to process visual information much faster, making them highly sensitive to movement and changes in their environment. According to research from Florida International University, flies can detect movements almost four times faster than humans.
3. How Fast Can a Fly Process Visual Information?
Flies can process visual information extremely fast. They can perceive up to 250 flashes per second, which is about four times faster than humans. This rapid processing speed allows them to react quickly to potential threats and navigate complex environments.
3.1. How Does Frame Rate Perception Affect Fly Behavior?
Frame rate perception is critical for survival. Their ability to see more frames per second allows them to react quickly to looming threats and avoid obstacles. In contrast, a movie made up of 24 frames per second would appear as a series of static images to a fly.
3.2. What Happens to a Fly’s Vision in Dim Light?
In dim light, a fly’s vision diminishes. They lose some ability to see fast movements due to the limited number of photons available. However, flies can compensate for this by relying on non-visual cues and erratic flight patterns to evade threats, which is crucial for understanding how they survive in varying conditions.
4. What Neural Adaptations Contribute to a Fly’s Vision?
Neural adaptations are crucial for fly vision. Flies use neural strategies like summation to enhance their vision in low light. Summation involves combining inputs from neighboring pixels or increasing the time they sample photons to form an image.
4.1. What Is Summation and How Does It Work in Fly Vision?
Summation is a neural strategy. It allows flies to gather more light in dark environments. By adding together inputs from neighboring pixels or increasing the sampling time, they can create an image even with limited photons. However, this comes at the cost of image sharpness.
4.2. How Do These Neural Adaptations Affect Reaction Time?
Neural adaptations can influence reaction time. Although summation helps in low light, it can slow down the fly’s reaction time because they need more photons to be sure of what they are seeing. This trade-off between clarity and speed is critical for survival in different environments.
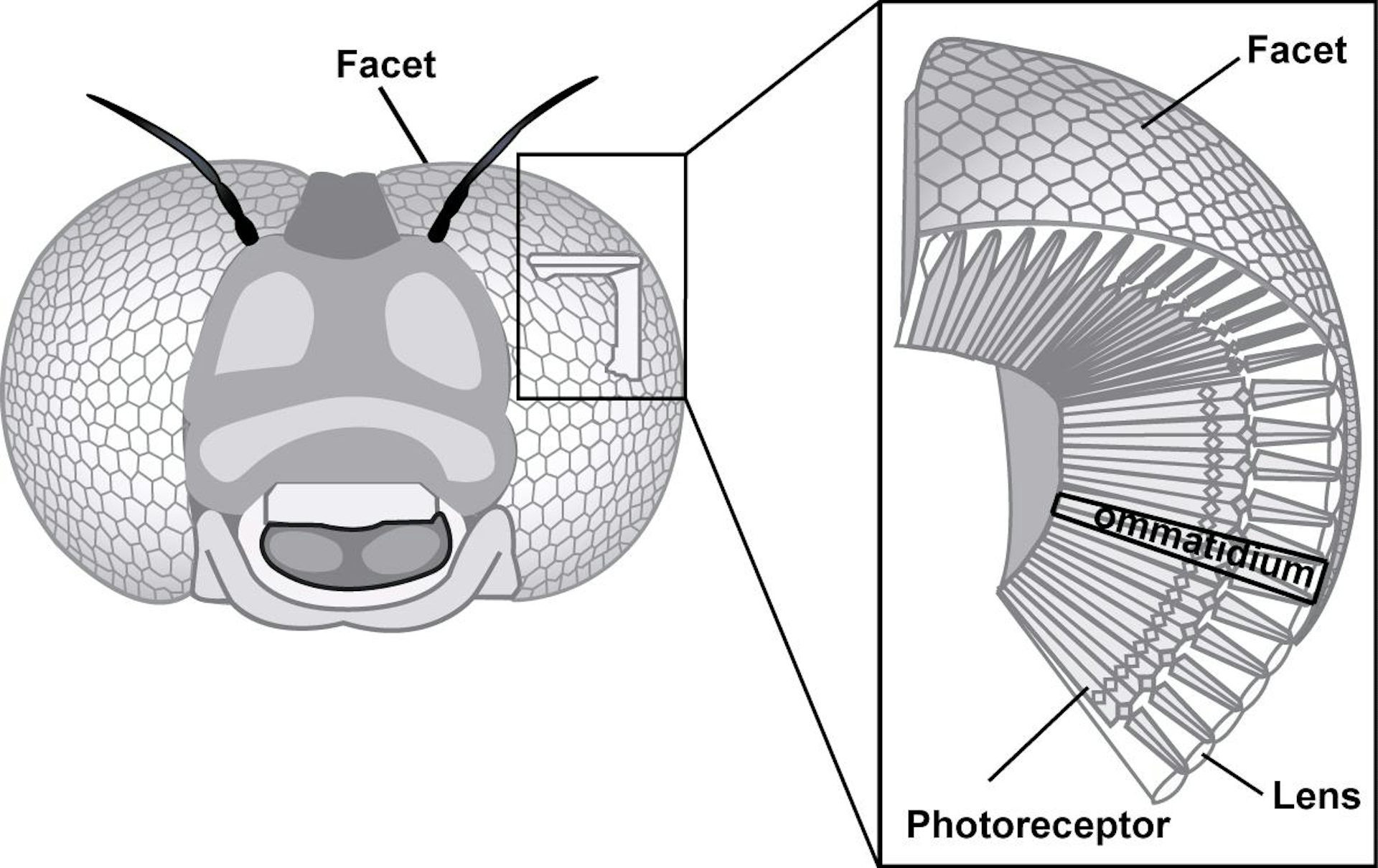 An illustration of a fly eye, showing tiny hexagonal facets and the photoreceptor layer under these facets.
An illustration of a fly eye, showing tiny hexagonal facets and the photoreceptor layer under these facets.
5. How Do Flies Prepare for Takeoff and Quick Flight Maneuvers?
Flies prepare for takeoff quickly. After detecting a looming threat, fruit flies can adjust their posture in just one-fifth of a second before taking off. This rapid preparation allows them to evade predators and navigate complex environments.
5.1. What Role Do Legs, Wings, and Halteres Play in Flight?
Legs, wings, and halteres are essential for flight. Predatory flies coordinate these body parts to quickly catch their prey mid-flight. Halteres, which are dumbbell-shaped remnants of wings, are used for sensing in-air rotations, providing crucial balance and maneuverability.
5.2. How Does Posture Adjustment Contribute to Evasive Maneuvers?
Posture adjustment is crucial for flight. Adjusting their posture rapidly allows flies to optimize their takeoff and initial flight trajectory. This preparation is critical for evading threats and performing complex maneuvers.
6. What Environmental Factors Affect Fly Vision?
Environmental factors significantly impact fly vision. Light levels, temperature, and air currents can all influence how well a fly can see and react to its surroundings.
6.1. How Does Light Intensity Influence Visual Acuity?
Light intensity directly affects visual acuity. In bright light, flies can see more clearly and process movements faster. In dim light, they rely on summation, which reduces sharpness but helps them detect some movement.
6.2. What Role Does Temperature Play in Fly Vision?
Temperature affects fly vision. Lower temperatures can slow down the physiological processes necessary for vision, reducing their reaction time. Higher temperatures can enhance these processes, improving their visual acuity and reaction speed.
7. How Can Understanding Fly Vision Inform Aviation Technology?
Understanding fly vision can greatly benefit aviation technology. The principles of compound eyes and rapid visual processing can inspire new designs for sensors and navigation systems in drones and aircraft.
7.1. Can Compound Eye Principles Be Applied to Drone Technology?
Yes, compound eye principles are applicable. Replicating the wide field of view and motion detection capabilities of compound eyes can enhance the performance of drones in surveillance, navigation, and obstacle avoidance.
7.2. What Are the Potential Benefits of Bio-Inspired Vision Systems in Aviation?
Bio-inspired vision systems offer numerous benefits. These include improved situational awareness, enhanced navigation in challenging environments, and more efficient detection of potential hazards. These advantages can significantly enhance the safety and performance of aircraft.
8. How Can You Outmaneuver a Fly?
Outmaneuvering a fly is challenging. Flies have evolved sophisticated escape mechanisms over millions of years. Instead of trying to swat them, using other methods such as fly traps and maintaining clean environments is more effective.
8.1. What Strategies Are Effective for Managing Flies Indoors?
Effective strategies include using fly traps, keeping surfaces clean, and properly storing food. Flypaper, UV light traps, and DIY traps made with apple cider vinegar and beer can also be effective.
8.2. How Can You Prevent Flies Outdoors?
Preventing flies outdoors involves removing stagnant water, maintaining clean yards, and properly disposing of waste. These measures eliminate breeding sites and reduce the fly population.
 A simple home-made fruit fly trap
A simple home-made fruit fly trap
9. What Are Some Misconceptions About Fly Vision?
Common misconceptions about fly vision are plentiful. One is that they only see the world in slow motion. While they can perceive more flashes per second than humans, their vision isn’t necessarily slow; it’s just different. Another misconception is that they have poor vision overall, but their motion detection is highly advanced.
9.1. Do Flies Only See in Slow Motion?
Flies do not only see in slow motion. They process visual information faster than humans. They can see more discrete flashes of light per second, allowing them to react quickly to movement, but their overall perception is not in slow motion.
9.2. Is Fly Vision Considered “Poor” Compared to Human Vision?
Fly vision is not necessarily poor but different. While their resolution is lower than human vision, their ability to detect rapid movements is superior. This adaptation is perfectly suited for their needs, such as evading predators and finding food.
10. What Research Is Being Conducted on Insect Vision?
Research on insect vision is ongoing. Scientists are studying how insects process visual information and use it to perform complex behaviors. This research aims to understand the neural mechanisms underlying insect vision and apply these insights to various fields, including robotics and artificial intelligence.
10.1. What Are Some Recent Discoveries in the Field of Insect Vision?
Recent discoveries include a better understanding of how flies use summation to see in low light and how they coordinate their body parts for rapid takeoff. Researchers are also exploring how insect vision can inspire new algorithms for computer vision.
10.2. How Can Research on Insect Vision Benefit Other Scientific Fields?
Research on insect vision can benefit numerous fields. It can inspire new designs for robots and drones, improve computer vision algorithms, and provide insights into the evolution of visual systems. This interdisciplinary research has broad implications for science and technology.
11. The Science Behind Swatting: Why Is It So Hard to Hit a Fly?
The difficulty in swatting a fly is due to their fast vision, quick reaction time, and ability to detect even the slightest movements. By the time you swing your hand, the fly has already processed the visual information and initiated an escape response.
11.1. How Do Flies Use Their Vision to Evade Threats?
Flies use their vision to detect approaching threats. Their compound eyes provide a wide field of view, allowing them to see movement from almost any direction. Once a threat is detected, their rapid processing speed allows them to react quickly and escape.
11.2. What Role Does Air Current Detection Play in Evading Swats?
Air current detection plays a crucial role. Flies have small hairs on their body that can sense changes in air currents, allowing them to detect an approaching hand even before they see it. This early warning system gives them a head start in their escape.
12. How Does the Environment of Daytona Beach, Florida Affect Fly Activity?
The environment of Daytona Beach, Florida, affects fly activity due to its warm, humid climate. These conditions are ideal for fly breeding and survival, leading to increased fly populations.
12.1. How Does Temperature and Humidity Influence Fly Behavior?
Temperature and humidity significantly influence fly behavior. Warm temperatures accelerate their life cycle and increase their activity levels. High humidity provides the moisture they need to survive and reproduce.
12.2. Are There Specific Types of Flies More Prevalent in Daytona Beach?
Specific types of flies more prevalent in Daytona Beach include house flies, fruit flies, and mosquitoes. These species thrive in the warm, humid conditions and are commonly found around homes and businesses.
13. How Can Flyermedia.net Help You Learn More About Aviation?
Flyermedia.net offers a wealth of information about aviation. From the science of flight to career opportunities in the industry, our website provides resources for aviation enthusiasts, students, and professionals.
13.1. What Resources Does Flyermedia.net Offer for Aviation Enthusiasts?
Flyermedia.net offers articles, news, and educational content for enthusiasts. Whether you’re interested in the history of flight, the latest aircraft technology, or the science behind aviation, you’ll find something to captivate your interest.
13.2. How Can Students Benefit from Flyermedia.net’s Aviation Information?
Students can benefit greatly. We provide resources on aviation schools, pilot training programs, and career paths in the industry. Our website is a valuable tool for anyone considering a career in aviation.
14. How Can Flyermedia.net Assist You in Finding a Flight Training Program?
Flyermedia.net can help you find the right flight training program. We offer a directory of aviation schools and flight training programs in the United States, including those in Daytona Beach, Florida.
14.1. What Information Is Available About Flight Schools in Daytona Beach?
Information available includes profiles of flight schools, details on their programs, and reviews from students. This helps you make an informed decision when choosing a flight training program.
14.2. How Does Flyermedia.net Help You Compare Different Aviation Schools?
Flyermedia.net helps you compare aviation schools by providing detailed information on their curriculum, instructors, facilities, and cost. This allows you to assess which school best fits your needs and goals.
15. What Career Opportunities Are Available in Aviation After Flight School?
After flight school, various career opportunities are available. These include becoming a commercial pilot, flight instructor, charter pilot, or working in aviation management and operations.
15.1. What Are the Requirements for Becoming a Commercial Pilot?
Requirements for becoming a commercial pilot typically include a commercial pilot certificate, meeting minimum flight hour requirements, passing written and practical exams, and meeting medical requirements.
15.2. How Can Flyermedia.net Help You Find Job Opportunities in Aviation?
Flyermedia.net can help you find job opportunities. We list job openings in the aviation industry and provide resources for career development. Whether you’re looking for a job as a pilot, mechanic, or air traffic controller, our website can assist you in your job search.
16. How Can You Stay Updated on Aviation News and Regulations?
Staying updated on aviation news and regulations is crucial for professionals. You can follow industry publications, aviation news websites, and regulatory agencies like the FAA.
16.1. What Are Some Reliable Sources for Aviation News?
Reliable sources for aviation news include Aviation Week, FlightGlobal, and industry-specific news outlets. These sources provide up-to-date information on industry trends, new technologies, and regulatory changes.
16.2. How Can You Keep Track of FAA Regulations and Updates?
You can keep track of FAA regulations and updates by visiting the FAA website, subscribing to their email updates, and attending industry conferences and webinars. Staying informed helps ensure compliance and safety.
17. How Does Understanding Fly Vision Enhance Flight Safety?
Understanding fly vision can enhance flight safety by inspiring the development of improved vision systems for aircraft and drones. These systems can help pilots better perceive their surroundings and avoid potential hazards.
17.1. Can Insect-Inspired Vision Systems Improve Aircraft Safety?
Insect-inspired vision systems can improve aircraft safety. By mimicking the wide field of view and motion detection capabilities of insect eyes, these systems can provide pilots with better situational awareness and enhance their ability to detect potential threats.
17.2. What Specific Technologies Can Be Developed Using These Principles?
Specific technologies that can be developed include advanced sensor arrays, improved obstacle detection systems, and enhanced navigation tools. These technologies can help reduce the risk of accidents and improve overall flight safety.
18. How Does Flyermedia.net Cover the Latest Innovations in Aviation?
Flyermedia.net covers the latest innovations in aviation. We provide articles and news on new aircraft technologies, sustainable aviation practices, and advancements in air traffic management.
18.1. What Are Some Recent Technological Advancements in Aviation?
Recent technological advancements include the development of electric and hybrid aircraft, advancements in autonomous flight systems, and improvements in air traffic management technology.
18.2. How Is Aviation Becoming More Sustainable?
Aviation is becoming more sustainable through the development of alternative fuels, improvements in engine efficiency, and the implementation of more efficient flight routes. These efforts aim to reduce the industry’s environmental impact.
19. How Can the Study of Fly Vision Contribute to Robotics?
The study of fly vision can significantly contribute to robotics. By understanding how flies process visual information, engineers can design more efficient and effective vision systems for robots.
19.1. How Can Insect Vision Be Applied to Robot Navigation?
Insect vision can be applied to robot navigation by mimicking the compound eye structure and motion detection capabilities. This can enable robots to navigate complex environments and avoid obstacles more effectively.
19.2. What Are the Potential Benefits of Insect-Inspired Robotics?
Potential benefits of insect-inspired robotics include improved navigation, enhanced obstacle avoidance, and more efficient use of computational resources. These advantages can make robots more versatile and capable in various applications.
20. What Educational Opportunities Are Available Through Flyermedia.net?
Educational opportunities available through Flyermedia.net include articles, tutorials, and resources on various aviation-related topics. Whether you’re a student, enthusiast, or professional, you’ll find something to expand your knowledge.
20.1. What Topics Are Covered in Flyermedia.net’s Aviation Tutorials?
Topics covered in Flyermedia.net’s aviation tutorials include the principles of flight, aircraft systems, navigation, meteorology, and aviation regulations. These tutorials provide a comprehensive overview of the aviation industry.
20.2. How Can These Resources Help You Pursue a Career in Aviation?
These resources can help you prepare for a career in aviation by providing you with the knowledge and skills you need to succeed. Whether you’re pursuing a career as a pilot, mechanic, or air traffic controller, our website can support your educational journey.
Fly vision is a remarkable adaptation that allows these tiny creatures to thrive in a complex world. By understanding the science behind their vision, we can gain insights into the evolution of visual systems and apply these principles to various fields, including aviation, robotics, and artificial intelligence. Explore flyermedia.net today to discover more about the captivating world of aviation and unlock your potential in the skies.
Visit flyermedia.net or contact us at Address: 600 S Clyde Morris Blvd, Daytona Beach, FL 32114, United States. Phone: +1 (386) 226-6000 to learn more about our services and how we can help you achieve your aviation dreams.
FAQ: Understanding Fly Vision
1. How many lenses does a fly have in its eye?
A fly has hundreds to thousands of individual lenses called facets in its compound eye, each contributing to its overall vision.
2. Can flies see in the dark?
Flies can see in the dark, but their vision is diminished. They rely on summation to gather more light, which reduces image sharpness and slows down reaction time.
3. What is summation in the context of fly vision?
Summation is a neural strategy that flies use to enhance their vision in low light by combining inputs from neighboring pixels or increasing the time they sample photons.
4. How quickly can flies react to movement?
Flies can react extremely quickly to movement, processing up to 250 flashes per second, about four times faster than humans.
5. Why is it so hard to swat a fly?
It is hard to swat a fly because of their fast vision, quick reaction time, and ability to detect even the slightest changes in air currents.
6. How does temperature affect fly vision?
Temperature affects fly vision, with lower temperatures slowing down physiological processes necessary for vision and higher temperatures enhancing these processes.
7. Can compound eye principles be applied to drone technology?
Yes, compound eye principles can be applied to drone technology to enhance their field of view and motion detection capabilities.
8. What are halteres and what role do they play in flight?
Halteres are dumbbell-shaped remnants of wings used for sensing in-air rotations, providing crucial balance and maneuverability during flight.
9. What is the typical career path after flight school?
A typical career path after flight school includes becoming a commercial pilot, flight instructor, charter pilot, or working in aviation management and operations.
10. How can Flyermedia.net assist in finding a flight training program?
flyermedia.net provides a directory of aviation schools and flight training programs, detailed information on programs, and reviews from students to help make an informed decision.