How Do Fruit Flies Mate? Fruit fly mating involves intricate courtship rituals, including serenading, dancing, and chasing. This comprehensive guide, brought to you by flyermedia.net, explores the fascinating details of fruit fly reproduction, from the initial attraction to the act of mating, offering insights into their behavior and the factors influencing their reproductive success. Understanding these tiny creatures can reveal broader insights into behavioral science and genetics, enriching our knowledge of the natural world and even sparking new ideas in aviation and beyond.
1. What is the Fruit Fly Mating Ritual?
The fruit fly mating ritual involves a complex series of behaviors performed by the male to attract and mate with a female. A male fruit fly woos a female through a multi-step courtship, beginning with orientation, followed by singing, dancing, licking, and attempting copulation. This intricate process ensures successful reproduction.
- Orientation: The male fruit fly first orients himself toward the female, often approaching her from behind or the side. This initial step is crucial for initiating the courtship sequence.
- Singing: Male fruit flies sing to females by vibrating their wings, creating a species-specific song. According to research from Princeton Neuroscience Institute, the song varies in complexity depending on the proximity of the male to the female.
- Dancing: After singing, the male fruit fly engages in a courtship dance, where he moves around the female, often tapping her abdomen with his legs. This dance is a visual signal to the female, further enticing her to mate.
- Licking: The male may also lick the female’s genitalia, which serves to stimulate her and prepare her for mating. This behavior is a tactile component of the courtship ritual.
- Attempting Copulation: If the female is receptive, she will stop moving and allow the male to mount her and attempt copulation. This final step leads to the transfer of sperm and fertilization.
2. Why Do Male Fruit Flies Sing During Courtship?
Male fruit flies sing during courtship to attract and stimulate females, using species-specific songs to convey their interest and readiness to mate. According to Mala Murthy, the Karol and Marnie Marcin ’96 Professor and the director of the Princeton Neuroscience Institute, this song is a form of communication, similar to a conversation. The male adjusts his song based on the female’s behavior, creating a dynamic interaction that influences her receptiveness to mating.
- Attraction: The primary function of the song is to attract the female’s attention. The specific patterns and rhythms in the song can be highly attractive to females of the same species.
- Stimulation: The song also serves to stimulate the female, making her more receptive to mating. The vibrations and sounds produced by the male’s wings can trigger physiological responses in the female that prepare her for copulation.
- Species Recognition: Fruit fly songs are species-specific, meaning that each species has its unique song pattern. This helps females identify and choose mates of their own species, ensuring successful reproduction.
- Assessment of Male Quality: The complexity and quality of the song can also provide information about the male’s genetic fitness and overall health. Females may use these cues to select the best possible mate for their offspring.
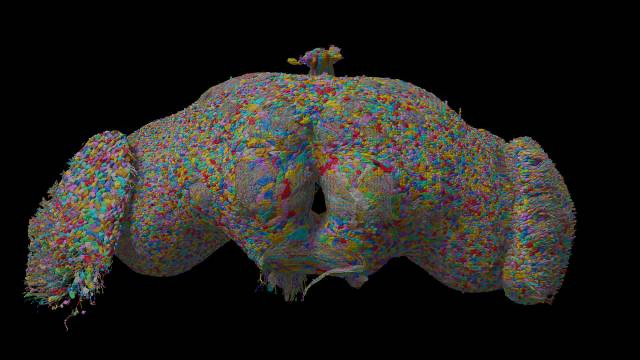 A colorful web of lines tracing out the complete set of neurons and their connections in a fruit fly brain
A colorful web of lines tracing out the complete set of neurons and their connections in a fruit fly brain
A detailed connectome map showing the complex neural connections in a fruit fly brain.
3. How Do Female Fruit Flies Choose Their Mates?
Female fruit flies choose their mates based on a variety of factors, including the male’s song, dance, size, and overall health, ensuring they select partners that will produce healthy offspring. According to studies in behavioral ecology, these criteria help ensure reproductive success and genetic diversity.
- Song Quality: Females often prefer males with more complex and elaborate songs, as these songs may indicate better genetic quality. The rhythm, tempo, and structure of the song are all assessed by the female.
- Dance Performance: The vigor and coordination of the male’s dance can also influence female choice. A well-coordinated dance may signal good motor skills and overall fitness.
- Size and Physical Condition: Larger males may be preferred due to their ability to provide more resources or better genes to the offspring. The female also assesses the male’s physical condition, looking for signs of health and vitality.
- Pheromones: Chemical signals, or pheromones, play a role in mate selection. Males emit pheromones that can attract females, while females also release pheromones that signal their receptivity to mating.
- Previous Mating Experience: A female’s previous mating experiences can influence her future mate choices. If she had a positive experience with a particular male, she might be more likely to choose a similar mate in the future.
4. What Role Does Proximity Play in Fruit Fly Mating?
Proximity plays a crucial role in fruit fly mating, acting as a trigger for changes in male behavior and song complexity. According to research from the Princeton Neuroscience Institute, a male fruit fly’s brain has a “toggle switch” that is engaged when he is close to a female, allowing him to sing more complex songs.
- Initiation of Courtship: Proximity is often the first step in initiating courtship. A male fruit fly must be close enough to detect a female’s presence and begin the courtship ritual.
- Switching Song Complexity: As the male gets closer to the female, his song becomes more complex. The switch from simple pulse songs to more elaborate sine songs is directly related to how close he is to the female.
- Assessment of Female Receptivity: Proximity allows the male to assess the female’s receptivity. If she slows down or turns toward him, he will continue his courtship. If she moves away, he may adjust his strategy or give up.
- Facilitating Copulation: Close proximity is essential for copulation to occur. The male must be able to mount the female and successfully transfer sperm.
- Neural Circuit Activation: Research has shown that specific neural circuits in the male fruit fly’s brain are activated by proximity, influencing his behavior and song patterns.
5. How Long Does Fruit Fly Courtship Last?
Fruit fly courtship can last for about 20 minutes, during which the male sings, dances, and pursues the female until she slows down enough to mate. According to Mala Murthy from the Princeton Neuroscience Institute, this extended courtship allows the female to assess the male’s suitability as a mate and ensures that she is receptive to mating.
- Assessment Period: The length of the courtship provides the female with ample time to evaluate the male’s qualities, including his song, dance, and physical condition.
- Ensuring Receptivity: The male’s persistent courtship behavior can help to stimulate the female and increase her receptivity to mating. The longer the courtship, the more likely she is to be ready for copulation.
- Competition: In some cases, multiple males may compete for the attention of a single female. The length of the courtship can be influenced by the presence of other males and the need to outcompete them.
- Species Variation: The duration of courtship can vary among different species of fruit flies. Some species may have shorter courtship rituals, while others may have longer ones.
- Environmental Factors: Environmental conditions, such as temperature and light, can also affect the length of courtship. For example, courtship may be shorter in stressful or unfavorable conditions.
6. What Happens After Fruit Flies Mate?
After fruit flies mate, the female stores sperm and lays fertilized eggs, while the male may seek additional mating opportunities. The female becomes less receptive to other males and focuses on nurturing her offspring.
- Sperm Storage: The female fruit fly can store sperm from multiple males in specialized organs called spermathecae. This allows her to fertilize eggs over a period of several days or weeks.
- Egg Laying: The female lays her fertilized eggs on or near a food source, such as rotting fruit. The eggs hatch into larvae, which feed and grow before pupating and eventually emerging as adult flies.
- Reduced Receptivity: After mating, the female becomes less receptive to other males. This is due to physiological changes that make her less attractive and receptive to courtship.
- Male Behavior: The male may continue to court other females in an effort to maximize his reproductive success. He may also provide some level of paternal care, although this is less common in fruit flies than in some other insects.
- Nutritional Changes: Mating can affect the female’s nutritional needs and feeding behavior. She may require more protein and other nutrients to support egg production and development.
7. How Often Do Fruit Flies Mate?
Fruit flies can mate multiple times throughout their adult lives, with females typically mating more frequently than males. The exact frequency depends on factors such as food availability, temperature, and the presence of potential mates.
- Female Mating Frequency: Female fruit flies can mate several times, storing sperm from different males. This allows them to fertilize eggs over an extended period.
- Male Mating Frequency: Male fruit flies also mate multiple times, although their mating frequency may be limited by the availability of receptive females and competition from other males.
- Environmental Influences: Food availability and temperature can influence mating frequency. In favorable conditions, fruit flies may mate more frequently.
- Genetic Factors: Genetic factors can also play a role in mating frequency. Some individuals may be more sexually active than others due to genetic variations.
- Population Density: In dense populations, mating frequency may increase due to the higher likelihood of encountering potential mates.
8. What Are the Genetic Factors Influencing Fruit Fly Mating Behavior?
Genetic factors play a significant role in influencing fruit fly mating behavior, affecting everything from courtship song to mate choice. Studies in genetics have identified specific genes and gene networks that control different aspects of mating behavior.
- Courtship Song Genes: Several genes have been identified that influence the production and perception of courtship song. These genes affect the structure and function of the nervous system, as well as the muscles that control wing movements.
- Mate Choice Genes: Genes involved in mate choice affect the ability of females to recognize and respond to male courtship signals. These genes can influence the expression of receptors for pheromones and other chemical signals.
- Sex Determination Genes: Genes that determine sex also play a role in mating behavior. These genes regulate the development of sex-specific structures and behaviors, such as the male’s ability to sing and dance.
- Behavioral Polymorphisms: Genetic variations can lead to behavioral polymorphisms, where individuals within a population exhibit different mating behaviors. These variations can be maintained by natural selection if they provide some advantage in certain environments.
- Epigenetic Effects: Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone modification, can also influence mating behavior by altering gene expression. These effects can be passed down from one generation to the next, leading to transgenerational inheritance of mating behavior.
Mala Murthy, the Karol and Marnie Marcin ’96 Professor and the director of the Princeton Neuroscience Institute.
9. How Does the Environment Affect Fruit Fly Mating?
The environment significantly affects fruit fly mating by influencing factors like food availability, temperature, and the presence of competitors, which in turn impact courtship behavior and mating success. Studies in ecology and evolutionary biology have shown how these environmental factors can shape mating strategies.
- Food Availability: Access to nutritious food sources can increase mating frequency and success. Well-fed fruit flies are more likely to engage in courtship and mating than those that are undernourished.
- Temperature: Temperature affects the metabolic rate and activity level of fruit flies. Optimal temperatures promote higher mating rates, while extreme temperatures can inhibit mating behavior.
- Light: Light levels can influence the timing of mating. Some species of fruit flies are more active during the day, while others are more active at night.
- Presence of Competitors: The presence of other males can affect courtship behavior and mating success. Males may engage in competitive behaviors, such as aggressive displays or increased singing, to attract females.
- Habitat Complexity: Complex habitats with diverse resources and hiding places can provide more opportunities for courtship and mating. These habitats can also reduce the risk of predation, allowing fruit flies to engage in mating behavior more freely.
- Chemical Exposure: Exposure to certain chemicals, such as pesticides or pollutants, can disrupt mating behavior and reduce reproductive success. These chemicals can interfere with the nervous system and hormone signaling, leading to impaired courtship and mating.
10. What Research Has Been Done on Fruit Fly Mating Behavior?
Extensive research has been conducted on fruit fly mating behavior, providing valuable insights into genetics, neuroscience, and evolutionary biology. These studies have used a variety of techniques, including genetic manipulation, behavioral observation, and neural imaging.
- Genetic Studies: Genetic studies have identified specific genes that control different aspects of mating behavior, such as courtship song, mate choice, and sexual receptivity. These studies have provided insights into the genetic basis of behavior and the evolution of mating strategies.
- Neuroscience Studies: Neuroscience studies have investigated the neural circuits and brain regions involved in mating behavior. These studies have used techniques such as neural imaging and optogenetics to map out the neural pathways that control courtship and mating.
- Evolutionary Studies: Evolutionary studies have examined the evolution of mating behavior in fruit flies, focusing on the selective pressures that have shaped courtship rituals and mate choice preferences. These studies have provided insights into the adaptive significance of mating behavior and the role of sexual selection in evolution.
- Behavioral Studies: Behavioral studies have focused on the details of courtship behavior, including the sequence of actions, the signals exchanged between males and females, and the factors that influence mating success. These studies have used detailed observation and video analysis to document the intricacies of fruit fly courtship.
- Mathematical Modeling: Mathematical models have been developed to simulate mating behavior and predict the outcome of courtship interactions. These models can help to understand the complex dynamics of mating behavior and the factors that influence reproductive success. According to Princeton University’s resources, researchers are using LEAP (LEAP Estimates Animal Pose) and its next generation SLEAP (Social LEAP Estimates Animal Poses), both deep-learning-based motion-capture tools developed by a previous Princeton collaboration, that quantified exactly how the flies are moving and where they are in relation to each other.
11. How Can Understanding Fruit Fly Mating Benefit Other Fields?
Understanding fruit fly mating behavior can benefit other fields by providing insights into genetics, neuroscience, and evolutionary biology that are applicable to more complex organisms, including humans. The relatively simple nervous system and rapid life cycle of fruit flies make them an ideal model for studying fundamental biological processes.
- Genetics: Studies of fruit fly mating behavior have identified genes that are involved in a variety of other behaviors, including learning, memory, and social interaction. These genes may also play a role in human behavior and mental health.
- Neuroscience: The neural circuits that control fruit fly mating behavior are similar to those found in other animals, including humans. Understanding these circuits can provide insights into the neural basis of behavior and the development of new treatments for neurological disorders.
- Evolutionary Biology: Studies of fruit fly mating behavior have provided insights into the evolution of sexual selection and the adaptive significance of different mating strategies. These insights can be applied to other species, including humans, to understand the evolution of human mating behavior.
- Behavioral Ecology: The principles of behavioral ecology that have been developed through the study of fruit flies can be applied to other species, including humans, to understand how behavior is shaped by the environment and social interactions.
- Artificial Intelligence: The neural circuits that control fruit fly mating behavior can be used as a model for developing new algorithms and architectures for artificial intelligence. These models can help to create more intelligent and adaptive robots and computer systems.
12. What are Some Common Misconceptions About Fruit Fly Mating?
There are several common misconceptions about fruit fly mating, including the belief that they mate randomly and that females have no control over the process. In reality, fruit fly mating is a complex and highly regulated process.
- Random Mating: It is often assumed that fruit flies mate randomly, but this is not the case. Females actively choose their mates based on a variety of factors, including the male’s song, dance, and physical condition.
- Female Passivity: Another misconception is that females are passive participants in the mating process. In reality, females play an active role in courtship, evaluating potential mates and deciding whether or not to mate with them.
- Simple Behavior: Fruit fly mating behavior is often seen as simple and unsophisticated, but it is actually quite complex. The courtship ritual involves a series of intricate actions and signals, and the outcome of courtship can be influenced by a variety of factors.
- Lack of Learning: It is sometimes assumed that fruit flies are incapable of learning and that their mating behavior is entirely determined by genetics. However, studies have shown that fruit flies can learn from their experiences and adjust their mating behavior accordingly.
- Irrelevance to Humans: Some people believe that fruit fly mating behavior is irrelevant to humans, but this is not the case. Studies of fruit fly mating behavior have provided valuable insights into genetics, neuroscience, and evolutionary biology that are applicable to more complex organisms, including humans.
13. Where Can I Learn More About Fruit Fly Mating?
You can learn more about fruit fly mating from scientific journals, university websites, and educational resources like flyermedia.net, which offer detailed information and research findings. These sources provide a wealth of knowledge for anyone interested in this fascinating topic.
- Scientific Journals: Journals such as Nature, Science, and the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) publish cutting-edge research on fruit fly mating behavior.
- University Websites: Websites of universities that conduct research on fruit flies, such as Princeton University and the California Institute of Technology (Caltech), often feature articles and videos about their research.
- Educational Resources: Websites like flyermedia.net provide educational articles and resources on a variety of topics, including fruit fly mating behavior.
- Books: Several books have been written about fruit flies and their behavior, including “The Fly: Six Legs, and Nearly 200 Million Years” by Jonathan Balcombe and “Drosophila Protocols” by Christiane Nusslein-Volhard.
- Online Courses: Online courses on genetics, neuroscience, and evolutionary biology often include modules on fruit fly mating behavior.
14. What are the Ethical Considerations in Studying Fruit Fly Mating?
Ethical considerations in studying fruit fly mating primarily involve ensuring humane treatment and minimizing harm, as well as adhering to scientific integrity and transparency in research practices. While fruit flies are simple organisms, responsible research practices are still essential.
- Humane Treatment: Researchers should ensure that fruit flies are treated humanely and that their welfare is considered throughout the study. This includes providing appropriate living conditions and minimizing stress.
- Minimizing Harm: Research procedures should be designed to minimize harm to fruit flies. This may involve using non-invasive techniques and avoiding unnecessary suffering.
- Scientific Integrity: Researchers should adhere to the principles of scientific integrity, including honesty, accuracy, and objectivity. This includes reporting all data accurately and avoiding any form of scientific misconduct.
- Transparency: Research methods and results should be transparent and accessible to the public. This allows other scientists to replicate and verify the findings and promotes public trust in science.
- Regulatory Compliance: Researchers should comply with all relevant regulations and guidelines regarding the use of animals in research. This includes obtaining ethical approval from institutional review boards and following best practices for animal care.
15. How Can I Prevent Fruit Flies From Mating in My Home?
To prevent fruit flies from mating in your home, eliminate food sources, maintain cleanliness, and use traps to control their population. These methods reduce the likelihood of fruit flies finding suitable breeding grounds and reproducing.
- Eliminate Food Sources: Fruit flies are attracted to fermenting fruits and vegetables, so it is important to keep these items stored properly. Dispose of overripe or rotting produce promptly.
- Maintain Cleanliness: Clean up spills and messes immediately, especially those involving sugary or fermented substances. Regularly clean drains and garbage disposals, as these can be breeding grounds for fruit flies.
- Use Traps: Set up fruit fly traps to capture and kill adult flies. These traps can be made at home using a mixture of apple cider vinegar and dish soap or purchased from a store.
- Seal Entry Points: Seal any cracks or openings in windows and doors to prevent fruit flies from entering your home.
- Regular Cleaning: Regularly clean and sanitize areas where food is prepared or stored. This will help to eliminate food sources and prevent fruit flies from breeding.
- Monitor and Inspect: Regularly monitor your home for signs of fruit flies and inspect potential breeding sites. This will allow you to take action quickly if a fruit fly infestation develops.
In conclusion, understanding the intricate mating rituals of fruit flies offers valuable insights into genetics, neuroscience, and evolutionary biology. From the complex courtship songs to the selective mate choices of females, these tiny creatures provide a wealth of information that can benefit various fields of study. Visit flyermedia.net to explore more fascinating facts about the natural world and stay updated on the latest research and discoveries.
FAQ Section
1. What attracts fruit flies to my house?
- Fruit flies are attracted to ripe, rotting, or fermenting fruits and vegetables, as well as sugary liquids like spilled juice or alcohol.
2. How quickly do fruit flies reproduce?
- Fruit flies can complete their life cycle in as little as 8-10 days under optimal conditions, allowing for rapid population growth.
3. Can fruit flies transmit diseases?
- While fruit flies themselves do not directly transmit diseases, they can carry bacteria and other microorganisms from contaminated sources to food.
4. What is the best way to get rid of fruit flies?
- The best way to get rid of fruit flies is to eliminate their food sources, clean up any spills or messes, and use fruit fly traps to capture and kill adult flies.
5. Are fruit flies harmful to humans?
- Fruit flies are generally not harmful to humans, but they can be a nuisance and contaminate food.
6. How long do fruit flies live?
- Adult fruit flies typically live for about 40-50 days, depending on environmental conditions.
7. What is the purpose of fruit fly courtship?
- The purpose of fruit fly courtship is to attract a mate and ensure successful reproduction through species-specific songs and dances.
8. Do both male and female fruit flies sing?
- No, only male fruit flies sing during courtship to attract females.
9. How do female fruit flies store sperm?
- Female fruit flies store sperm in specialized organs called spermathecae, allowing them to fertilize eggs over an extended period.
10. What role do pheromones play in fruit fly mating?
- Pheromones act as chemical signals that attract mates and indicate receptivity to mating, playing a crucial role in fruit fly courtship.
Call to Action
Are you fascinated by the intricate world of fruit fly mating and eager to learn more about the science behind it? Visit flyermedia.net today to discover a wealth of information on genetics, neuroscience, and evolutionary biology. Explore our resources and stay informed about the latest discoveries in the natural world. Don’t miss out – satisfy your curiosity and expand your knowledge with flyermedia.net!