Do peacock flies fly? Absolutely! Peacock flies are indeed capable of flight, and their vibrant wing displays are just one fascinating aspect of these insects. Flyermedia.net is your go-to source for unraveling the mysteries of the insect world, including the captivating peacock fly. Learn more about their unique behaviors, habitats, and the role they play in the ecosystem. Dive in and explore the world of entomology with us, discovering everything from insect flight patterns to ecological impact and biodiversity.
1. What Exactly Are Peacock Flies? A Comprehensive Look
Peacock flies, scientifically known as Callopistromyia annulipes, belong to the Ulidiidae family, a group of flies characterized by their vibrant wing patterns and unique display behaviors. These eye-catching insects are not just another fly; they are a testament to the beauty and complexity found within the insect kingdom. Their distinctive appearance and behaviors make them a subject of fascination for entomologists and nature enthusiasts alike.
1.1 Identifying Characteristics of Peacock Flies
Peacock flies boast several key features that set them apart:
- Wing Patterns: The most striking feature is their intricately patterned wings, often resembling eyespots or iridescent markings.
- Size and Shape: Typically small to medium-sized, their body shape is similar to other fly species, but their wing patterns make them instantly recognizable.
- Display Behavior: Peacock flies are known for their unique display behaviors, where they raise or flutter their wings to attract mates or deter predators.
1.2 Distinguishing Peacock Flies from Peahen Flies
While both belong to the same genus (Callopistromyia), there are key differences between peacock flies (C. annulipes) and peahen flies (C. strigula):
| Feature | Peacock Fly (C. annulipes) | Peahen Fly (C. strigula) |
|---|---|---|
| Wing Width | Wider wings | Narrower wings |
| Wing Display | Wings held above the body | Wings held out to the sides |
| Geographic Range | Widespread in North America | More restricted distribution |
These distinctions, while subtle, are important for accurate identification and understanding their respective ecological roles.
1.3 Habitat and Distribution of Peacock Flies
C. annulipes is widespread across the United States and can be found in several Canadian provinces, including British Columbia, Alberta, and Ontario. On the other hand, C. strigula is found in Manitoba, Ontario and Saskatchewan as well as several States. According to research from Pintilioaie and Manci, in July 2020, this species has spread into Europe as well, no doubt via human means. Their adaptability allows them to thrive in various environments, from forests to urban gardens.
2. Unveiling the Mystery: How Do Peacock Flies Fly?
Peacock flies, like other members of the Diptera order (true flies), possess a single pair of functional wings that power their flight. Their flight mechanism involves rapid wing movements and precise coordination to achieve lift, propulsion, and maneuverability.
2.1 The Mechanics of Fly Flight
The act of flying isn’t easy. Here’s a basic look at what goes into how it works.
- Wing Structure: Fly wings are thin, membranous structures supported by a network of veins that provide strength and flexibility.
- Flight Muscles: Powerful flight muscles, both direct and indirect, control the wing movements. Direct flight muscles attach directly to the wing base, while indirect muscles distort the thorax, causing the wings to move.
- Halteres: These modified hindwings act as gyroscopic stabilizers, helping the fly maintain balance and orientation during flight.
2.2 Peacock Fly Flight Characteristics
Although their flight mechanics are similar to other flies, peacock flies exhibit some unique characteristics:
- Agility: They demonstrate agile flight, allowing them to quickly change direction and hover in place.
- Display Flight: Their flight is often integrated with their display behavior, using wing movements to enhance their visual signals.
- Speed: They are not particularly fast fliers, as their primary focus is on display rather than rapid movement.
2.3 The Role of Wings in Flight and Display
The wings of peacock flies serve a dual purpose:
- Flight: The wings enable them to move efficiently through their environment, search for food, and escape predators.
- Display: The vibrant patterns and movements of their wings are crucial for attracting mates and communicating with other individuals.
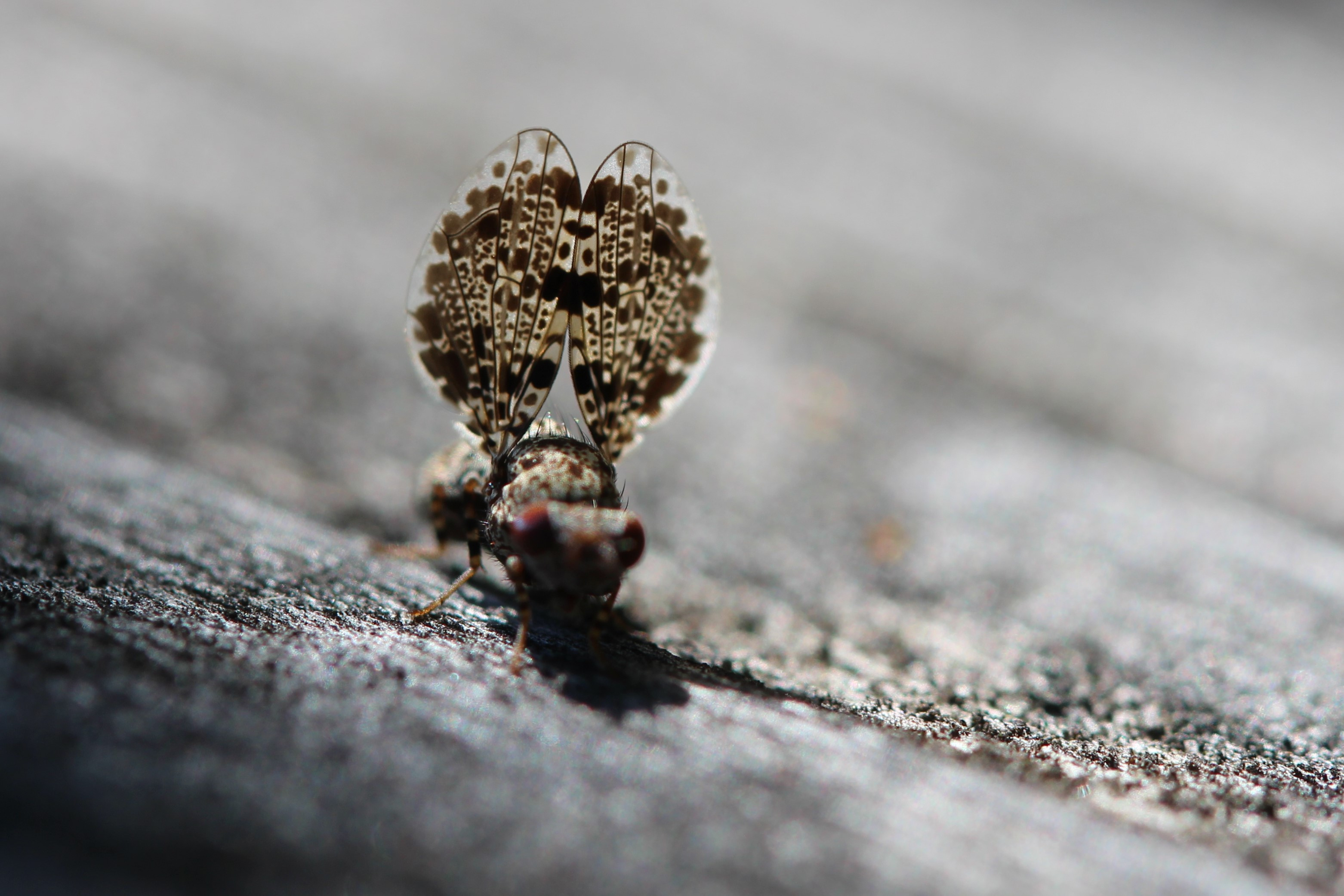 Peacock Fly (*Callopistromyia annulipes*) displaying its wings.
Peacock Fly (*Callopistromyia annulipes*) displaying its wings.
3. Decoding the Peacock Fly’s Wing Display: More Than Just Flight
The wing display of peacock flies is a complex behavior with multiple functions, including mate attraction, predator deterrence, and intraspecific communication. Understanding these displays provides valuable insights into their social behavior and ecological interactions.
3.1 Mate Attraction Through Wing Displays
One of the primary functions of the wing display is to attract potential mates. Both males and females engage in these displays, suggesting mutual mate choice.
- Visual Signaling: The vibrant patterns on their wings serve as visual signals that attract the attention of potential partners.
- Courtship Rituals: The wing movements and postures are part of elaborate courtship rituals that facilitate mate selection.
- Mutual Selection: Both sexes display, indicating that both males and females are selective in their mate choice.
3.2 Predator Deterrence: Mimicry and Deception
Another fascinating hypothesis is that the wing patterns of peacock flies mimic the appearance of jumping spiders, which are visual predators of insects. According to research from Hill, David, A. P. C., Abhijith, and Burini, in July 2019, this mimicry could deter predators by exploiting the visual system of jumping spiders, causing them to hesitate before attacking.
- Jumping Spider Mimicry: The wing patterns resemble the face of a jumping spider, potentially deterring these predators.
- Visual Deterrent: The patterns may manipulate the spider’s perception, causing them to perceive the fly as another spider rather than prey.
- Brief Delay: Even a brief delay in the predator’s attack could provide the fly with an opportunity to escape.
3.3 Intraspecific Communication: Signaling Between Individuals
Wing displays also play a role in communication between individuals of the same species.
- Territorial Defense: Displays may be used to defend territories or resources from rivals.
- Social Signaling: The displays could convey information about the fly’s health, status, or intentions.
- Coordination: Displays might help coordinate group behaviors, such as swarming or migration.
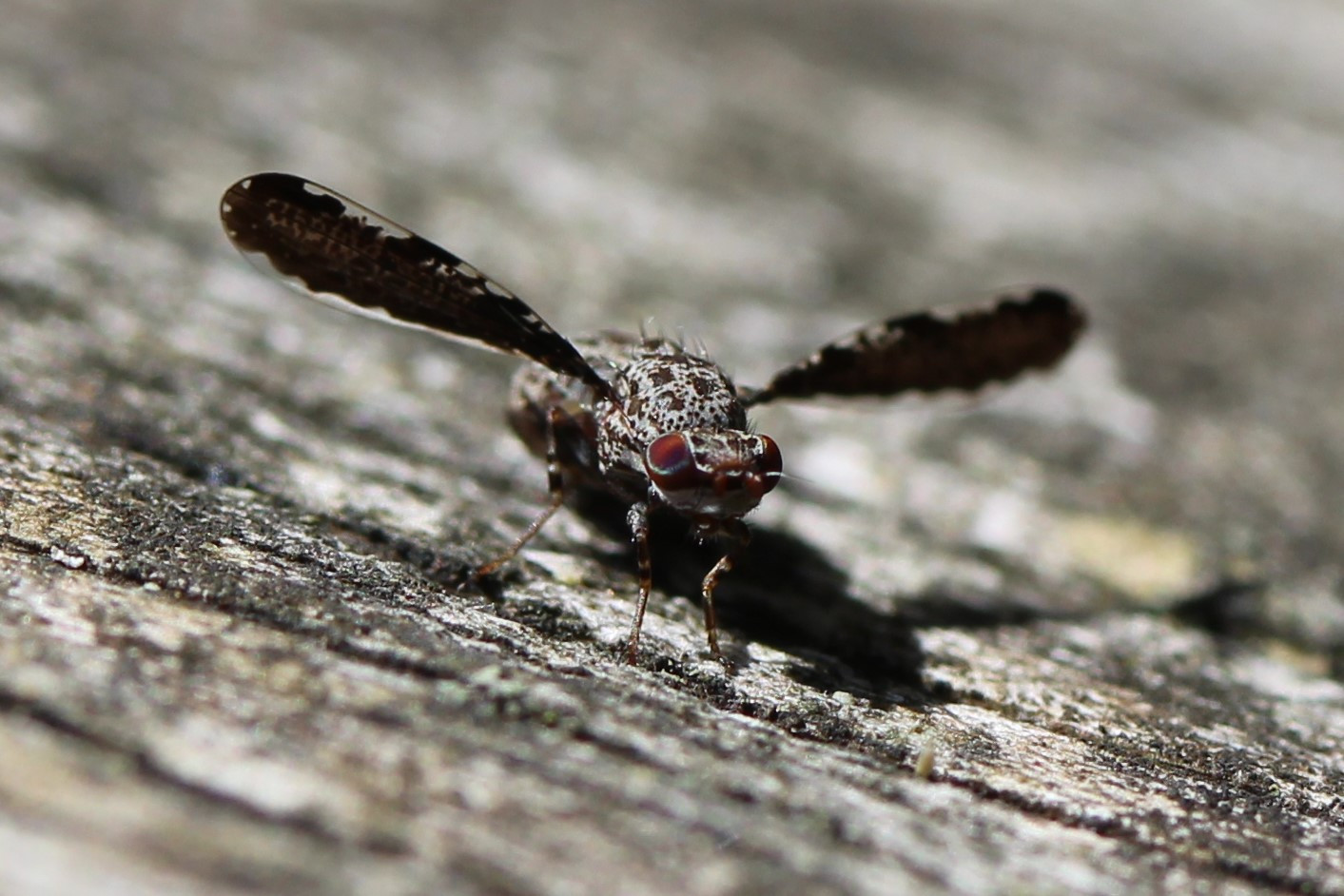 Peahen Fly (*Callopistromyia strigula*) displaying its wings horizontally.
Peahen Fly (*Callopistromyia strigula*) displaying its wings horizontally.
4. What Do Peacock Fly Larvae Eat? Diet and Life Cycle
The life cycle and dietary habits of peacock flies are intriguing, particularly the larval stage. These larvae play a role in their ecosystems, contributing to decomposition and nutrient cycling.
4.1 Larval Diet and Habitat
Peacock fly larvae typically feed on decaying organic matter, such as dead wood or fungi within dead wood. According to research from van der Linden, in July 2018, Callopistromyia larvae were found feeding on the inner bark of a boxelder tree (Acer negundo).
- Decomposers: They act as decomposers, breaking down organic material and releasing nutrients back into the environment.
- Habitat: Larvae are commonly found beneath the bark of deciduous trees, where they have access to their food source.
4.2 The Complete Life Cycle of a Peacock Fly
The life cycle of peacock flies involves several stages:
- Egg: The life cycle begins with the laying of eggs, typically on or near their food source.
- Larva: The larva emerges from the egg and feeds voraciously, growing through several instars (stages) as it molts its skin.
- Pupa: The larva pupates, forming a protective puparium around itself.
- Adult: The adult fly emerges from the puparium, ready to reproduce and continue the cycle.
4.3 Importance of Larvae in the Ecosystem
Larvae play a crucial role in the ecosystem:
- Nutrient Cycling: By breaking down organic matter, they release essential nutrients that support plant growth and other organisms.
- Food Source: They serve as a food source for other insects, birds, and small animals.
- Decomposition: They aid in the decomposition process, preventing the buildup of organic waste.
5. Where Can You Spot Peacock Flies in the USA? Distribution and Habitats
Understanding the distribution and habitat preferences of peacock flies is essential for spotting them in the wild.
5.1 Geographic Distribution in the United States
Peacock flies (C. annulipes) are widely distributed across the United States, particularly in regions with deciduous forests and abundant decaying wood.
- Eastern United States: They are commonly found in states such as New York, Pennsylvania, and Massachusetts.
- Midwestern United States: States like Ohio, Illinois, and Michigan also have populations of peacock flies.
- Western United States: They can be found in areas like California, Oregon, and Washington.
5.2 Preferred Habitats of Peacock Flies
They thrive in specific types of environments:
- Deciduous Forests: Forests with trees that lose their leaves annually provide ample dead wood for larval development.
- Wooded Areas: Parks, gardens, and other wooded areas with decaying organic matter are also suitable habitats.
- Near Water Sources: Areas near streams, ponds, or other water sources may provide additional moisture and resources for these flies.
5.3 Tips for Spotting Peacock Flies
Here are some tips to increase your chances of spotting peacock flies:
- Look for Displaying Adults: Scan conspicuous surfaces like railings, leaves, and tree trunks for displaying adults.
- Visit Deciduous Forests: Explore deciduous forests and wooded areas during the warmer months.
- Check Decaying Wood: Examine decaying wood for larvae or puparia.
- Use a Camera: Bring a camera to capture photos of these beautiful insects, helping you identify them later.
6. What Does Peacock Fly Mimicry Mean?
Mimicry in peacock flies refers to their wing patterns resembling jumping spiders, potentially deterring predators. This section explores the concept of mimicry in more detail, focusing on its significance in the natural world and its specific application to peacock flies.
6.1 Understanding Mimicry in Nature
Mimicry is a phenomenon where one species evolves to resemble another species or object. This can provide various advantages, such as protection from predators or increased success in attracting prey.
- Batesian Mimicry: A harmless species evolves to resemble a harmful one, deterring predators.
- Müllerian Mimicry: Two or more harmful species evolve to resemble each other, reinforcing the warning signal to predators.
- Aggressive Mimicry: A predator evolves to resemble a harmless species, allowing it to approach prey more easily.
6.2 How Peacock Flies Utilize Mimicry
Peacock flies are thought to employ mimicry by having wing patterns that resemble the faces of jumping spiders. This is called mimicry.
- Visual Deterrent: The wing patterns may act as a visual deterrent, causing jumping spiders to hesitate or avoid attacking.
- Exploiting Predator Perception: The mimicry exploits the visual system of jumping spiders, which are highly visual predators.
6.3 The Evolutionary Significance of Mimicry
Mimicry is a powerful evolutionary adaptation that can significantly impact the survival and reproductive success of a species.
- Increased Survival: By deterring predators, mimicry can increase the chances of survival for the mimetic species.
- Reproductive Success: Mimicry can also enhance reproductive success by allowing individuals to live longer and produce more offspring.
- Coevolution: Mimicry often leads to coevolution between the mimic and the model, driving further adaptations in both species.
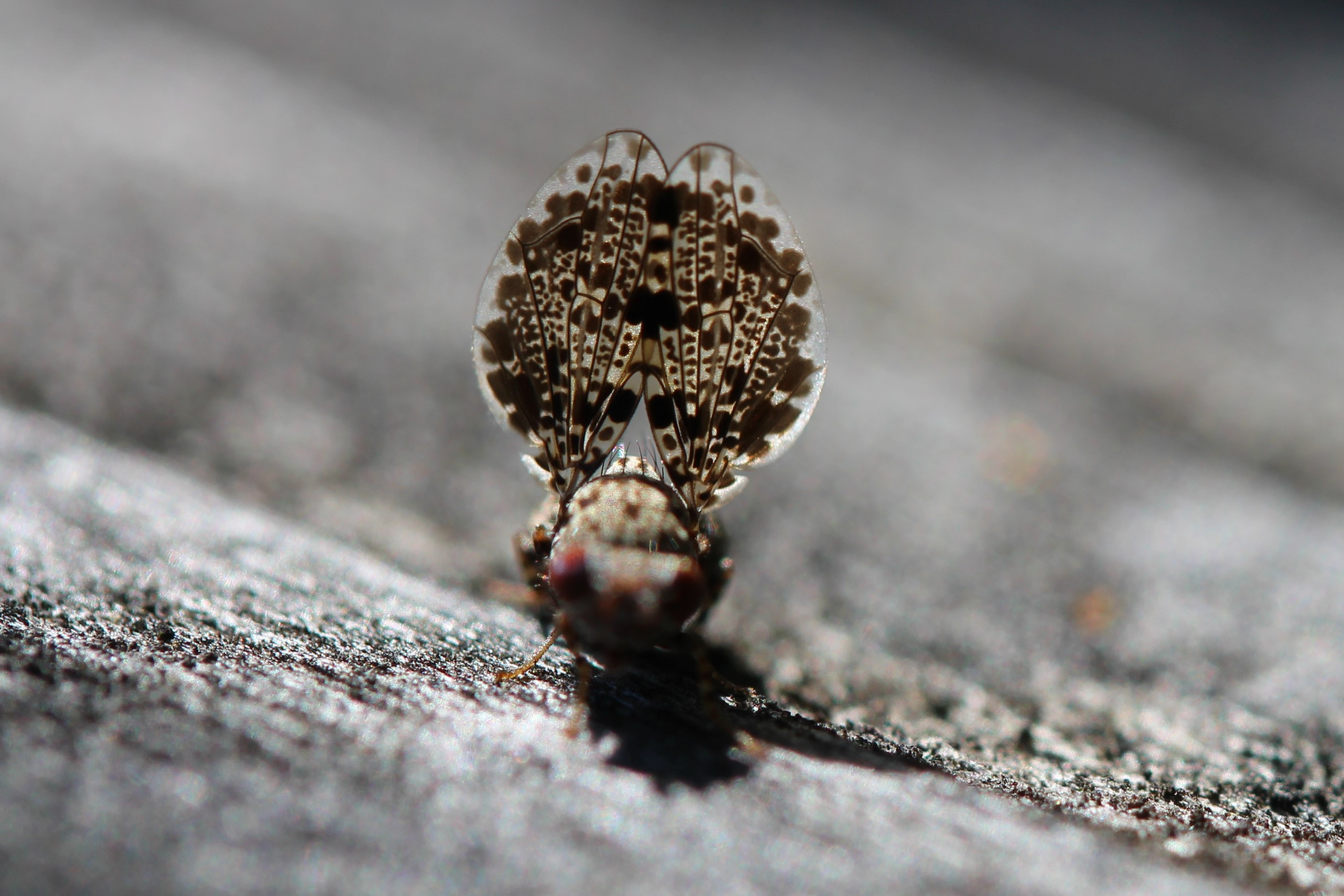 Close-up of a Peacock Fly's wing pattern, showing resemblance to a Jumping Spider.
Close-up of a Peacock Fly's wing pattern, showing resemblance to a Jumping Spider.
7. Exploring the Broader World of Flies: Why Study Diptera?
The order Diptera, which includes flies, is one of the most diverse and ecologically important groups of insects. Studying flies provides valuable insights into evolution, ecology, and the functioning of ecosystems.
7.1 The Ecological Importance of Flies
Flies play numerous crucial roles in ecosystems:
- Pollination: Many fly species are important pollinators, transferring pollen between flowers and facilitating plant reproduction.
- Decomposition: Larvae of many flies are decomposers, breaking down organic matter and recycling nutrients.
- Predation: Some flies are predators, controlling populations of other insects and invertebrates.
- Food Source: Flies serve as a food source for a wide range of animals, including birds, reptiles, and other insects.
7.2 The Diversity of Diptera
The order Diptera is incredibly diverse, with thousands of species exhibiting a wide range of adaptations and behaviors.
- Morphological Diversity: Flies exhibit a wide range of body shapes, sizes, and colors.
- Behavioral Diversity: They display diverse behaviors, including complex mating rituals, social interactions, and foraging strategies.
- Ecological Diversity: Flies occupy a wide range of ecological niches, from aquatic environments to terrestrial habitats.
7.3 Why Flies Matter to Humans
Flies have significant impacts on human health, agriculture, and the environment:
- Disease Transmission: Some flies transmit diseases to humans and animals, posing a public health risk.
- Agricultural Pests: Certain flies are agricultural pests, damaging crops and reducing yields.
- Beneficial Insects: Other flies are beneficial, providing pollination services and controlling pest populations.
8. How Flyermedia.net Can Help You Learn More About Flies
Flyermedia.net is your ultimate resource for exploring the fascinating world of flies and other insects. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or nature enthusiast, our website offers a wealth of information and resources to help you learn more about these incredible creatures.
8.1 Comprehensive Information and Resources
Our website provides detailed information on a wide range of topics related to flies, including:
- Species Profiles: In-depth profiles of various fly species, including their identification, distribution, and ecology.
- Life Cycle Information: Detailed descriptions of the life cycles of flies, from egg to adult.
- Behavioral Studies: Insights into the behaviors of flies, including their mating rituals, foraging strategies, and social interactions.
- Ecological Roles: Discussions of the ecological roles of flies, including their importance as pollinators, decomposers, and predators.
8.2 Educational Articles and Blog Posts
We regularly publish educational articles and blog posts on various aspects of fly biology, ecology, and conservation. Our content is written by experts in the field and is designed to be accessible to a wide audience.
- Latest Research: Stay up-to-date on the latest research findings related to flies.
- Conservation Efforts: Learn about conservation efforts aimed at protecting fly populations and their habitats.
- DIY Projects: Discover fun and educational DIY projects related to flies, such as building a fly trap or creating a fly-friendly garden.
8.3 Community Engagement and Interaction
Flyermedia.net is more than just a website; it’s a community of insect enthusiasts. We encourage you to engage with us and other members of our community through:
- Forums: Participate in discussions on various topics related to flies and other insects.
- Social Media: Follow us on social media for the latest updates, photos, and videos.
- Events: Attend our webinars, workshops, and other events to learn from experts and connect with fellow enthusiasts.
9. What Aviation Careers are Available in the USA?
The aviation industry in the USA offers a wide array of exciting and rewarding career paths. From pilots soaring through the skies to engineers designing the next generation of aircraft, there’s a niche for every skill set and passion. Flyermedia.net is your comprehensive resource for navigating the world of aviation careers.
9.1 Pilot Careers
Pilots are the face of aviation, responsible for safely transporting passengers and cargo across the globe.
- Airline Pilots: Fly commercial aircraft for major airlines, requiring extensive training and certification.
- Cargo Pilots: Transport goods and materials for freight companies, often operating on flexible schedules.
- Corporate Pilots: Fly private jets for businesses and individuals, providing personalized travel experiences.
- Flight Instructors: Teach aspiring pilots the skills and knowledge needed to earn their licenses.
9.2 Aviation Maintenance and Engineering Careers
These professionals ensure the safety and reliability of aircraft through meticulous maintenance and innovative engineering.
- Aircraft Mechanics: Inspect, repair, and maintain aircraft systems, adhering to strict regulatory standards.
- Avionics Technicians: Specialize in the maintenance and repair of aircraft electronic systems, including navigation and communication equipment.
- Aerospace Engineers: Design and develop aircraft and spacecraft, pushing the boundaries of aviation technology.
9.3 Air Traffic Control Careers
Air traffic controllers play a critical role in managing the flow of air traffic, ensuring the safe and efficient movement of aircraft.
- Air Traffic Controllers: Monitor and direct aircraft movements, providing guidance to pilots and preventing collisions.
- Traffic Management Specialists: Analyze air traffic patterns and develop strategies to optimize airspace utilization.
9.4 Airport Operations Careers
Airport operations professionals manage the day-to-day activities of airports, ensuring smooth and efficient operations.
- Airport Managers: Oversee all aspects of airport operations, including safety, security, and customer service.
- Ground Handling Staff: Provide essential services such as baggage handling, aircraft fueling, and passenger assistance.
9.5 Other Aviation Careers
The aviation industry also encompasses a variety of other specialized roles.
- Aviation Safety Inspectors: Enforce safety regulations and conduct inspections to ensure compliance.
- Aviation Insurance Underwriters: Assess risks and provide insurance coverage for aviation-related activities.
- Aviation Lawyers: Provide legal counsel to aviation companies and individuals, navigating complex regulatory issues.
10. Where Can You Find Aviation Training in Daytona Beach, USA?
Daytona Beach, Florida, is a renowned hub for aviation training, offering a wide range of programs and institutions to help aspiring aviators achieve their dreams. If you’re looking to kickstart your aviation career, Daytona Beach is the place to be.
10.1 Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University
Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University is one of the world’s leading aviation and aerospace universities, offering a comprehensive range of degree programs and flight training courses. Address: 600 S Clyde Morris Blvd, Daytona Beach, FL 32114, United States. Phone: +1 (386) 226-6000. Website: flyermedia.net.
- Flight Training: Embry-Riddle’s flight training program is highly regarded, providing students with the skills and experience needed to become successful pilots.
- Aeronautical Engineering: The university’s aerospace engineering program is one of the best in the world, producing innovative engineers who shape the future of aviation.
10.2 Daytona State College
Daytona State College offers affordable and accessible aviation training programs, providing students with a pathway to aviation careers.
- Aviation Maintenance Technology: Daytona State’s aviation maintenance technology program prepares students for careers as aircraft mechanics and avionics technicians.
- Air Traffic Control: The college’s air traffic control program provides students with the knowledge and skills needed to become air traffic controllers.
10.3 Phoenix East Aviation
Phoenix East Aviation is a flight school offering accelerated flight training programs for aspiring pilots.
- Accelerated Flight Training: Phoenix East’s accelerated programs allow students to earn their pilot licenses in a shorter timeframe.
- International Student Programs: The school welcomes international students, providing them with the opportunity to pursue aviation careers in the United States.
10.4 Other Flight Schools and Training Centers
In addition to the major institutions listed above, Daytona Beach is home to numerous other flight schools and training centers, each offering unique programs and approaches to aviation education.
- Epic Flight Academy: Offers flight training programs for both domestic and international students.
- Airline Transport Professionals (ATP): Provides accelerated flight training programs for those seeking to become airline pilots.
FAQ: Your Burning Questions About Peacock Flies Answered
1. Can peacock flies bite humans?
No, peacock flies do not bite humans. They are not blood-feeding insects and do not have mouthparts designed for biting.
2. Are peacock flies harmful?
Peacock flies are not harmful to humans or the environment. They play a beneficial role in ecosystems as decomposers and pollinators.
3. What is the lifespan of a peacock fly?
The lifespan of a peacock fly varies depending on environmental conditions, but it is typically a few weeks to a few months.
4. What attracts peacock flies to an area?
Peacock flies are attracted to areas with decaying organic matter, such as dead wood and fungi, which serve as food sources for their larvae.
5. How can I attract peacock flies to my garden?
To attract peacock flies to your garden, provide a habitat with decaying wood, leaf litter, and flowering plants.
6. What is the purpose of the peacock fly’s wing patterns?
The wing patterns of peacock flies serve multiple purposes, including mate attraction, predator deterrence, and intraspecific communication.
7. Are peacock flies related to peacocks?
Peacock flies are not related to peacocks. The name “peacock fly” refers to the resemblance of their wing patterns to the colorful plumage of peacocks.
8. How do peacock flies reproduce?
Peacock flies reproduce sexually, with both males and females engaging in elaborate courtship displays to attract mates.
9. What is the conservation status of peacock flies?
Peacock flies are not currently considered to be threatened or endangered. However, habitat loss and degradation could pose a threat to their populations in the future.
10. Where can I find more information about peacock flies?
You can find more information about peacock flies on flyermedia.net, as well as in scientific publications, entomological databases, and field guides.
Ready to dive deeper into the captivating world of aviation and entomology? Visit flyermedia.net today to explore our extensive resources, connect with fellow enthusiasts, and discover the endless possibilities that await you in the skies and beyond. Whether you’re seeking flight training, career advice, or simply a place to fuel your passion, flyermedia.net is your trusted partner on your journey to success.