Do Bounce Houses Fly Away, posing a danger to children and adults? The answer is yes, bounce houses can indeed fly away, especially under certain weather conditions. Flyermedia.net explores the risks associated with wind and bounce houses, providing insights and safety measures for responsible use and safe aviation.
1. What Causes Bounce Houses to Fly Away?
Bounce houses fly away primarily due to strong winds that generate enough lift to overcome the anchoring and weight of the structure. Several factors contribute to this:
- Wind Speed: High winds, especially gusts, can exert significant force on the large surface area of a bounce house.
- Anchoring: Inadequate or improperly installed anchors fail to secure the bounce house to the ground.
- Design: The aerodynamic design of bounce houses can make them susceptible to lifting in windy conditions.
- Location: Placement in open areas or on elevated surfaces exposes the bounce house to greater wind forces.
To understand how these elements combine to cause a bounce house to fly away, it’s critical to know what causes the wind.
1.1 Meteorological Conditions
Meteorological conditions, such as cold fronts, dust devils, and thunderstorm-related winds, increase the risk of bounce houses becoming airborne. John Knox, a geography professor at the University of Georgia, explains that these weather events can create “sneaky” winds that catch people off guard. Even winds as low as 25 mph can pose a significant threat.
- Cold Fronts: Rapid changes in temperature and wind direction can generate strong gusts.
- Dust Devils: Localized, rotating columns of air can lift lightweight objects.
- Thunderstorm Winds: Downdrafts and outflow boundaries can produce sudden and intense winds.
1.2 Impact of Geography
The geography of an area also plays a vital role in wind conditions. Open fields, coastal regions, and elevated areas are more prone to high winds. Buildings and natural barriers can create wind tunnels or deflect winds, intensifying their effects. According to the National Weather Service (NWS), understanding local weather patterns and geographical features is crucial for assessing wind risks.
2. What Are the Statistics on Bounce House Accidents?
A study by the University of Georgia documented 132 wind-related bounce house accidents worldwide from 2000 to 2021, resulting in at least 479 injuries and 28 deaths. The study highlights the serious consequences of inadequate safety measures and a lack of regulations.
2.1 Underreported Incidents
John Knox noted that the actual number of accidents may be higher than reported. Many incidents go undocumented because they do not make it onto the internet or are not reported to authorities. This underreporting underscores the need for greater awareness and vigilance in using bounce houses.
2.2 Factors Contributing to Accidents
Over 70% of bounce house accidents are attributed to specific meteorological causes. These accidents often occur when wind speeds are lower than the regulatory gold standard set by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), indicating that even seemingly safe conditions can be hazardous.
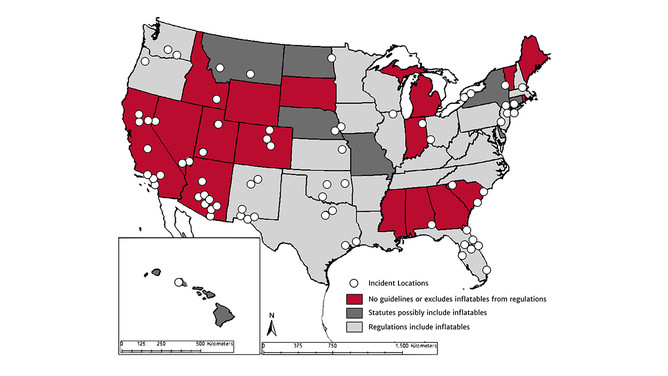 Bounce house accidents often occur in states with minimal regulations, emphasizing the need for stringent safety measures.
Bounce house accidents often occur in states with minimal regulations, emphasizing the need for stringent safety measures.
3. What Are the Regulations and Standards for Bounce House Safety?
Regulations for bounce house safety vary significantly across the United States. Seventeen states have no guidelines or explicitly exclude inflatables from regulation. Nineteen states cite ASTM standards, which set limits on wind speed and require a meteorologically knowledgeable attendant for commercial bounce houses.
3.1 ASTM Standards
ASTM standards recommend that bounce houses not be used in wind speeds exceeding 25 mph. These standards also outline requirements for anchoring, setup, and supervision. However, even adherence to these standards may not eliminate all risks, as wind conditions can change rapidly and unpredictably.
3.2 State-Specific Regulations
Some states have implemented more stringent regulations than others. For example, states with comprehensive regulations may require permits, inspections, and specific safety protocols for bounce house operators. These regulations aim to ensure that bounce houses are set up and operated safely, minimizing the risk of accidents.
3.3 Lack of Uniformity
The lack of uniform regulations across the U.S. poses a challenge for ensuring bounce house safety. The inconsistent standards can create confusion for operators and parents, making it difficult to assess the true risk. Advocates for stricter regulations argue that a standardized approach is needed to protect children and adults from wind-related accidents.
4. How to Ensure Bounce House Safety in Windy Conditions?
Ensuring bounce house safety in windy conditions requires a multi-faceted approach, including proper setup, continuous monitoring, and adherence to safety guidelines. Here are some steps to mitigate the risks:
- Check Weather Conditions: Monitor weather forecasts and be aware of potential wind gusts.
- Proper Anchoring: Use appropriate anchors and ensure they are securely installed.
- Supervision: Always have a responsible adult supervise the bounce house.
- Wind Speed Limits: Do not use the bounce house if wind speeds exceed 25 mph.
- Clear Surroundings: Keep the area around the bounce house clear of obstacles.
- Emergency Plan: Have a plan in place in case of sudden weather changes.
4.1 Detailed Safety Checklist
To further enhance safety, consider the following detailed checklist:
| Aspect | Action |
|---|---|
| Weather | Check the forecast for wind speed, gusts, and potential thunderstorms. Use weather apps or websites that provide real-time updates. |
| Anchoring | Use ground stakes that are at least 18 inches long and specifically designed for bounce houses. Ensure each anchor point is securely fastened to the ground. |
| Placement | Position the bounce house on a flat, level surface away from trees, fences, and power lines. Avoid areas prone to high winds or drafts. |
| Supervision | Assign a dedicated supervisor who is responsible for monitoring the bounce house and enforcing safety rules. The supervisor should be trained in emergency procedures. |
| Wind Monitoring | Use a handheld anemometer to measure wind speed at the location. Regularly check wind conditions and be prepared to deflate the bounce house if wind speeds increase. |
| Emergency | Keep a first-aid kit nearby and ensure the supervisor knows how to respond to injuries. Have a communication plan in place for contacting emergency services. |
| Maintenance | Regularly inspect the bounce house for damage or wear. Ensure all seams, zippers, and safety netting are in good condition. |
| User Guidelines | Establish clear rules for users, including limiting the number of children allowed at one time, prohibiting food and drinks inside the bounce house, and ensuring children remove shoes and sharp objects before entering. |
4.2 Expert Recommendations
Experts recommend that parents and operators take a proactive approach to bounce house safety. This includes educating themselves on potential risks, following safety guidelines, and being prepared to take immediate action if conditions become unsafe. The Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) also provides safety guidelines and recommendations for inflatable amusement rides.
5. What Are the Legal Aspects of Bounce House Accidents?
Legal aspects of bounce house accidents encompass liability, insurance, and potential lawsuits. Understanding these aspects is crucial for both operators and users of bounce houses.
5.1 Liability
Liability for bounce house accidents typically falls on the operator or owner of the bounce house. This includes ensuring the equipment is properly maintained, set up, and supervised. Negligence, such as failure to secure the bounce house or ignoring weather warnings, can result in legal action.
5.2 Insurance
Insurance coverage is essential for bounce house operators to protect against potential liabilities. General liability insurance can cover damages and injuries resulting from accidents. Some policies may also include coverage for wind-related incidents. It’s important to review insurance policies carefully to understand the extent of coverage and any exclusions.
5.3 Lawsuits
Lawsuits arising from bounce house accidents can involve claims for personal injury, property damage, and wrongful death. Plaintiffs may seek compensation for medical expenses, lost wages, pain and suffering, and other damages. Legal outcomes often depend on the specific circumstances of the accident and the degree of negligence involved.
6. How Can Technology Improve Bounce House Safety?
Technology offers several opportunities to improve bounce house safety, including advanced monitoring systems, smart anchoring solutions, and weather forecasting tools.
6.1 Advanced Monitoring Systems
Advanced monitoring systems can provide real-time data on wind speed, temperature, and other environmental factors. These systems can alert operators to potentially hazardous conditions and automatically deflate the bounce house if wind speeds exceed safe limits.
6.2 Smart Anchoring Solutions
Smart anchoring solutions use sensors to monitor the tension and stability of anchors. If an anchor becomes loose or compromised, the system can alert the operator and take corrective action.
6.3 Weather Forecasting Tools
Weather forecasting tools provide accurate and timely weather information, allowing operators to make informed decisions about bounce house usage. These tools can integrate with monitoring systems to provide comprehensive safety alerts.
6.4 Examples of Technological Applications
- Anemometers: Handheld anemometers can measure wind speed on-site, providing immediate feedback on conditions.
- Weather Apps: Mobile weather apps offer real-time forecasts and alerts, helping operators stay informed about potential weather changes.
- GPS Tracking: GPS tracking systems can monitor the location of bounce houses, preventing theft and ensuring they are set up in designated areas.
- Remote Deflation Systems: Remote deflation systems allow operators to quickly deflate a bounce house from a distance in case of emergency.
7. What Role Does Education Play in Preventing Bounce House Accidents?
Education is a key component in preventing bounce house accidents. Raising awareness among operators, parents, and users about the risks and safety measures can significantly reduce the number of incidents.
7.1 Training for Operators
Training programs for bounce house operators should cover topics such as proper setup, anchoring techniques, weather monitoring, and emergency procedures. Certified training programs can ensure operators have the knowledge and skills to operate bounce houses safely.
7.2 Safety Campaigns for Parents
Safety campaigns can educate parents about the risks associated with bounce houses and provide tips for safe usage. These campaigns can use social media, public service announcements, and community events to reach a wide audience.
7.3 Educational Materials for Users
Educational materials, such as brochures and posters, can inform users about safety rules and guidelines. These materials should be displayed prominently at bounce house locations.
7.4 Resources for Learning
- Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC): Provides safety guidelines and recommendations for inflatable amusement rides.
- American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM): Sets standards for bounce house safety, including wind speed limits and anchoring requirements.
- University of Georgia Study: Offers data and insights on wind-related bounce house accidents.
- Flyermedia.net: Provides resources and information on aviation safety and related topics.
8. Do Insurance Companies Have Specific Requirements for Bounce House Coverage?
Insurance companies often have specific requirements for bounce house coverage to mitigate their financial risk. These requirements can include inspections, safety protocols, and adherence to industry standards.
8.1 Inspection Requirements
Insurance companies may require regular inspections of bounce houses to ensure they are in good condition and meet safety standards. These inspections can identify potential hazards and ensure they are addressed promptly.
8.2 Safety Protocols
Insurance policies may mandate specific safety protocols, such as proper anchoring, supervision, and weather monitoring. Failure to comply with these protocols can result in denial of coverage in the event of an accident.
8.3 Industry Standards
Adherence to industry standards, such as those set by ASTM, is often a requirement for insurance coverage. Compliance with these standards demonstrates a commitment to safety and can reduce the risk of accidents.
8.4 Factors Affecting Insurance Rates
Several factors can affect insurance rates for bounce house coverage, including:
- Location: Areas prone to high winds or severe weather may have higher rates.
- Safety Record: Operators with a history of accidents or safety violations may face increased premiums.
- Coverage Limits: Higher coverage limits and broader coverage options can result in higher rates.
- Deductibles: Lower deductibles may lead to higher premiums.
9. How Does the Design and Structure of a Bounce House Affect Its Susceptibility to Wind?
The design and structure of a bounce house significantly affect its susceptibility to wind. Aerodynamic factors, materials used, and overall stability contribute to how well a bounce house can withstand windy conditions.
9.1 Aerodynamic Factors
Bounce houses with large, flat surfaces are more susceptible to lifting in high winds. Designs that incorporate aerodynamic features, such as rounded edges and tapered shapes, can help reduce wind resistance.
9.2 Material Strength
The strength and durability of the materials used in a bounce house affect its ability to withstand wind forces. Heavy-duty, reinforced materials are more resistant to tearing and damage in windy conditions.
9.3 Stability Features
Stability features, such as reinforced seams, multiple anchor points, and internal bracing, can enhance a bounce house’s ability to remain grounded in windy conditions. These features help distribute wind forces and prevent structural failure.
9.4 Examples of Design Improvements
- Rounded Edges: Reduce wind resistance and prevent lifting.
- Reinforced Seams: Prevent tearing and structural failure.
- Multiple Anchor Points: Distribute wind forces and enhance stability.
- Internal Bracing: Provide additional support and prevent collapse.
10. What Emerging Trends are Shaping the Future of Bounce House Safety?
Several emerging trends are shaping the future of bounce house safety, including technological innovations, stricter regulations, and increased awareness among consumers.
10.1 Technological Innovations
Technological innovations, such as advanced monitoring systems and smart anchoring solutions, are improving the ability to detect and respond to hazardous conditions. These technologies can enhance safety and reduce the risk of accidents.
10.2 Stricter Regulations
Advocates for stricter regulations are pushing for standardized safety requirements across the U.S. These regulations may include mandatory inspections, certified training programs for operators, and stricter wind speed limits.
10.3 Increased Awareness
Increased awareness among consumers is driving demand for safer bounce house practices. Parents and users are becoming more informed about the risks and are seeking out operators who prioritize safety.
10.4 Future Outlook
The future of bounce house safety is likely to involve a combination of technological advancements, regulatory changes, and increased consumer awareness. By embracing these trends, the industry can create a safer environment for children and adults to enjoy bounce houses.
FAQ: Bounce Houses and Wind Safety
1. What is the maximum wind speed for a bounce house?
The maximum recommended wind speed for operating a bounce house is 25 mph, as per ASTM standards.
2. How do I anchor a bounce house properly?
Use ground stakes that are at least 18 inches long and designed for bounce houses, securing each anchor point firmly into the ground.
3. What should I do if the wind picks up while the bounce house is in use?
Immediately evacuate the bounce house and deflate it to prevent it from becoming airborne.
4. Are there any states with specific regulations for bounce houses?
Yes, nineteen U.S. states’ laws or regulations explicitly cite ASTM standards. However, regulations vary widely across the country.
5. Can I use a bounce house indoors to avoid wind risks?
Yes, using a bounce house indoors eliminates the risk of wind-related accidents, provided there is sufficient space and adequate ventilation.
6. What type of insurance do I need to operate a bounce house business?
You typically need general liability insurance to cover damages and injuries resulting from accidents.
7. How often should I inspect my bounce house for safety?
Regular inspections should be conducted before each use to identify any damage or wear that could compromise safety.
8. What are the signs that a bounce house is not safely anchored?
Signs include loose anchors, tilting, or movement of the bounce house in windy conditions.
9. Can adults use bounce houses safely?
Adults can use bounce houses, but it’s important to adhere to weight limits and safety guidelines to prevent injuries.
10. Where can I find more information on bounce house safety?
Additional information can be found at the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC), American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), and on websites like flyermedia.net.
Fly High with Safety: Trust Flyermedia.net for Your Aviation Insights
At Flyermedia.net, we provide comprehensive resources for aviation enthusiasts, professionals, and anyone passionate about the world of flight. From aviation safety tips to industry news, we are your go-to source for accurate, up-to-date information. For example, at Flyermedia.net, you can find the best aviation schools in USA and aviation news to explore opportunities within the aviation sector.
Whether you’re seeking information on flight training, aviation technology, or travel tips, Flyermedia.net delivers the insights you need to navigate the skies safely. So, visit flyermedia.net today to learn more about aviation.
Address: 600 S Clyde Morris Blvd, Daytona Beach, FL 32114, United States
Phone: +1 (386) 226-6000
Website: flyermedia.net
Let flyermedia.net be your trusted co-pilot in the journey of aviation, and help you navigate the world of aviation with expertise, experience, authority, and trust.