Keeping flies away from cows is crucial for their health and productivity, and flyermedia.net is here to provide comprehensive solutions. Using garlic mineral salts and other preventative measures can significantly reduce fly populations, improving animal welfare and farm economics. Discover the best strategies for fly control in cattle.
1. What Are the Benefits of Keeping Flies Away From Cows?
Keeping flies away from cows significantly enhances their health, temperament, and overall productivity. Reducing fly populations minimizes stress, prevents disease transmission, and allows cattle to thrive.
Improved Animal Health and Temperament
Cows constantly swatting flies expend vital energy that should be used for eating and resting. This is especially critical for nursing mothers and young calves. According to research from the University of Kentucky College of Agriculture, effective horn fly control can result in an additional 12 to 20 pounds of weight gain per calf over the summer and reduced weight loss for nursing cows. Each horn fly feeds up to 30 times daily, draining blood and essential nutrients, potentially leading to anemia. Flies not only disrupt foraging but also steal vital nutrition.
Fly-defensive behaviors like stamping, kicking, and head-throwing can lead to injuries for both cattle and humans. Furthermore, flies spread viral, bacterial, and parasitic diseases, compromising the immune defenses of animals. Effective pest prevention reduces disease spread and hide damage.
Boosted Production and Cost Savings
Reducing biting pests greatly benefits animal health and the farm’s bottom line. A study by the University of Arkansas, Fayetteville, found that cattle production losses due to horn flies in the United States range from $730 to $876 million annually. Whether your operation relies on cattle weight or milk production, controlling horn flies can lead to significant savings. Investing in fly repellent results in beneficial weight gain, increased milk production, and improved overall productivity.
2. How Does Garlic Mineral Salt Help in Biting Pest Prevention?
Garlic mineral salt, such as Redmond 10 Fine with Garlic, offers a natural and effective solution for preventing biting pests in cattle. It combines essential minerals with the fly-repelling properties of garlic.
 Garlic salt for cattle fly control
Garlic salt for cattle fly control
Convenience of Garlic Salts
Garlic mineral salts offer a convenient method for fly control. Tired of constantly reapplying fly sprays, rollers, and dust bags? Using cattle’s natural cravings for mineral salt to administer fly repellent simplifies the process. Instead of coercing animals, simply provide a delicious spread of natural garlic mineral salt and let the cattle do the work. Unlike chemical treatments that require rotation to prevent resistance, cattle do not develop a resistance to garlic, simplifying your fly control strategy.
Garlic as a Natural Fly Repellent
Garlic works as a natural fly repellent because, once ingested, it emits an odor through the pores in the hide and the breath. This odor drives biting pests away from the skin, shallow blood vessels, and sensitive areas like the eyes and nose. Ranchers report significant reduction in fly populations with garlic mineral salt.
Cost-Effectiveness of Garlic Salts
Garlic salts provide multiple benefits in a single product, saving your farm money. Since cows always need mineral salts, using garlic-infused options makes them less attractive to pests.
Safety of Garlic
Garlic doesn’t taint milk or meat quality. When ingested, garlic oils are metabolized through the skin, repelling biting pests without affecting the taste or quality of your products.
Effectiveness of Garlic Salts
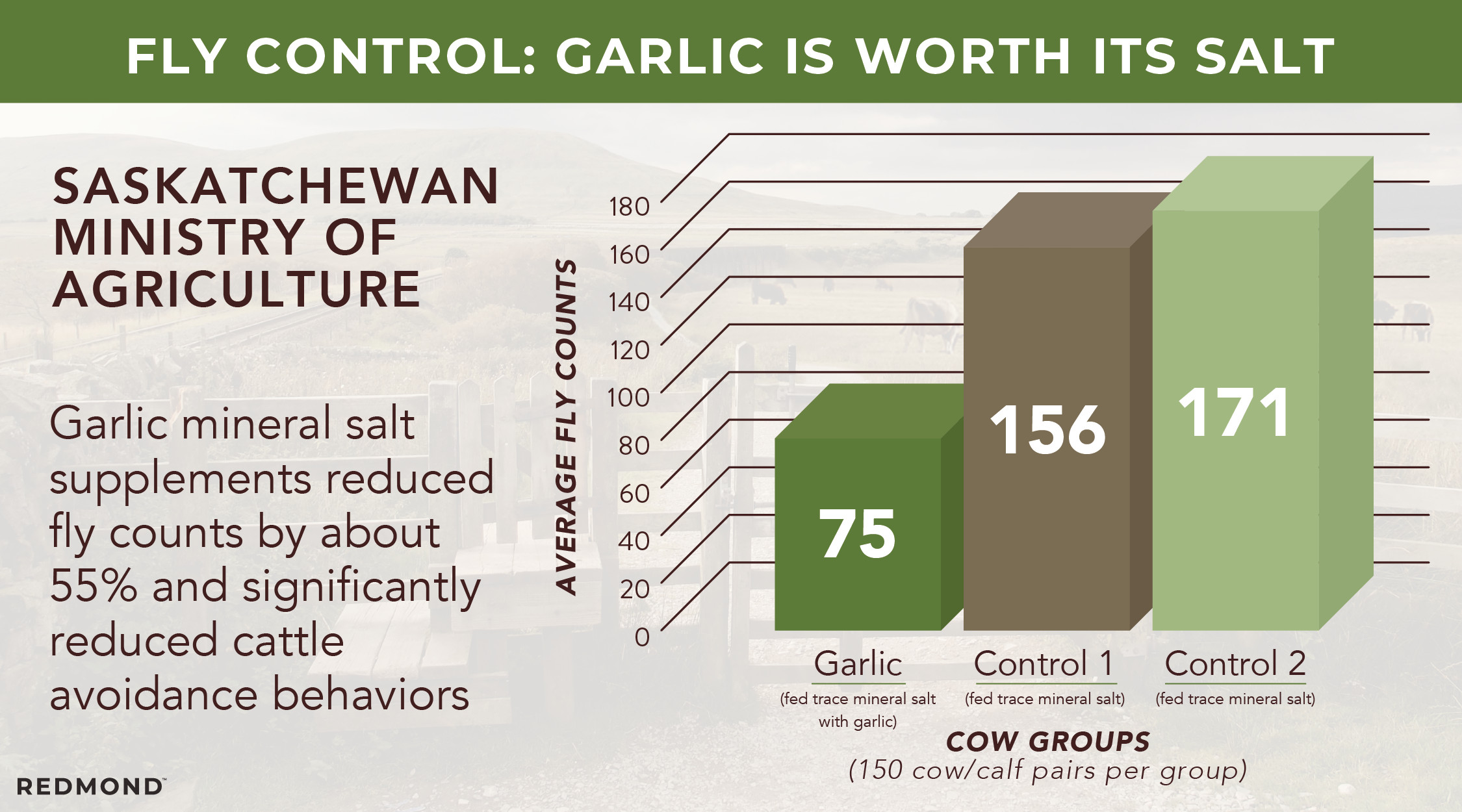
Garlic mineral salt is a natural and effective pest repellent. Unlike topical sprays that require frequent reapplication and lose efficacy in rain or mud, garlic mineral salt works year-round. The Saskatchewan Department of Agriculture conducted a field test on garlic mineral salt, finding that the garlic mineral salt group had about 55% fewer flies than the control groups. They also observed less fly avoidance behaviors, allowing the animals to graze and rest more comfortably.
3. What Are Some Effective Strategies for Natural Fly Control in Cattle?
Effective natural fly control strategies include using garlic mineral salt, implementing beneficial insects, managing manure, and ensuring good pasture management. These methods reduce fly populations without relying on harsh chemicals.
Beneficial Insects
Introducing beneficial insects like parasitic wasps and dung beetles can help control fly populations naturally. Parasitic wasps lay their eggs inside fly pupae, killing the developing flies. Dung beetles break down manure, reducing breeding sites for flies.
- Parasitic Wasps: These tiny wasps are natural enemies of flies. They target fly pupae, preventing them from developing into adult flies.
- Dung Beetles: By breaking down manure, dung beetles reduce the habitat for fly larvae, minimizing fly breeding sites.
Pasture Management
Proper pasture management helps reduce fly breeding sites. Rotate pastures to prevent manure buildup and keep grass mowed to reduce humidity and shade, making the environment less attractive to flies.
- Rotate Pastures: This prevents manure buildup in one area, reducing fly breeding sites.
- Keep Grass Mowed: This reduces humidity and shade, making the pasture less attractive to flies.
Manure Management
Effective manure management is crucial for controlling fly populations. Regularly remove manure from barns and feeding areas to eliminate breeding sites. Composting manure can also help reduce fly populations, as the composting process kills fly larvae.
- Regular Removal: Removing manure from barns and feeding areas eliminates fly breeding sites.
- Composting: Composting manure kills fly larvae, reducing the overall fly population.
4. What Are the Different Types of Flies That Affect Cattle?
Different types of flies, including horn flies, face flies, stable flies, and house flies, can affect cattle, each posing unique challenges to animal health and productivity. Understanding these differences is essential for targeted fly control.
Horn Flies
Horn flies are small, blood-sucking flies that typically congregate on the backs and sides of cattle. They cause significant irritation, leading to reduced grazing time and weight gain.
- Habitat: Horn flies live primarily on cattle, feeding frequently throughout the day.
- Impact: They cause irritation, reduce grazing time, and decrease weight gain in cattle.
Face Flies
Face flies feed on secretions around the eyes and nose of cattle, causing irritation and spreading diseases like pinkeye.
- Habitat: Face flies feed on secretions around the eyes and nose of cattle.
- Impact: They cause irritation and spread diseases like pinkeye.
Stable Flies
Stable flies are biting flies that feed on the lower legs of cattle. Their painful bites cause cattle to stomp their feet and bunch together, reducing grazing efficiency.
- Habitat: Stable flies breed in decaying organic matter and feed on the lower legs of cattle.
- Impact: Their painful bites cause cattle to stomp and bunch, reducing grazing efficiency.
House Flies
House flies are nuisance pests that can transmit diseases. They breed in manure and decaying organic matter, contaminating feed and water sources.
- Habitat: House flies breed in manure and decaying organic matter.
- Impact: They transmit diseases and contaminate feed and water sources.
5. What Are the Economic Impacts of Fly Infestations on Cattle Farms?
Fly infestations can cause significant economic losses on cattle farms due to reduced weight gain, decreased milk production, increased veterinary costs, and hide damage. Effective fly control is an investment that pays off.
Reduced Weight Gain
Fly infestations cause cattle to spend more time trying to avoid flies and less time grazing. This leads to reduced weight gain, which is especially detrimental for cattle raised for meat production. The University of Kentucky College of Agriculture estimates that horn fly control can result in an additional 12 to 20 pounds of weight gain per calf over the summer.
Decreased Milk Production
Dairy cows that are constantly bothered by flies experience stress, leading to decreased milk production. The energy that should be used for milk production is instead spent on defensive behaviors. Studies have shown that effective fly control can significantly increase milk yields.
Increased Veterinary Costs
Flies transmit various diseases, such as pinkeye and mastitis, which can increase veterinary costs. Treating these diseases requires medication and veterinary care, adding to the economic burden of fly infestations.
Hide Damage
Fly bites can cause skin irritation and lesions, leading to hide damage. This reduces the value of the hides, resulting in economic losses for cattle farmers.
6. What Role Does Diet Play in Natural Fly Control for Cattle?
Diet plays a crucial role in natural fly control for cattle, with certain feed additives like garlic and diatomaceous earth helping to repel flies and reduce their impact.
Garlic as a Feed Additive
Garlic is a natural fly repellent when added to cattle feed. The sulfur compounds in garlic are excreted through the skin and breath, creating an odor that deters flies. This natural method is effective and doesn’t harm the cattle.
- Mechanism: Sulfur compounds in garlic repel flies when excreted through the skin and breath.
- Benefits: Natural, effective, and harmless to cattle.
Diatomaceous Earth (DE)
Diatomaceous earth is a natural substance made from fossilized algae. When added to cattle feed, it can help control internal parasites and reduce fly breeding in manure.
- Mechanism: DE damages the exoskeletons of insects, leading to dehydration and death.
- Benefits: Controls internal parasites and reduces fly breeding in manure.
Apple Cider Vinegar (ACV)
Adding apple cider vinegar to cattle water can also help repel flies. ACV changes the pH of the animal’s skin, making it less attractive to flies.
- Mechanism: ACV changes the pH of the animal’s skin, making it less attractive to flies.
- Benefits: Simple, natural, and can improve overall health.
7. What Are the Environmental Considerations of Using Different Fly Control Methods?
Environmental considerations are important when choosing fly control methods. Natural methods like garlic mineral salt and beneficial insects are environmentally friendly, while chemical insecticides can have negative impacts on the ecosystem.
Natural Methods
Natural fly control methods, such as garlic mineral salt, beneficial insects, and proper manure management, are environmentally friendly and sustainable. These methods reduce fly populations without harming other organisms or polluting the environment.
- Benefits: Environmentally friendly, sustainable, and safe for cattle and other organisms.
- Examples: Garlic mineral salt, beneficial insects, and proper manure management.
Chemical Insecticides
Chemical insecticides can be effective for fly control, but they can also have negative impacts on the environment. Insecticides can harm beneficial insects, contaminate water sources, and lead to insecticide resistance in fly populations.
- Drawbacks: Can harm beneficial insects, contaminate water sources, and lead to insecticide resistance.
- Considerations: Use insecticides judiciously and follow label instructions to minimize environmental impact.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a comprehensive approach to pest control that combines multiple strategies, including natural methods and judicious use of chemical insecticides. IPM minimizes environmental impact while effectively controlling fly populations.
- Approach: Combines natural methods with judicious use of chemical insecticides.
- Benefits: Minimizes environmental impact while effectively controlling fly populations.
8. How Can Cattle Farmers Implement an Effective Fly Control Program?
Implementing an effective fly control program involves monitoring fly populations, using a combination of control methods, and adapting the program to changing conditions.
Monitoring Fly Populations
Regularly monitor fly populations to assess the effectiveness of control measures. Use fly traps, sticky traps, or visual counts to track fly numbers. This data can help you determine when and where to implement control measures.
- Methods: Fly traps, sticky traps, and visual counts.
- Purpose: To assess the effectiveness of control measures and determine when to implement new strategies.
Combining Control Methods
Use a combination of control methods to achieve the best results. This may include using garlic mineral salt, implementing beneficial insects, managing manure, and using insecticides when necessary. Combining methods can prevent fly populations from developing resistance to any single control strategy.
- Strategies: Garlic mineral salt, beneficial insects, manure management, and judicious use of insecticides.
- Benefits: Prevents fly populations from developing resistance to control strategies.
Adapting the Program
Adapt the fly control program to changing conditions. Fly populations can fluctuate depending on weather, season, and other factors. Be prepared to adjust control measures as needed to maintain effective fly control.
- Factors: Weather, season, and other environmental conditions.
- Importance: Flexibility ensures continued effectiveness of the fly control program.
9. What Resources Are Available for Cattle Farmers Seeking Fly Control Information?
Cattle farmers can access valuable fly control information from university extension services, veterinary professionals, and agricultural supply companies, ensuring they have the knowledge and tools for effective pest management.
University Extension Services
University extension services offer research-based information and resources on fly control for cattle. These services provide publications, workshops, and on-site consultations to help farmers develop effective fly control programs.
- Offerings: Publications, workshops, and on-site consultations.
- Benefits: Research-based information and customized solutions.
Veterinary Professionals
Veterinary professionals can provide valuable advice on fly control and disease prevention. They can help diagnose fly-related health problems in cattle and recommend appropriate treatment and prevention strategies.
- Services: Advice on fly control, disease prevention, diagnosis of fly-related health problems, and treatment recommendations.
- Benefits: Expert guidance and personalized care for cattle.
Agricultural Supply Companies
Agricultural supply companies offer a range of fly control products, including garlic mineral salt, insecticides, traps, and other supplies. These companies can provide information on product selection and application.
- Products: Garlic mineral salt, insecticides, traps, and other fly control supplies.
- Services: Information on product selection and application.
10. How Do Weather Conditions Affect Fly Populations and Control Strategies?
Weather conditions significantly impact fly populations, influencing breeding rates, activity levels, and the effectiveness of control strategies. Understanding these effects is crucial for adapting fly control programs.
Temperature
Temperature plays a critical role in fly development and activity. Warmer temperatures accelerate fly breeding cycles, leading to rapid population increases. Conversely, cooler temperatures slow down development and reduce activity.
- Warm Temperatures: Accelerate breeding cycles, leading to rapid population increases.
- Cool Temperatures: Slow down development and reduce activity.
Rainfall
Rainfall can both help and hinder fly control efforts. While moisture is necessary for fly breeding, heavy rainfall can wash away manure and other breeding materials, reducing fly populations. However, standing water can also create new breeding sites.
- Moderate Rainfall: Provides moisture for breeding.
- Heavy Rainfall: Washes away manure, reducing breeding sites, but can also create new breeding sites in standing water.
Humidity
High humidity levels favor fly development and survival. Flies thrive in moist environments, so reducing humidity in barns and pastures can help control fly populations.
- High Humidity: Favors fly development and survival.
- Control: Reducing humidity in barns and pastures can help control fly populations.
Wind
Wind can disrupt fly activity and disperse fly populations. Windy conditions make it difficult for flies to feed and breed, reducing their impact on cattle.
- Windy Conditions: Disrupt fly activity and disperse fly populations.
- Impact: Reduces the ability of flies to feed and breed.
To discover more on how to protect your investments and cattle, and to stay informed on the latest advancements in natural pest control, visit flyermedia.net, your go-to source for all things aviation and related agricultural tips.
Address: 600 S Clyde Morris Blvd, Daytona Beach, FL 32114, United States.
Phone: +1 (386) 226-6000.
Website: flyermedia.net.
 Repel flies natural with Redmond 10 Fine with Garlic
Repel flies natural with Redmond 10 Fine with Garlic
Call to Action: Are you ready to protect your cattle from flies and improve your farm’s productivity? Visit flyermedia.net today to explore our range of natural fly control solutions and discover expert tips for effective pest management. Fly high with flyermedia.net – where your agricultural success takes flight.
FAQ: Keeping Flies Away From Cows
1. Why is it important to control flies around cows?
Controlling flies around cows is vital for improving their health, reducing stress, preventing disease transmission, and increasing overall productivity. Flies can cause significant economic losses due to reduced weight gain and decreased milk production.
2. What are the most common types of flies that affect cattle?
The most common types of flies that affect cattle include horn flies, face flies, stable flies, and house flies. Each type poses unique challenges and requires targeted control strategies.
3. How does garlic mineral salt help in fly control?
Garlic mineral salt acts as a natural fly repellent. When ingested, the garlic emits an odor through the cow’s skin and breath, deterring flies from landing and feeding.
4. Are there any natural methods to control flies on cattle?
Yes, there are several natural methods to control flies on cattle, including using garlic mineral salt, introducing beneficial insects (such as parasitic wasps and dung beetles), managing manure effectively, and ensuring good pasture management practices.
5. What is Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for fly control?
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a comprehensive approach that combines multiple strategies, including natural methods and judicious use of chemical insecticides, to minimize environmental impact while effectively controlling fly populations.
6. How can weather conditions affect fly populations?
Weather conditions such as temperature, rainfall, humidity, and wind can significantly impact fly populations. Warmer temperatures and high humidity favor fly development, while heavy rainfall can wash away breeding sites.
7. Can diet influence fly control in cattle?
Yes, diet can play a role in fly control. Adding certain feed additives like garlic and diatomaceous earth (DE) to cattle feed can help repel flies and reduce their impact.
8. What are the economic impacts of fly infestations on cattle farms?
Fly infestations can cause significant economic losses due to reduced weight gain, decreased milk production, increased veterinary costs, and hide damage. Effective fly control is an investment that pays off.
9. Where can cattle farmers find more information on fly control?
Cattle farmers can access valuable fly control information from university extension services, veterinary professionals, and agricultural supply companies. flyermedia.net also provides comprehensive solutions and expert tips for effective pest management.
10. How often should I monitor fly populations on my farm?
Regular monitoring of fly populations is crucial to assess the effectiveness of control measures. Monitoring should be done frequently, especially during peak fly season, using methods such as fly traps, sticky traps, or visual counts.
