Flying is often perceived as risky, but Why Is Flying Safer Than Driving? Flying, especially on commercial airlines, incorporates multiple layers of safety measures, strict regulations, and highly trained professionals, often making it a safer mode of transportation compared to driving. Explore aviation safety, safety regulations and risk management with flyermedia.net.
1. Comparing Aviation and Road Accident Statistics
Comparing driving and flying safety requires understanding different statistical reporting methods. While the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) measures accidents per 100 million vehicle miles traveled, the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) reports accidents per 100,000 flight hours. Let’s delve into these metrics to understand the relative safety of each mode of transport.
1.1. How Do Accident Rates Differ Between Driving and Flying?
Accident rates differ significantly. NHTSA reported 1.37 fatalities per 100 million vehicle miles in 2021. The NTSB reported 0.95 fatalities per 100,000 flight hours for general aviation (GA). Due to the disparity in the number of vehicles versus airplanes, a direct comparison requires a common metric.
1.2. What Is the Common Metric for Comparing Driving and Flying Risk?
A 2020 study provided a common metric: fatal car crashes per million hours driven. This research indicated 0.6 to 0.7 fatal car crashes per million hours driven. This adjustment allows for a more equitable comparison between driving and flying risks.
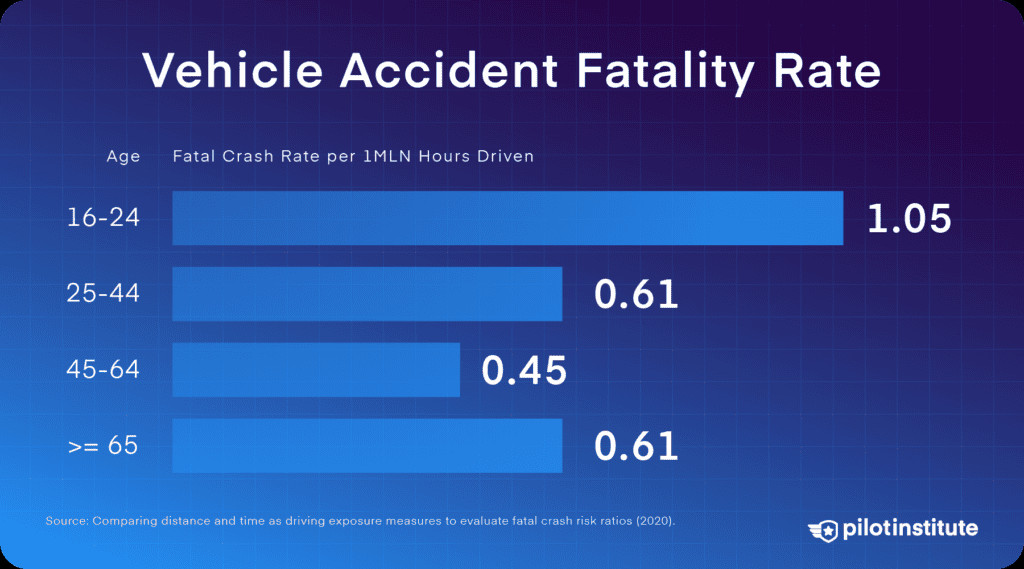 Vehicle accident fatality rate by age
Vehicle accident fatality rate by age
1.3. How Does Motorcycle Safety Compare to Driving and Flying?
Motorcycle accidents are significantly more dangerous. NHTSA data indicates about 16 to 18 fatal motorcycle accidents per million hours ridden, approximately 27 times more frequent than car accidents per vehicle mile.
2. General Aviation vs. Driving: A Detailed Comparison
General Aviation (GA) includes all flying activities other than commercial and military. Comparing GA to driving provides nuanced insights into aviation safety.
2.1. How Safe Is General Aviation Compared to Driving?
GA flying is riskier than driving. According to the NTSB, there were 9.5 fatal GA crashes per million flight hours in 2021, roughly 14 times the driving fatality rate.
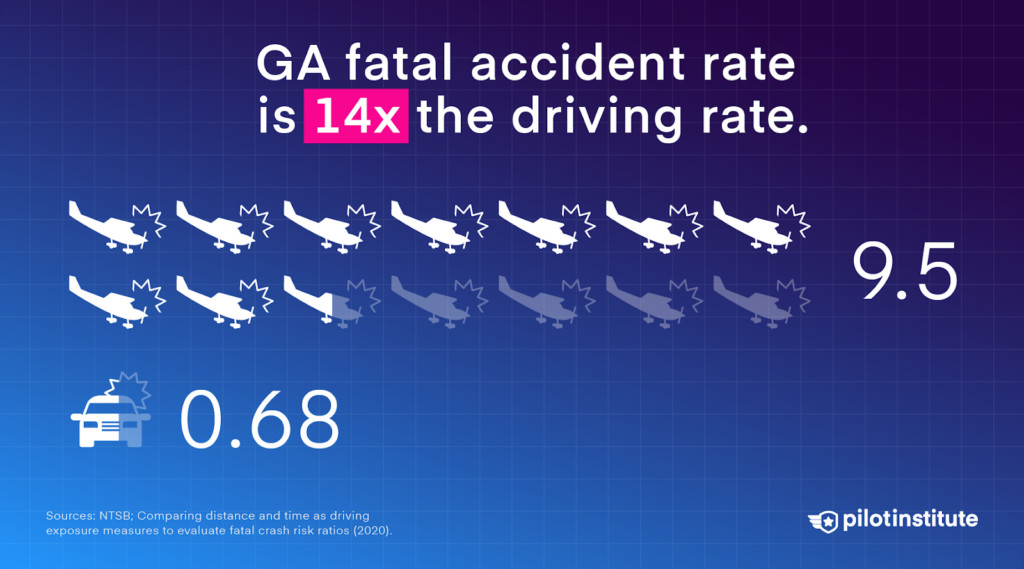 The GA fatal accident rate is roughly 14 times that of driving
The GA fatal accident rate is roughly 14 times that of driving
2.2. What Are the Accident Rate Trends in General Aviation?
Overall GA accident rates have fluctuated. Analyzing trends from 2012 to 2021 provides a comprehensive view of the evolving safety landscape in general aviation.
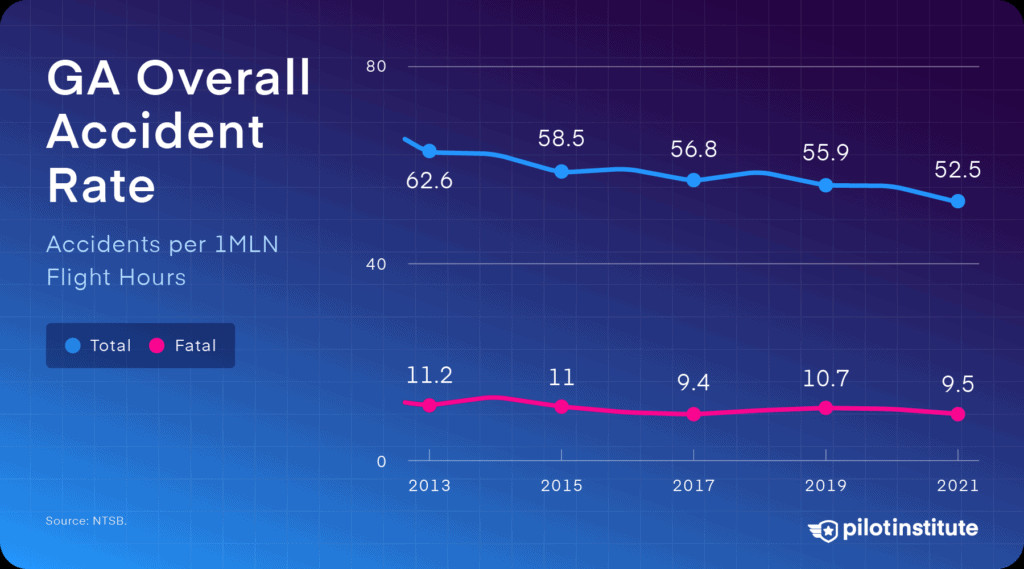 GA overall accident rate: 2012-2021
GA overall accident rate: 2012-2021
2.3. How Does Corporate Aviation Compare to Personal Flights in Terms of Safety?
Corporate aviation is relatively safe. From 2012 to 2021, it saw only 0.48 fatal accidents per million flight hours. This contrasts sharply with personal flights.
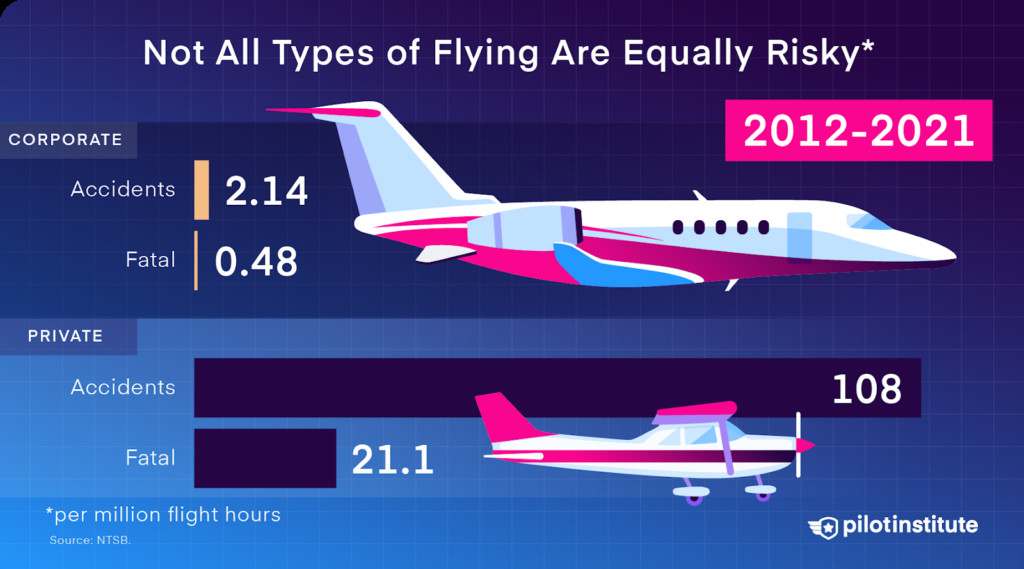 Corporate GA flying is quite safe compared to private flights
Corporate GA flying is quite safe compared to private flights
2.4. What Is the Safety Record of Personal Flights?
Personal flights are riskier. They account for 67% of GA accidents and 72% of GA fatalities. Between 2012 and 2021, personal flights had 21.1 fatal accidents per million flight hours, over 27 times the driving fatality rate.
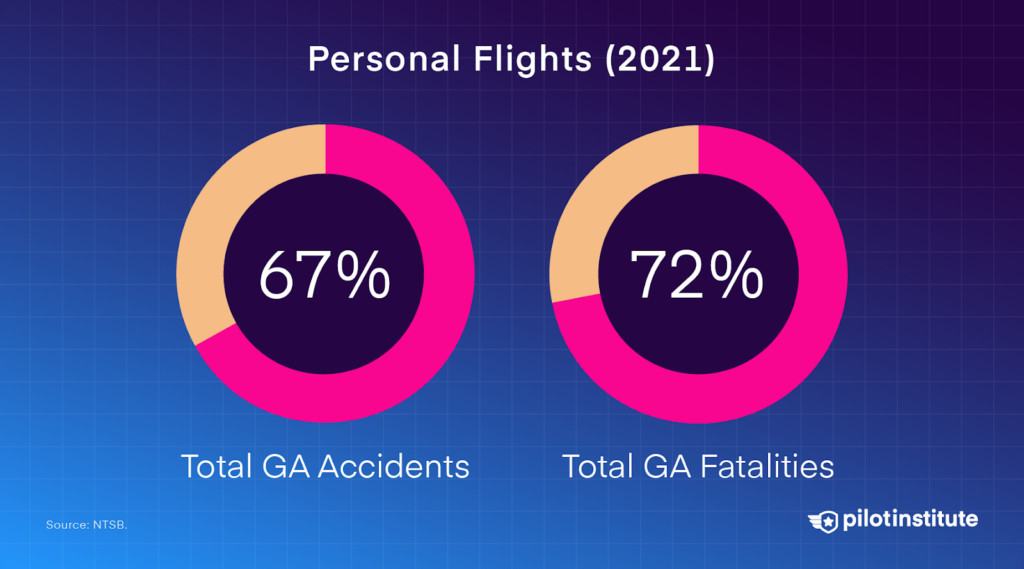 Personal flights account for the majority of total GA accidents and fatalities
Personal flights account for the majority of total GA accidents and fatalities
2.5. How Do Instructional Flights Compare in Safety?
Instructional flights are safer. They saw 2.3 fatal accidents per million flight hours, only 3.4 times more dangerous than driving, and a 52% decrease since 2012.
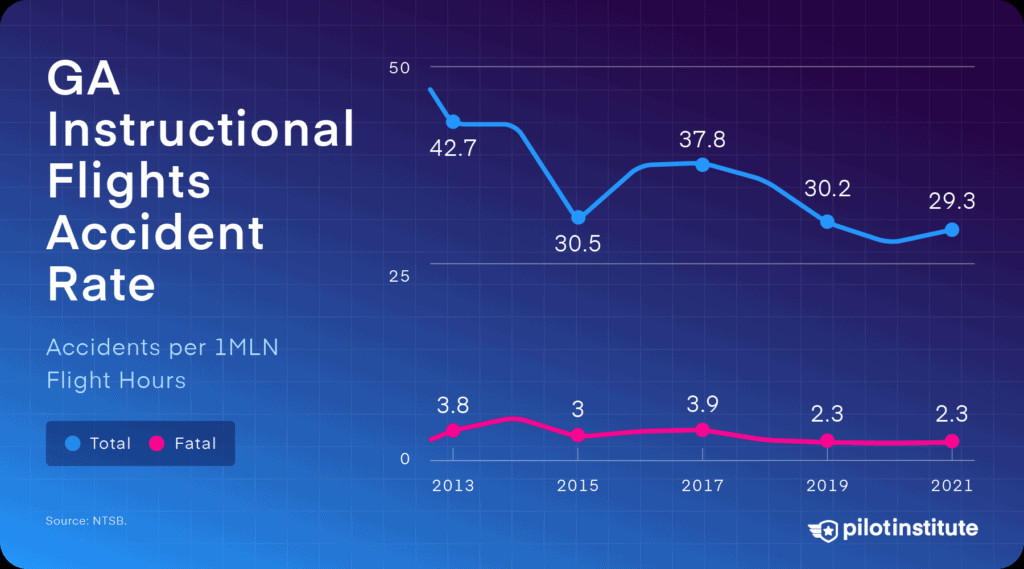 GA instructional flights accident rate: 2012-2021
GA instructional flights accident rate: 2012-2021
3. Identifying Risk Factors in General Aviation
Understanding the primary causes of accidents in GA is essential for improving safety. The AOPA’s Richard G. McSpadden Report categorizes accidents into Pilot-related, Mechanical, and Other/Unknown causes, offering a structured framework for analysis.
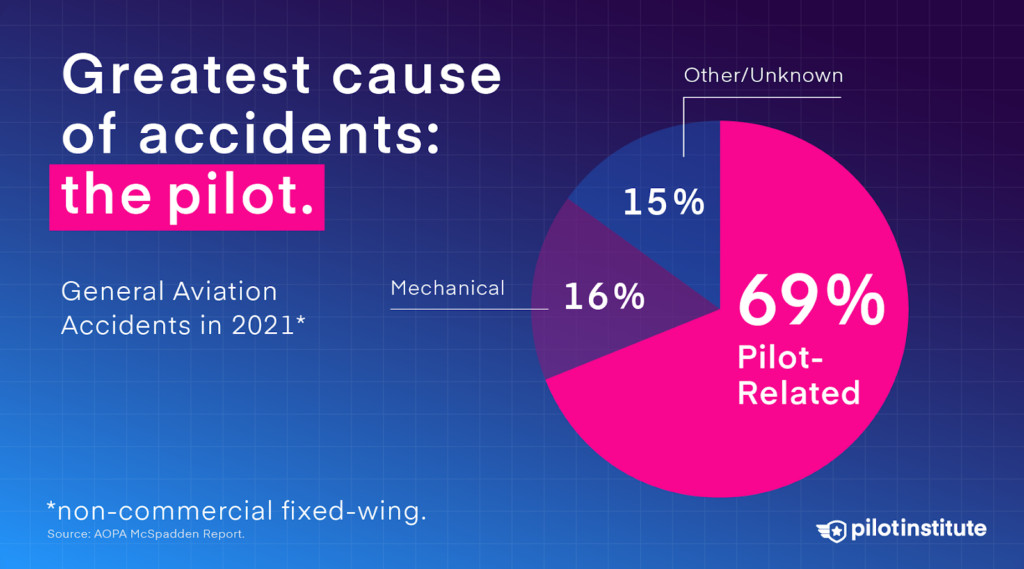 The greatest cause of GA accidents is the pilot
The greatest cause of GA accidents is the pilot
3.1. What Role Do Unknown Causes Play in GA Accidents?
Unknown causes constitute a significant portion. In 2021, 15% of all accidents and 28% of fatal ones had no clear cause, hindering learning and prevention efforts.
3.2. How Significant Are Mechanical Issues in GA Accidents?
Mechanical failures are the second most common cause. They comprised about 16% of all accidents but only 7% of fatal ones in 2021.
3.3. What Types of Mechanical Issues Are Most Prevalent?
Engine issues are the most significant. However, of the 57 engine failures reported in 2021, only six were fatal, indicating that many engine failures are manageable emergencies.
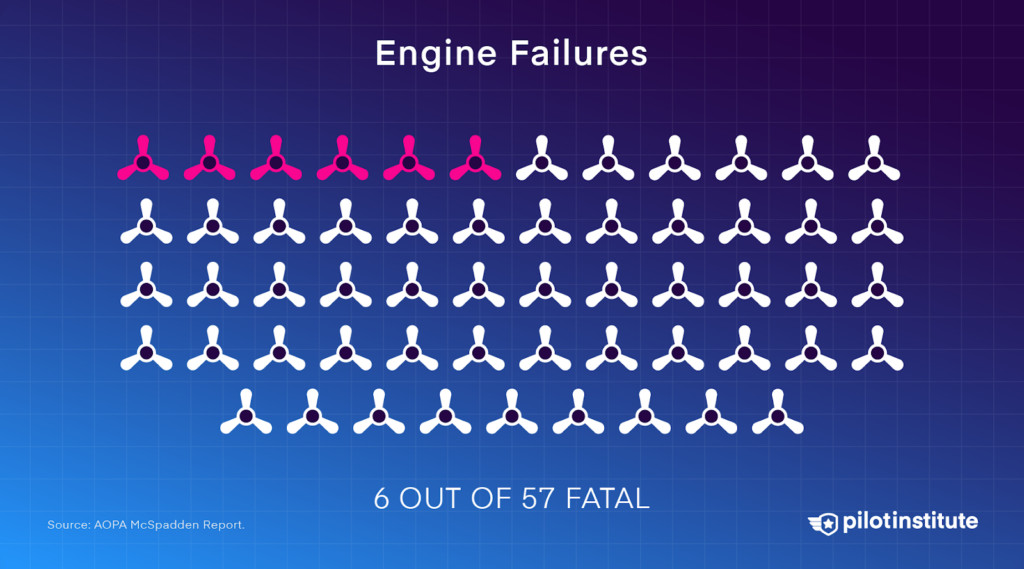 Six out of 57 engine failure accidents in 2021 were fatal
Six out of 57 engine failure accidents in 2021 were fatal
3.4. What Are the Primary Causes of Engine Failures?
The causes of engine failures vary. AOPA found that 30% have no clear cause, 16% are due to maintenance issues, and 17% are due to structural failures. Preventable problems like carb ice or fuel issues account for the rest.
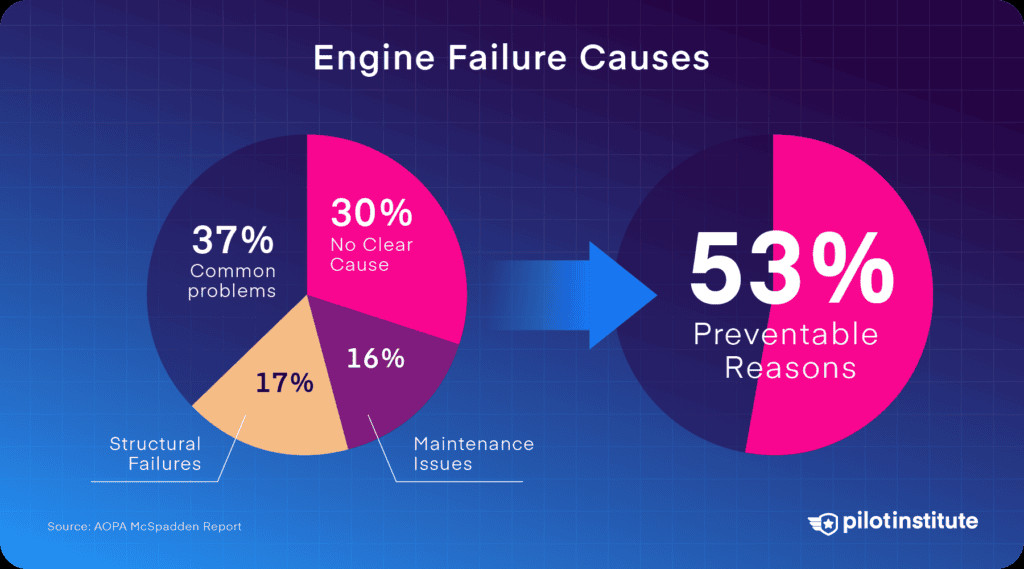 A diagram depicting the reasons for engine failures
A diagram depicting the reasons for engine failures
3.5. How Do Fuel-Related Issues Contribute to GA Accidents?
Fuel-related accidents occur in three main ways: fuel contamination, fuel starvation (due to selecting the wrong tank or switch position), and fuel exhaustion (running out of fuel due to poor planning).
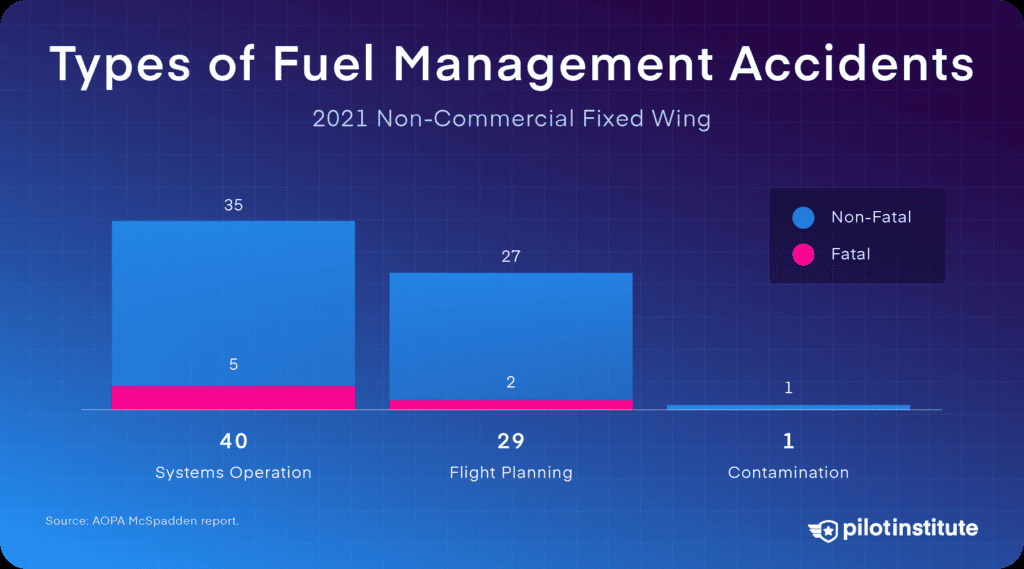 Types of GA fuel management accidents
Types of GA fuel management accidents
3.6. How Prevalent Are Pilot-Related Causes in GA Accidents?
Pilot error is the leading cause. In 2021, the pilot was deemed at fault in 69% of all GA accidents (647 out of 938), highlighting the critical role of human factors.
3.7. What Are the Most Common Pilot-Related “Defining Events” in GA Accidents?
The NTSB classifies these causes as “defining events.” Loss of control in-flight (LOC-I) is the most common and most fatal defining event.
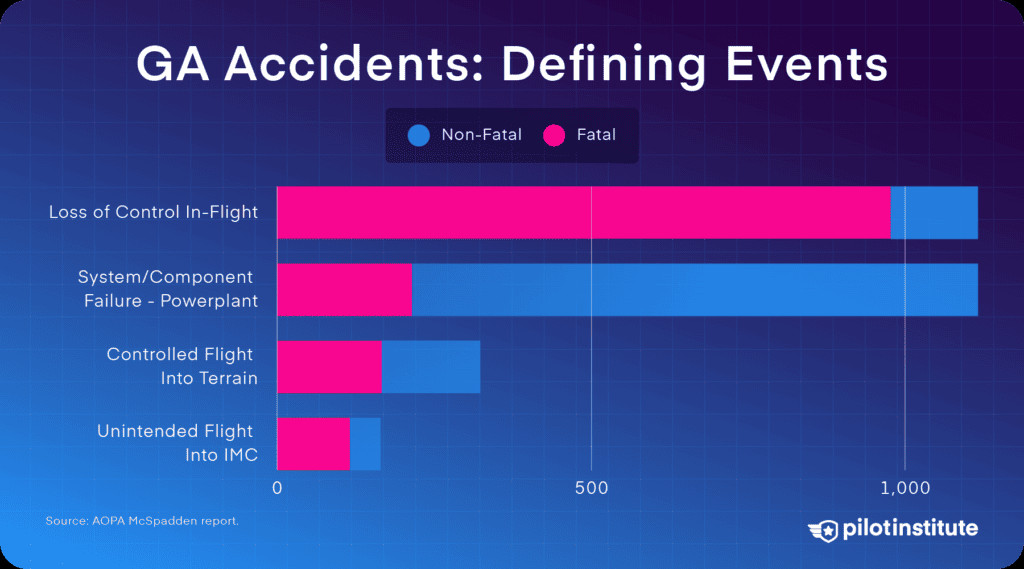 A selection of GA accident defining events
A selection of GA accident defining events
3.8. What Is Loss of Control In-Flight (LOC-I) and Why Is It So Dangerous?
LOC-I typically involves the pilot losing control of the airplane due to factors like flying too slow or making uncoordinated control inputs. Half of these accidents involve stalls and spins in the traffic pattern during maneuvering flight, which are often unrecoverable.
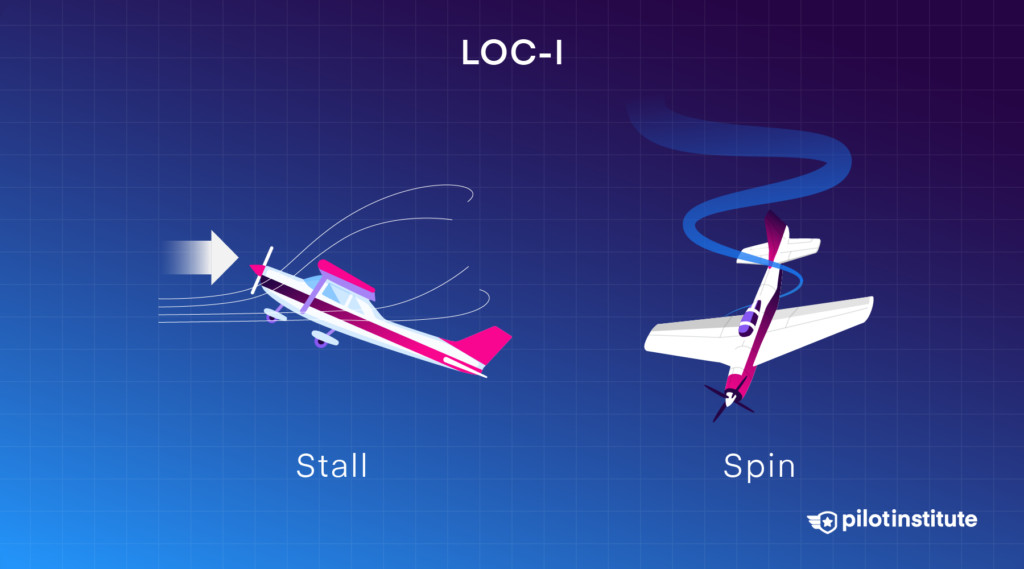 Loss of Control In-Flight: the leading cause of fatal accidents
Loss of Control In-Flight: the leading cause of fatal accidents
3.9. How Do Landing Accidents Typically Occur?
Landing accidents are common, but less fatal. The most common landing accident is loss of control.
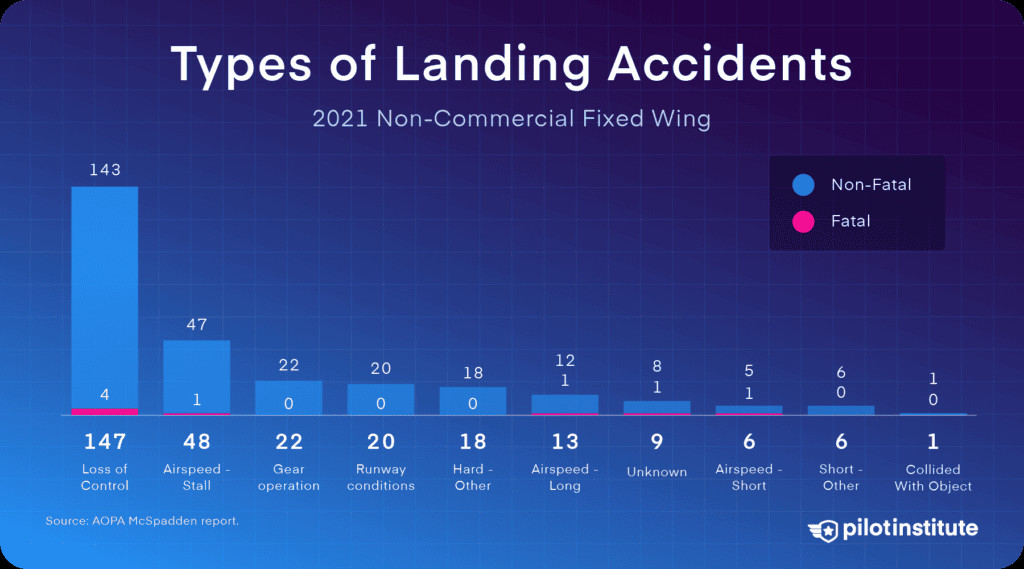 Types of GA landing accidents
Types of GA landing accidents
3.10. What Makes Takeoff and Climb Accidents Particularly Dangerous?
Takeoff and climb accidents have a higher fatality rate because the airplane is in a low-energy, low-altitude state with a high angle of attack, leaving little room for error in an emergency.
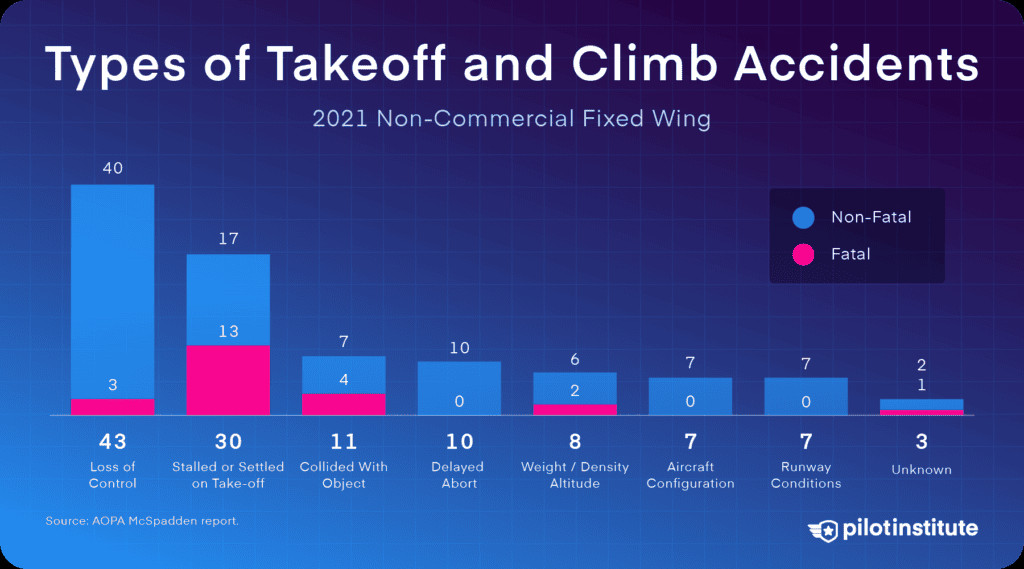 Types of GA takeoff and climb accidents
Types of GA takeoff and climb accidents
3.11. What Is Controlled Flight Into Terrain (CFIT)?
Controlled Flight Into Terrain (CFIT) is an unintended collision with the ground or obstacle, often due to a loss of situational awareness or attempts to push below minimums during instrument procedures.
 Controlled Flight into Terrain: a top cause of fatal accidents
Controlled Flight into Terrain: a top cause of fatal accidents
3.12. How Dangerous Is Unintended VFR Flight into IMC?
Unintended VFR flight into instrument meteorological conditions is extremely dangerous. Accidents caused by flying visually into clouds or low visibility had a 71% fatality rate in 2021.
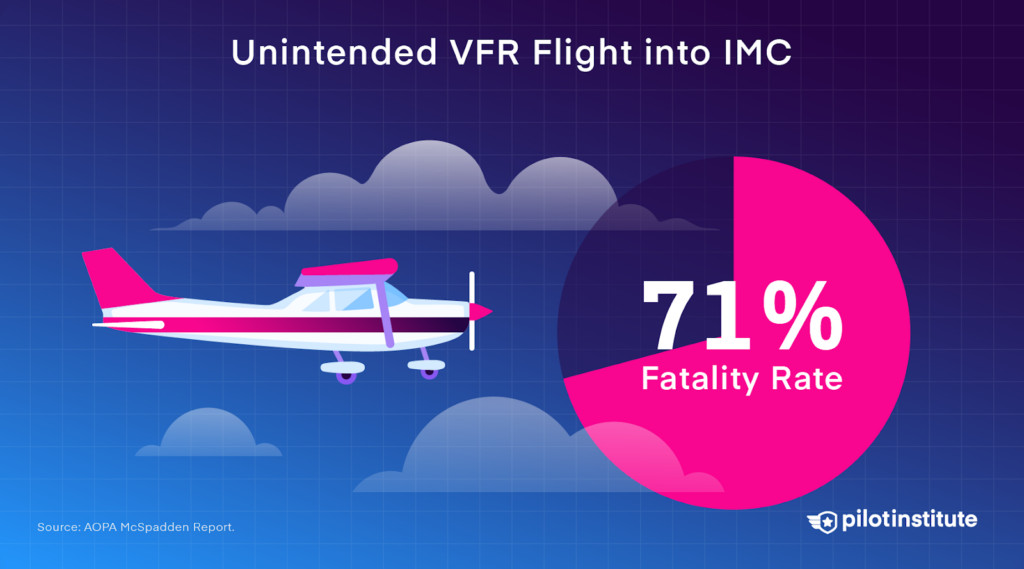 Unintended VFR flight into IMC has a 71% fatality rate
Unintended VFR flight into IMC has a 71% fatality rate
3.13. What Role Does Weather Play in GA Accidents?
Weather-related accidents are significant. Poor IFR technique and icing were deadly in 2021.
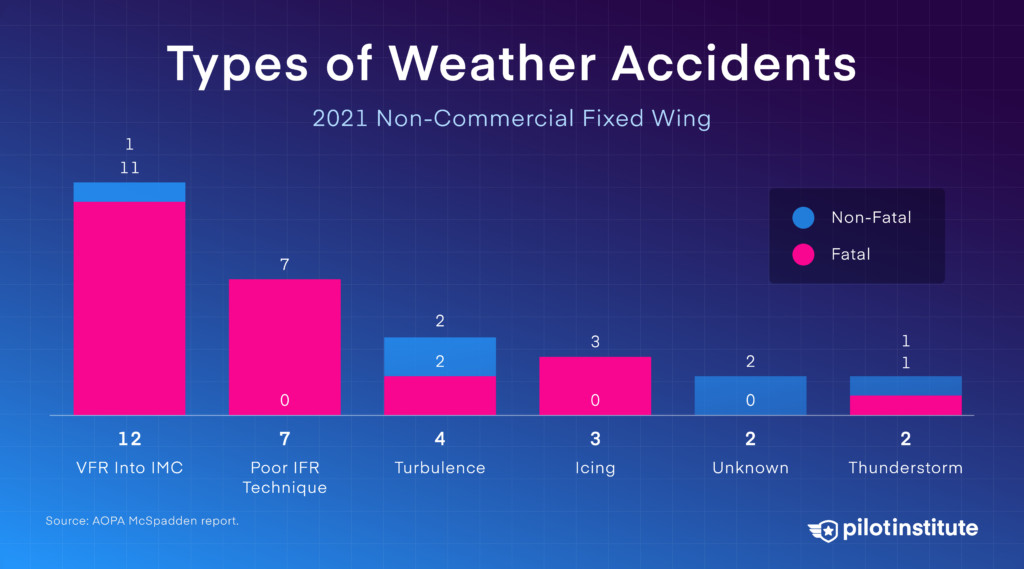 Types of GA weather accidents
Types of GA weather accidents
4. Enhancing Safety: Measures and Best Practices in Aviation
While GA flying might never be as safe as driving, significant measures can be taken to reduce risk. Emphasizing proficiency over mere currency (legal compliance) is key.
4.1. Why Are Instructional Flights Safer Than Personal Flights?
Instructional flights are safer for several reasons: supervised environments, structured operations, risk-averse cultures, high maintenance standards for training aircraft, and more proficient pilots (instructors).
4.2. What Key Factors Contribute to the Safety of Instructional Flights?
Key factors include a supervised environment, structured operations that discourage risk-taking, rigorous maintenance of training aircraft, and the high proficiency of flight instructors.
4.3. What Can GA Pilots Learn From the Safety Mindset of Airlines?
GA pilots can model their safety mindset after airlines, which are structured and risk-averse operations with highly trained and proficient pilots. This involves disciplined decision-making and continuous improvement.
5. Key Safety Measures and Best Practices in Aviation Safety
To enhance safety in general aviation, various measures and best practices can be implemented. Let’s look at some of the key strategies that contribute to safer flying.
5.1. What Role Does Regular Aircraft Maintenance Play in Aviation Safety?
Regular and thorough aircraft maintenance is vital. This includes adhering to manufacturer guidelines, conducting pre-flight inspections, and addressing any mechanical issues promptly. Proper maintenance helps prevent mechanical failures, which, while less frequent than pilot-related errors, can lead to serious accidents.
5.2. How Does Pilot Training and Proficiency Affect Aviation Safety?
Comprehensive pilot training and maintaining proficiency are crucial. This involves not only completing the initial training required for certification but also engaging in ongoing education, recurrent training, and regular practice flights. Proficiency ensures pilots are prepared to handle various flight conditions and emergencies.
5.3. What Is the Importance of Weather Awareness and Decision-Making in Aviation Safety?
Being aware of weather conditions and making informed decisions based on them is essential. Pilots should thoroughly check weather forecasts before each flight, understand the potential impact of adverse weather, and be prepared to delay or cancel flights when necessary. Avoiding flying in conditions beyond their capabilities is a key aspect of weather-related safety.
5.4. How Does the Use of Advanced Technology Contribute to Aviation Safety?
Advanced technology plays a significant role in enhancing safety. Modern avionics, GPS navigation, autopilot systems, and weather radar provide pilots with critical information and assistance. Properly utilizing these technologies can significantly reduce the risk of accidents caused by navigation errors, loss of situational awareness, or adverse weather conditions.
5.5. What Role Does Effective Communication Play in Aviation Safety?
Effective communication between pilots, air traffic control, and other crew members is essential for maintaining a safe flying environment. Clear and concise communication ensures everyone is aware of the aircraft’s position, intentions, and any potential hazards. Proper communication protocols help prevent misunderstandings and errors that could lead to accidents.
5.6. How Does Risk Management Contribute to Aviation Safety?
Implementing a proactive risk management approach is crucial for identifying and mitigating potential hazards. This involves assessing the risks associated with each flight, developing strategies to minimize those risks, and continuously monitoring and adjusting those strategies as needed. Effective risk management helps pilots make informed decisions and avoid unnecessary dangers.
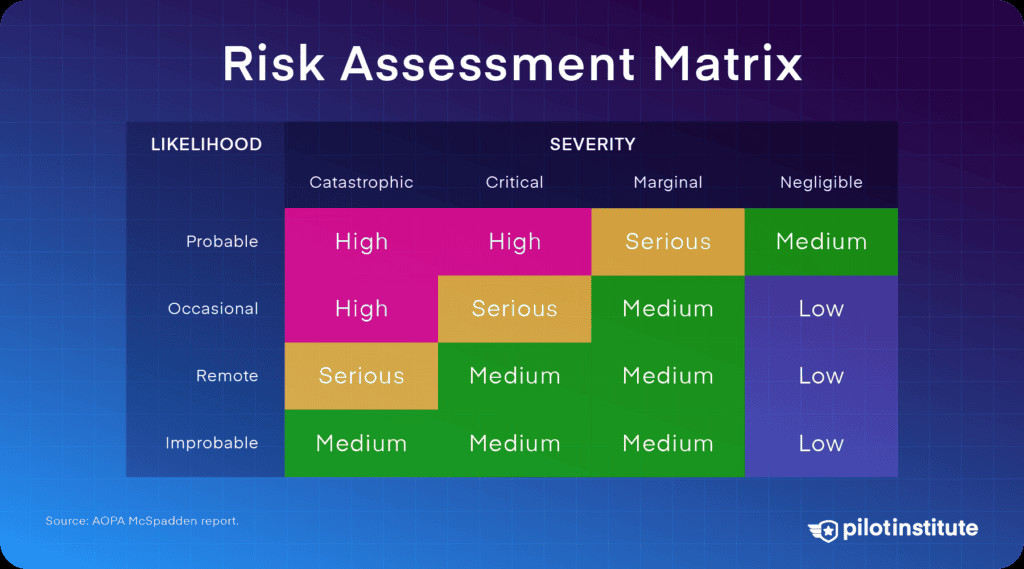 FAA Risk Assessment Matrix
FAA Risk Assessment Matrix
5.7. What Are the Best Practices for Emergency Preparedness in Aviation?
Being prepared for emergencies is a critical aspect of aviation safety. Pilots should be thoroughly trained on how to handle various emergency situations, such as engine failures, fires, and medical emergencies. Conducting regular emergency drills and having a well-defined emergency plan can significantly improve the chances of a successful outcome in the event of an actual emergency.
6. The Role of Aviation Safety Organizations and Regulations
Several organizations and regulatory bodies play crucial roles in ensuring aviation safety. Understanding their functions and contributions is essential for appreciating the multi-faceted approach to safety in aviation.
6.1. How Does the FAA Contribute to Aviation Safety?
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is the primary regulatory body for aviation in the United States. Its responsibilities include setting and enforcing safety standards, certifying pilots and aircraft, and managing air traffic. The FAA’s rigorous oversight helps ensure that all aspects of aviation adhere to the highest safety standards.
6.2. What Role Does the NTSB Play in Aviation Safety?
The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) is an independent federal agency responsible for investigating transportation accidents, including aviation accidents. The NTSB’s investigations aim to determine the causes of accidents and issue safety recommendations to prevent future incidents. These recommendations often lead to changes in regulations, procedures, or training programs.
6.3. How Does ICAO Contribute to Global Aviation Safety?
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) is a United Nations agency that sets standards and regulations for international aviation. ICAO’s standards cover a wide range of topics, including air navigation, airport operations, and aircraft safety. By promoting consistent safety standards worldwide, ICAO helps ensure that international air travel remains as safe as possible.
6.4. What Role Do Aviation Safety Organizations Like AOPA Play?
Aviation safety organizations like the Aircraft Owners and Pilots Association (AOPA) play a vital role in promoting safety among pilots and aircraft owners. AOPA provides educational resources, safety training programs, and advocacy for policies that enhance safety. These organizations help create a culture of safety within the aviation community.
6.5. How Do Aircraft Manufacturers Contribute to Aviation Safety?
Aircraft manufacturers play a critical role in designing and producing safe aircraft. They must adhere to strict safety standards and regulations throughout the design, testing, and manufacturing processes. Manufacturers also provide ongoing support and maintenance guidance to ensure their aircraft remain safe throughout their operational life.
6.6. What Is the Importance of Continuous Improvement in Aviation Safety?
Aviation safety is not static; it requires continuous improvement and adaptation. Learning from past accidents, implementing new technologies, and refining procedures are essential for further enhancing safety. The aviation industry’s commitment to continuous improvement helps ensure that air travel remains one of the safest forms of transportation.
7. Exploring Aviation Training and Career Opportunities at flyermedia.net
Interested in pursuing a career in aviation? flyermedia.net is your go-to resource for comprehensive information on flight training, aviation news, and career opportunities in the USA. Discover the best flight schools, understand aviation regulations, and explore exciting career paths.
7.1. Finding the Right Flight School
Choosing the right flight school is a critical first step for aspiring pilots. flyermedia.net offers a directory of top-rated flight schools in the USA, along with detailed information on their programs, instructors, and facilities. Whether you’re looking for a Part 61 or Part 141 flight school, flyermedia.net can help you find the perfect fit.
7.2. Understanding Aviation Regulations
Navigating the complex world of aviation regulations can be challenging. flyermedia.net provides clear and concise explanations of FAA regulations, air traffic control procedures, and other essential information. Stay informed and compliant with the latest rules and guidelines.
7.3. Staying Updated on Aviation News
Keeping up-to-date with the latest aviation news is essential for pilots and aviation enthusiasts alike. flyermedia.net offers comprehensive coverage of industry trends, technological advancements, and safety updates. Stay informed and connected to the aviation community.
7.4. Exploring Aviation Career Opportunities
The aviation industry offers a wide range of career opportunities, from pilots and air traffic controllers to aircraft mechanics and aviation managers. flyermedia.net provides resources for exploring these career paths, including job listings, salary information, and educational requirements. Find your dream job in aviation.
7.5. Connecting with the Aviation Community
flyermedia.net is more than just a website; it’s a community of aviation professionals, enthusiasts, and students. Connect with like-minded individuals, share your experiences, and learn from others. Join the flyermedia.net community and take your aviation journey to new heights.
8. Conclusion: The Safer Skies Await
Flying, especially commercial aviation, maintains a strong safety record due to rigorous standards, advanced technology, and highly trained professionals. While general aviation presents higher risks than driving, understanding the factors involved and adhering to safety measures can significantly reduce those risks. As aviators, disciplined decision-making is paramount. For more information on flight training, aviation news, and career opportunities, visit flyermedia.net.
9. FAQ: Addressing Common Questions About Aviation Safety
9.1. Is Flying Really Safer Than Driving?
Yes, commercial airline flying is generally safer than driving due to stringent regulations, advanced technology, and highly trained professionals.
9.2. What Makes Commercial Aviation So Safe?
Commercial aviation benefits from rigorous maintenance, standardized procedures, and skilled pilots, resulting in a lower accident rate.
9.3. What Are the Main Causes of Accidents in General Aviation?
Pilot error, mechanical failures, and weather-related issues are the primary causes of accidents in general aviation.
9.4. How Can Pilots Reduce the Risk of Accidents?
Pilots can reduce risk through continuous training, adhering to safety protocols, and making informed decisions based on weather and aircraft conditions.
9.5. What Is the Role of the FAA in Ensuring Aviation Safety?
The FAA sets and enforces safety standards, certifies pilots and aircraft, and manages air traffic to ensure aviation safety in the United States.
9.6. How Do Weather Conditions Impact Aviation Safety?
Adverse weather conditions can significantly increase the risk of accidents. Pilots must be vigilant about weather awareness and avoid flying in conditions beyond their capabilities.
9.7. What Are the Key Differences Between Part 61 and Part 141 Flight Schools?
Part 61 flight schools offer more flexible training options, while Part 141 schools follow a structured curriculum approved by the FAA.
9.8. What Are the Essential Skills for a Successful Aviation Career?
Essential skills include strong decision-making abilities, excellent communication skills, and a commitment to safety and continuous learning.
9.9. How Can I Stay Updated on Aviation Safety News and Regulations?
Stay updated through resources like the FAA website, aviation safety organizations, and industry publications. You can find this information on flyermedia.net.
9.10. What Are the Latest Advancements in Aviation Technology Enhancing Safety?
Advanced avionics, GPS navigation, and weather radar are among the latest technologies enhancing safety by providing pilots with critical information and assistance.
Fly high and safe with flyermedia.net. Explore our website for more information on flight training, aviation news, and career opportunities. For any inquiries, feel free to contact us at: Address: 600 S Clyde Morris Blvd, Daytona Beach, FL 32114, United States. Phone: +1 (386) 226-6000.