Are you eager to learn how to fly a drone and experience the thrill of aerial navigation? At flyermedia.net, we provide a comprehensive guide, breaking down the fundamental controls and techniques you need to master drone flight, transforming you from a novice into a confident drone pilot. Dive in to discover the essential drone maneuvers, flight modes, and crucial safety tips, ensuring a seamless and enjoyable flight experience. Learn about remote control, aerial photography, and aviation safety.
1. What Are the Fundamental Drone Controls Every Beginner Should Know?
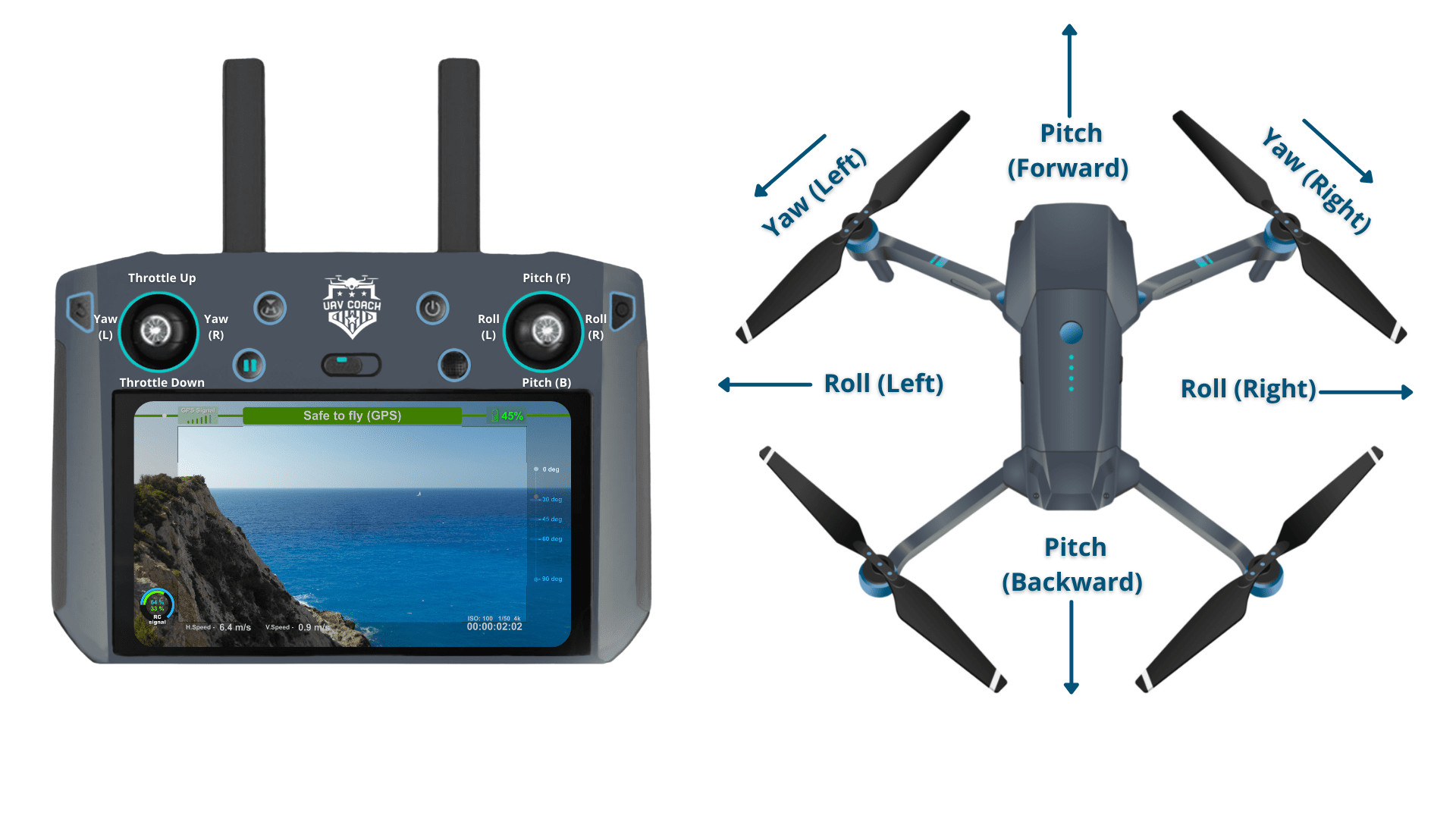
The fundamental drone controls every beginner should know include roll, pitch, yaw, and throttle. Mastering these controls is crucial for safe and effective drone operation. Understanding how each control affects the drone’s movement is the first step towards becoming a proficient pilot.
- Roll: Controls the drone’s lateral movement, moving it left or right by tilting the drone.
- Pitch: Controls the drone’s forward and backward movement by tilting the drone accordingly.
- Yaw: Controls the drone’s rotation, allowing it to turn left or right without moving in those directions.
- Throttle: Controls the drone’s altitude, increasing or decreasing its height.
Understanding the interplay between these controls is vital. For instance, combining throttle with yaw allows for smooth, coordinated turns, while using pitch and roll together enables controlled directional flight.
 Drone Controls
Drone Controls
2. How Does the Roll Control Affect a Drone’s Movement?
The roll control affects a drone’s movement by causing it to move laterally, either left or right. Activating the roll control tilts the drone, allowing it to move sideways in the direction of the tilt. This is achieved by adjusting the right stick on the controller.
- Moving Left: Pushing the right stick to the left causes the drone to roll to the right and move left.
- Moving Right: Pushing the right stick to the right causes the drone to roll to the left and move right.
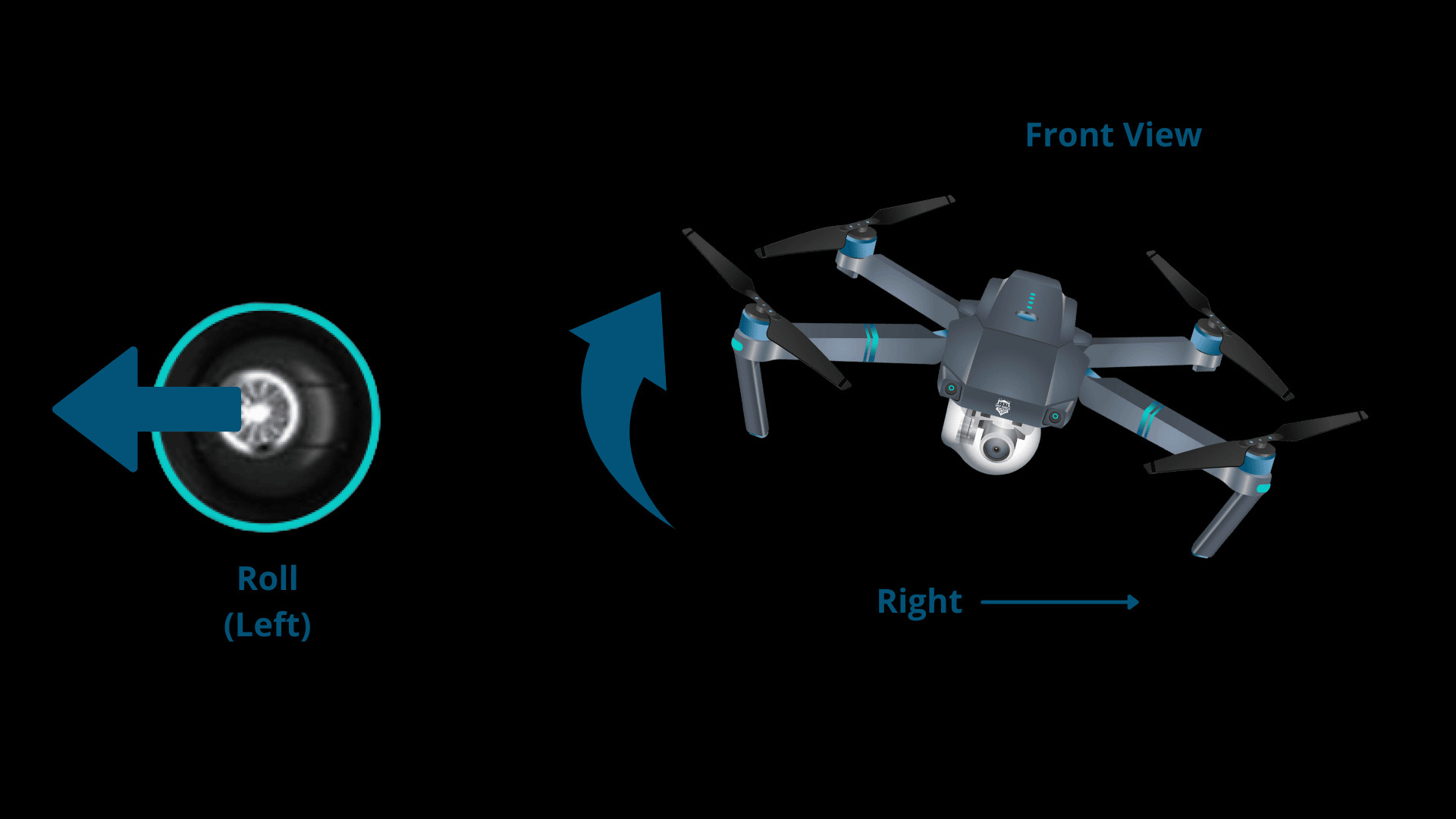 Drone Rolling Left
Drone Rolling Left
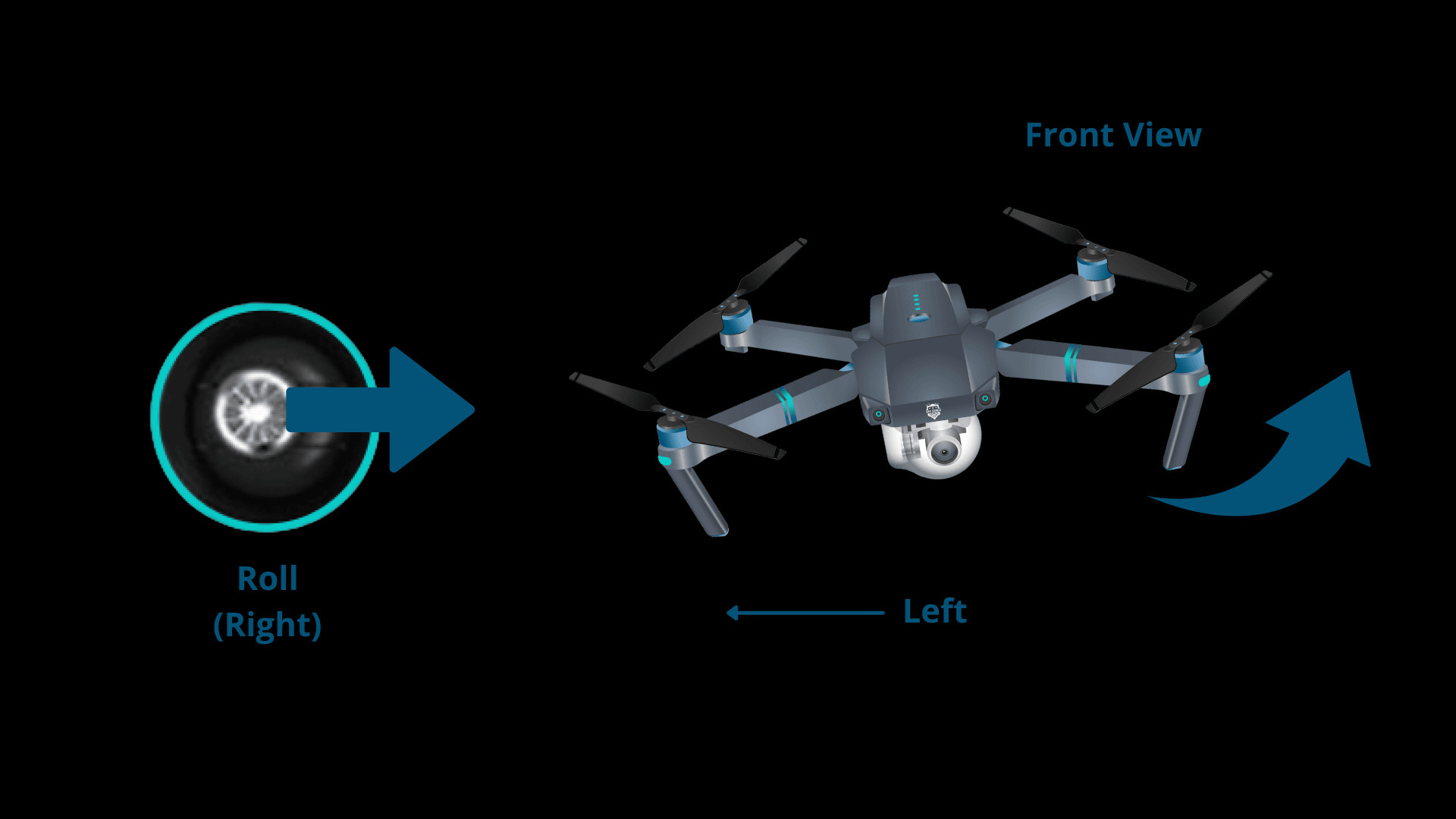 Drone Rolling Right
Drone Rolling Right
Understanding the roll control is essential for navigating the drone in tight spaces and making precise lateral adjustments. Practice in a controlled environment will help you become proficient in using this control.
3. How Does the Pitch Control Influence the Direction of a Drone?
The pitch control influences the direction of a drone by tilting it forward or backward, causing it to move in that direction. Pitch is controlled using the right stick on the remote.
- Moving Forward: Pushing the right stick forward causes the drone to tilt forward, moving it away from the pilot.
- Moving Backward: Pulling the right stick backward causes the drone to tilt backward, moving it toward the pilot.
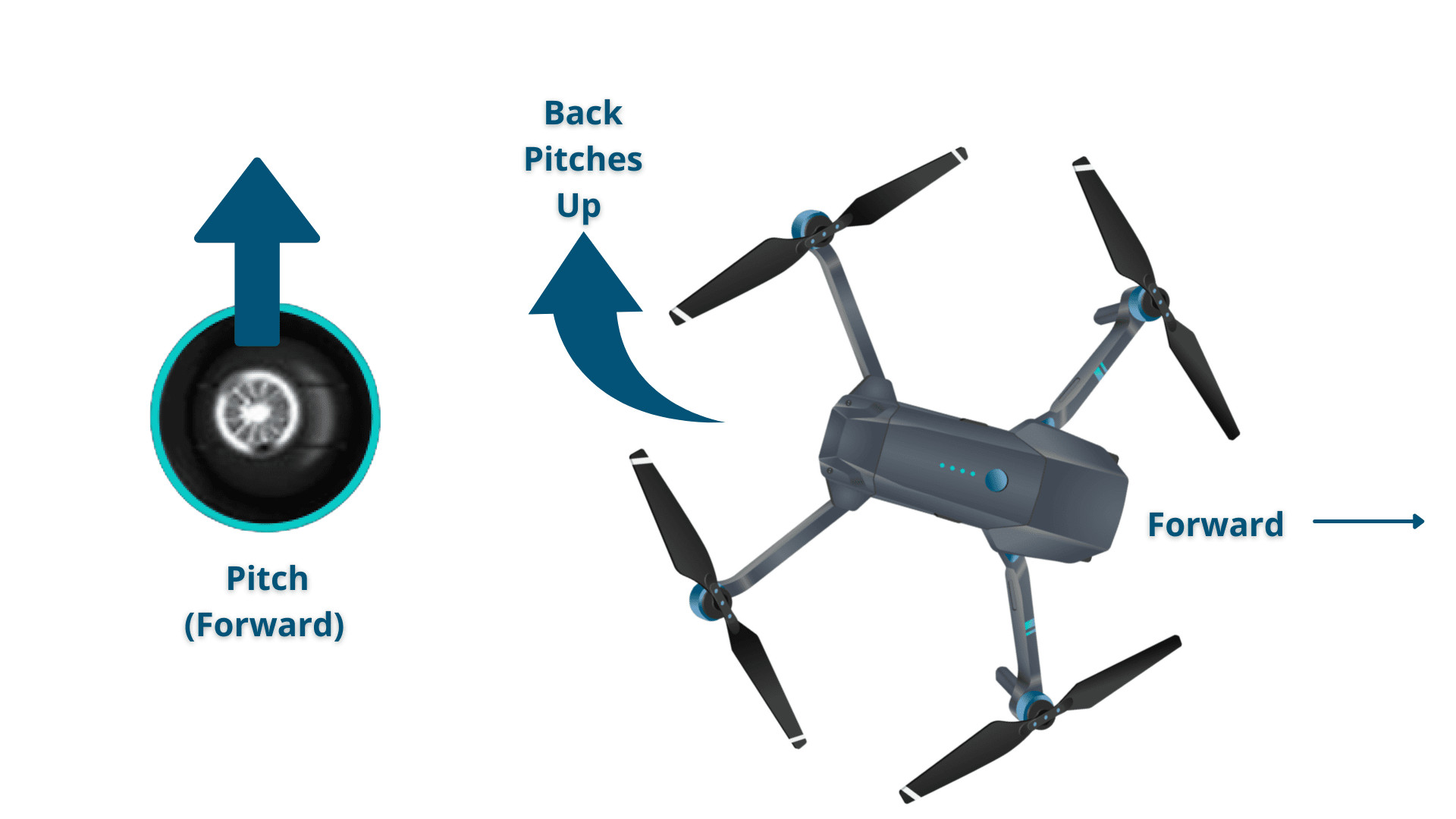 Drone Pitching Up
Drone Pitching Up
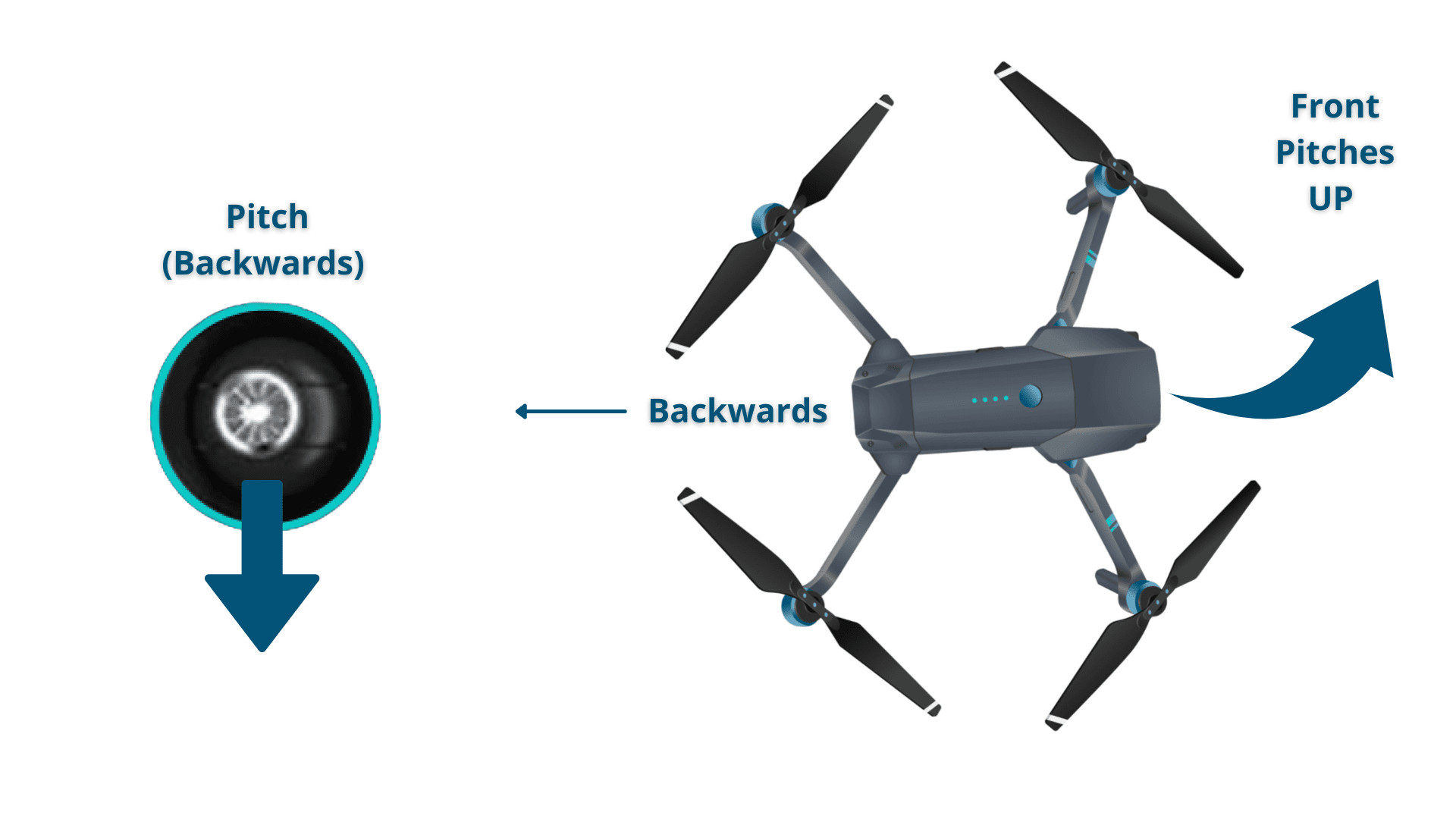 Drone Pitching Down
Drone Pitching Down
Pitch control is essential for navigating the drone over distances and adjusting its position relative to the pilot. Familiarize yourself with pitch control to maintain smooth and controlled flight.
4. What Role Does the Yaw Control Play in Drone Piloting?
The yaw control plays a crucial role in drone piloting by allowing the drone to rotate horizontally, changing the direction it faces without moving in that direction. Yaw is controlled using the left stick on the remote.
- Rotating Left: Pushing the left stick to the left causes the drone to rotate counter-clockwise.
- Rotating Right: Pushing the left stick to the right causes the drone to rotate clockwise.
Yaw control is particularly useful for:
- Changing Orientation: Adjusting the drone’s facing direction.
- Tracking Objects: Keeping a moving subject within the camera’s view.
- Composing Shots: Precisely positioning the drone for aerial photography and videography.
Mastering yaw control allows pilots to execute complex maneuvers and capture dynamic aerial footage.
5. Why Is the Throttle Control Important for Drone Flight?
The throttle control is critically important for drone flight as it manages the power to the drone’s propellers, directly affecting its altitude. The throttle is controlled using the left stick on the remote.
- Increasing Altitude: Pushing the left stick forward increases the throttle, causing the drone to ascend.
- Decreasing Altitude: Pulling the left stick backward decreases the throttle, causing the drone to descend.
Maintaining proper throttle control is essential for:
- Take-off and Landing: Safely lifting off the ground and gently landing.
- Altitude Management: Maintaining a consistent height during flight.
- Preventing Crashes: Avoiding obstacles and the ground by adjusting altitude.
Throttle control is one of the first skills new drone pilots should master to ensure stable and safe flight.
6. How Do I Handle Inverted Controls When Flying a Drone?
Handling inverted controls when flying a drone involves understanding that the drone’s orientation relative to the pilot changes the control inputs. When the drone is facing the pilot, the controls are inverted, meaning:
- Right Stick: Moving the right stick to the right moves the drone to the left, and vice versa.
- Pitch: Pushing the right stick forward moves the drone backward, and pulling it backward moves the drone forward.
To manage inverted controls:
- Visualize: Imagine you are sitting in the drone to reorient your perspective.
- Practice: Spend time practicing in an open area to become comfortable with the inverted controls.
- Use Headless Mode: Some drones have a headless mode that maintains the original orientation regardless of the drone’s direction.
Being aware of the drone’s orientation and adjusting your control inputs accordingly will help you maintain control and prevent accidents.
7. What Are Some Essential Drone Flight Modes?
Essential drone flight modes include:
- GPS Mode: Utilizes GPS to maintain a stable hover and position, making it easier for beginners to control the drone.
- Attitude Mode (ATTI): Deactivates GPS, relying on the drone’s sensors to maintain stability. This mode requires more skill but allows for smoother, more cinematic flight.
- Sport Mode: Increases the drone’s speed and agility, making it more responsive to control inputs. This mode is suitable for experienced pilots.
- Beginner Mode: Limits the drone’s speed and altitude, providing a safe environment for new pilots to learn.
- Intelligent Flight Modes: Offer automated flight patterns such as orbit, follow me, and waypoint navigation.
Understanding and utilizing these flight modes can enhance your drone flying experience and allow you to capture more dynamic and creative footage.
8. What Safety Precautions Should I Take Before Flying a Drone?
Before flying a drone, take these safety precautions:
- Check Weather Conditions: Avoid flying in strong winds, rain, or extreme temperatures.
- Inspect Drone: Ensure the drone is in good working condition, with fully charged batteries, secure propellers, and functional controls.
- Know Local Regulations: Understand and comply with local drone laws and regulations, including airspace restrictions and registration requirements.
- Choose a Safe Location: Select an open area away from obstacles, people, and sensitive infrastructure like airports and power lines.
- Maintain Line of Sight: Keep the drone within your visual line of sight at all times.
- Set a Return-to-Home Point: Ensure the return-to-home function is properly set in case of signal loss or low battery.
- Use a Spotter: If possible, have a spotter assist you in monitoring the drone and its surroundings.
Adhering to these safety precautions will minimize the risk of accidents and ensure a safe and enjoyable drone flying experience. For detailed regulations, refer to the FAA guidelines.
9. What Are the FAA Regulations I Need to Know?
FAA regulations for drone pilots include:
- Registration: Register your drone with the FAA if it weighs between 0.55 pounds (250 grams) and 55 pounds (25 kg).
- Remote ID: Drones must have Remote ID, broadcasting identification and location information.
- Part 107 Certification: If flying for commercial purposes, you must obtain a Part 107 certificate by passing an FAA knowledge test.
- Altitude Limits: Drones cannot be flown higher than 400 feet above ground level (AGL) in uncontrolled airspace.
- Airspace Restrictions: Avoid flying near airports, restricted airspace, and other sensitive areas without authorization. Use apps like B4UFLY to check airspace restrictions.
- Visual Line of Sight: Maintain visual line of sight with the drone at all times.
- Night Flying: Night flying requires anti-collision lights and completion of additional training.
- Operation Over People: Restrictions apply to flying over people, depending on the drone’s weight and Remote ID compliance.
Staying informed about and complying with FAA regulations is essential for legal and safe drone operation.
10. How Can I Improve My Drone Flying Skills?
You can improve your drone flying skills through:
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice in various conditions and environments helps build muscle memory and confidence.
- Take a Drone Flying Course: Enroll in a drone flying course to learn advanced techniques and safety procedures from experienced instructors.
- Use a Simulator: Practice with a drone simulator to get familiar with the controls and flight dynamics in a safe environment.
- Join a Drone Club: Connect with other drone enthusiasts to share tips, experiences, and learn from each other.
- Watch Tutorials: Watch online tutorials and instructional videos to learn new techniques and stay updated on industry best practices.
- Experiment with Flight Modes: Practice flying in different flight modes to understand their characteristics and how they affect the drone’s performance.
- Review Flight Footage: Analyze your flight footage to identify areas for improvement and track your progress.
Consistent effort and a commitment to learning will help you develop advanced drone flying skills and become a proficient pilot.
11. What Is the Importance of Pre-Flight Checks for Drones?
The importance of pre-flight checks for drones cannot be overstated, as these checks ensure the drone is safe and ready for flight, preventing potential accidents and equipment malfunctions. Key pre-flight checks include:
- Battery Levels: Ensuring both the drone and controller batteries are fully charged.
- Propeller Condition: Checking for any cracks, damage, or loose propellers.
- Firmware Updates: Verifying that the drone and controller have the latest firmware installed.
- Compass Calibration: Calibrating the compass to ensure accurate navigation.
- GPS Signal: Confirming a strong GPS signal for stable flight.
- Camera Functionality: Testing the camera to ensure it is recording properly.
- Control Responsiveness: Checking that all controls are responsive and functioning as expected.
- Weather Conditions: Assessing the weather to ensure it is safe to fly.
Performing thorough pre-flight checks will minimize the risk of in-flight issues and contribute to a safer and more enjoyable drone flying experience.
12. How Do Weather Conditions Affect Drone Flight?
Weather conditions significantly affect drone flight, impacting stability, visibility, and overall safety. Here’s how different weather elements can affect drone operation:
- Wind: Strong winds can cause instability, making it difficult to control the drone’s position and potentially leading to crashes.
- Rain: Rain can damage the drone’s electronics, causing malfunctions and reducing battery life. It also reduces visibility.
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures can affect battery performance, reducing flight time and potentially causing damage.
- Visibility: Fog, clouds, and haze can reduce visibility, making it difficult to maintain visual line of sight with the drone.
- Snow: Snow can accumulate on the drone, adding weight and affecting its aerodynamics. It can also damage electronics.
- Turbulence: Unstable air can cause sudden changes in altitude and direction, making it challenging to maintain control.
Always check the weather forecast before flying and avoid flying in adverse conditions to ensure the safety of your drone and those around you.
13. What Are Some Common Mistakes to Avoid When Learning to Fly a Drone?
Common mistakes to avoid when learning to fly a drone include:
- Ignoring Pre-Flight Checks: Skipping pre-flight checks can lead to flying with damaged or malfunctioning equipment.
- Flying in Unsafe Conditions: Flying in strong winds, rain, or near obstacles increases the risk of crashes.
- Exceeding Battery Limits: Flying until the battery is completely depleted can cause a sudden loss of power and a crash.
- Not Understanding Controls: Lack of familiarity with the drone’s controls can lead to erratic movements and loss of control.
- Flying Too Far Away: Exceeding the drone’s range or flying beyond visual line of sight can result in signal loss and difficulty in recovering the drone.
- Ignoring Regulations: Failing to comply with local drone laws and regulations can result in fines and penalties.
- Overconfidence: Becoming overconfident too quickly can lead to careless flying and increased risk of accidents.
By being aware of these common mistakes and taking steps to avoid them, new drone pilots can learn more safely and effectively.
14. What Are the Best Practices for Maintaining Drone Batteries?
Best practices for maintaining drone batteries include:
- Proper Storage: Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
- Partial Charging: Avoid fully charging or discharging batteries for long-term storage. Aim for a charge level of around 40-60%.
- Regular Use: Use batteries regularly to maintain their health. If storing for an extended period, discharge and recharge them periodically.
- Avoid Overcharging: Do not leave batteries on the charger after they are fully charged.
- Use Correct Charger: Only use the charger specifically designed for your drone’s batteries.
- Monitor Temperature: Avoid using or charging batteries when they are excessively hot or cold.
- Inspect for Damage: Regularly inspect batteries for signs of swelling, leaks, or damage.
Following these practices will help extend the lifespan and performance of your drone batteries.
15. How Important Is It to Calibrate the Drone’s Compass?
Calibrating the drone’s compass is very important because it ensures accurate navigation and stable flight. The compass helps the drone determine its orientation and direction, which is crucial for functions like GPS positioning, return-to-home, and intelligent flight modes.
Reasons why compass calibration is important:
- Accurate Positioning: Ensures the drone knows its exact location and direction.
- Stable Flight: Prevents erratic movements and helps the drone maintain a stable hover.
- Return-to-Home Functionality: Ensures the drone can accurately return to its take-off point in case of signal loss or low battery.
- Interference Mitigation: Compensates for magnetic interference from nearby objects or the environment.
Always calibrate the compass before each flight, especially when flying in a new location or after experiencing a crash, to ensure optimal performance and safety.
16. What Are the Key Considerations for Drone Aerial Photography and Videography?
Key considerations for drone aerial photography and videography include:
- Camera Settings: Understanding and adjusting camera settings such as ISO, aperture, shutter speed, and white balance to achieve desired image quality.
- Composition: Applying principles of composition such as the rule of thirds, leading lines, and symmetry to create visually appealing shots.
- Lighting: Considering the time of day and weather conditions to capture optimal lighting. Avoid harsh shadows and glare.
- Smooth Movements: Executing smooth and controlled drone movements to capture stable and cinematic footage.
- Resolution and Frame Rate: Selecting appropriate resolution and frame rate settings for your intended use.
- Gimbal Control: Using the gimbal to stabilize the camera and achieve smooth panning and tilting movements.
- Legal Restrictions: Being aware of and complying with local laws and regulations regarding drone photography and videography.
By mastering these considerations, you can capture stunning aerial photos and videos that showcase your creativity and technical skills.
17. How Can I Practice Drone Flying Indoors?
You can practice drone flying indoors by:
- Using a Mini Drone: Mini drones are smaller, lighter, and more suitable for indoor flight due to their size and maneuverability.
- Setting Up a Practice Area: Designate a safe area free from obstacles, pets, and people. Use soft barriers to prevent damage in case of crashes.
- Hovering Practice: Practice hovering in place to develop throttle control and stability.
- Basic Maneuvers: Practice basic maneuvers such as take-offs, landings, and controlled turns.
- Figure Eights: Practice flying figure eights to improve coordination and control.
- Using a Simulator: Use a drone simulator to practice in a virtual environment that mimics real-world flying conditions.
Practicing indoors can help you build confidence and develop essential skills before flying outdoors.
18. What Are the Benefits of Joining a Drone Flying Club?
The benefits of joining a drone flying club include:
- Networking: Connecting with other drone enthusiasts to share experiences, tips, and advice.
- Learning: Learning from experienced pilots and instructors through workshops, seminars, and group flights.
- Skill Development: Improving your flying skills through organized practice sessions and competitions.
- Legal Compliance: Staying updated on local laws, regulations, and best practices for safe and legal drone operation.
- Community Support: Receiving support and encouragement from fellow members.
- Group Activities: Participating in group flights, events, and community outreach programs.
- Access to Resources: Accessing shared resources such as training materials, equipment, and flying locations.
Joining a drone flying club can enhance your drone flying experience and provide valuable opportunities for learning, networking, and community engagement.
19. What Are Some Advanced Drone Maneuvers I Can Learn?
Some advanced drone maneuvers you can learn include:
- Orbiting: Flying the drone in a circle around a central point while maintaining a consistent distance and altitude.
- Tracking: Following a moving subject while keeping it within the camera’s view.
- First-Person View (FPV) Racing: Flying the drone through a course using FPV goggles for a more immersive experience.
- Cinematic Movements: Executing smooth and controlled movements to create cinematic footage.
- Precision Landings: Landing the drone accurately in a designated spot.
- Aerial Acrobatics: Performing flips, rolls, and other acrobatic maneuvers.
- Waypoint Navigation: Programming the drone to follow a pre-defined route using waypoints.
Learning these advanced maneuvers can elevate your drone flying skills and enable you to capture more dynamic and creative content.
20. What Are the Latest Technological Advancements in Drone Technology?
The latest technological advancements in drone technology include:
- Improved Battery Life: Advancements in battery technology have led to longer flight times and more efficient power management.
- Enhanced Sensors: Improved sensors such as obstacle avoidance systems, GPS, and visual positioning systems (VPS) enhance safety and stability.
- High-Resolution Cameras: Advancements in camera technology have resulted in higher resolution sensors, improved image stabilization, and better low-light performance.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered features such as object recognition, autonomous flight, and intelligent tracking are becoming more prevalent.
- 5G Connectivity: 5G connectivity enables faster data transfer, lower latency, and improved real-time control.
- Advanced Materials: The use of lightweight and durable materials such as carbon fiber and composites improves drone performance and durability.
- Remote Identification (Remote ID): Remote ID technology allows drones to broadcast their identification and location information, enhancing safety and accountability.
These advancements are transforming the capabilities and applications of drones, making them more versatile and accessible than ever before.
Ready to take your drone piloting skills to new heights? Visit flyermedia.net today to discover a wealth of information on drone training, aviation news, and exciting career opportunities in the aviation industry. Whether you’re looking for flight schools, the latest aviation technology updates, or job openings, flyermedia.net is your go-to resource.