Is Flying Safer Than Driving, or does the open road offer a less perilous journey? At flyermedia.net, we delve into the statistics, risk factors, and safety measures of both general aviation and driving to provide a comprehensive comparison. Explore aviation safety, transportation risks, and discover resources for aviation training and safety tips. Stay informed and make safer decisions with the latest insights on aviation accident prevention and air travel safety.
1. Understanding the Core Question: Is Flying as Safe as Driving?
Is flying safer than driving is a question many ponder before taking to the skies or hitting the road. The answer isn’t straightforward, as it depends on the type of flying being considered. Commercial air travel boasts an impressive safety record, but general aviation (GA) presents a different picture. Let’s break down the nuances of aviation safety and driving risks to understand which mode of transport is statistically safer.
2. General Aviation (GA) vs. Driving: A Statistical Comparison
How do the numbers stack up when comparing general aviation and driving? While it’s challenging to make a direct comparison due to differing reporting methods, a 2020 study offers valuable insights. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) measures accidents per 100 million vehicle miles traveled, reporting 1.37 fatalities per 100 million vehicle miles in 2021. On the other hand, the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) uses accidents per 100,000 flight hours, with 0.95 fatalities per 100,000 flight hours in the same year. To bridge this gap, the 2020 study found 0.6 to 0.7 fatal car crashes per million hours driven.
3. What Are the Accident Rates for Different Types of Transportation?
What are the specific accident rates for cars, motorcycles, and general aviation? According to NHTSA data, motorcycle accidents result in about 27 times more fatalities per vehicle mile than car accidents. This translates to approximately 16 to 18 fatal motorcycle accidents per million hours ridden. In comparison, general aviation had 9.5 fatal crashes per million flight hours in 2021, roughly 14 times the driving fatality rate.
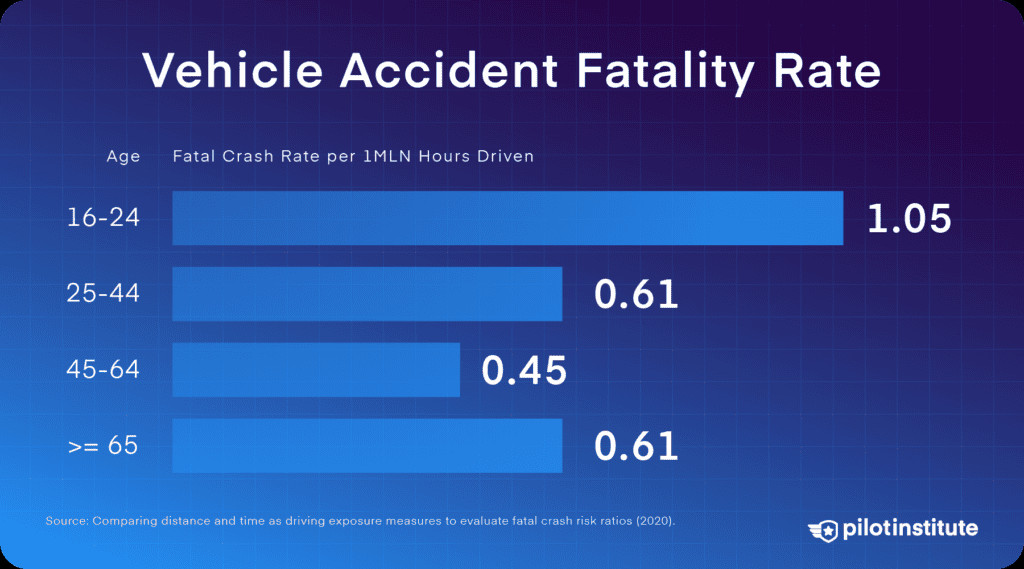 Vehicle accident fatality rate by age
Vehicle accident fatality rate by age
4. Diving Deeper: Personal Flights vs. Corporate Aviation
Is all general aviation equally risky? No. Corporate aviation, involving business jets, is relatively safe, with 0.48 fatal accidents per million flight hours between 2012 and 2021. Personal flights, however, tell a different story. These flights, often for leisure, account for 67% of GA accidents and 72% of GA fatalities. Between 2012 and 2021, personal flights experienced 21.1 fatal accidents per million flight hours, over 27 times the driving fatality rate.
5. Instructional Flights: How Safe Is Flight Training?
How does flight training compare in terms of safety? Instructional flights reported 2.3 fatal accidents per million flight hours, a 52% decrease since 2012. This makes flight training only 3.4 times more dangerous than driving, highlighting the benefits of structured environments and supervised operations.
6. Identifying the Primary Risk Factors in General Aviation
What factors contribute to accidents in general aviation? The AOPA’s Richard G. McSpadden Report categorizes accidents into pilot-related, mechanical, and other/unknown causes. Pilot error is the leading cause, accounting for 69% of all incidents.
7. The Role of Unknown Causes in Aviation Accidents
What about accidents with unclear causes? In 2021, 15% of all accidents and 28% of fatal ones lacked a clear cause. These incidents are challenging as they prevent learning and improvement in safety measures.
8. Mechanical Failures: A Significant Yet Manageable Risk
How significant are mechanical failures in aviation accidents? Mechanical issues account for about 16% of all accidents but only 7% of fatal ones in 2021. Engine failures, while concerning, are often manageable emergencies.
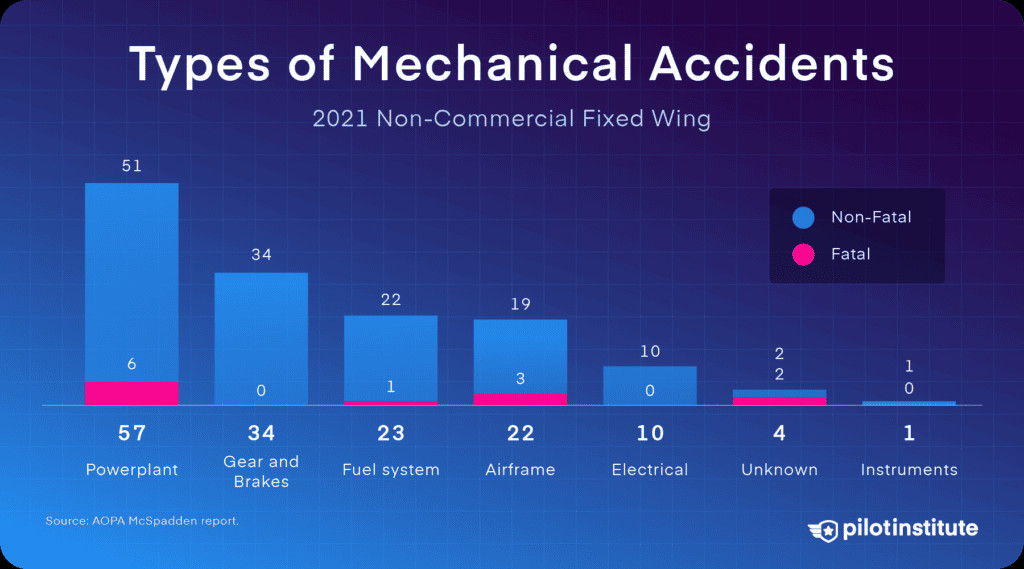 Types of GA mechanical accidents
Types of GA mechanical accidents
9. Understanding Engine Failure Causes and Prevention
What are the primary causes of engine failures, and how can they be prevented? AOPA found that 30% of engine failures have no clear cause, while maintenance issues account for 16%, and structural failures 17%. Preventable problems like carb ice or fuel issues make up the remainder. Pilots and mechanics contribute to about half of all engine failures, indicating a significant area for improvement through better training and maintenance practices.
10. Fuel Management: Avoiding Fuel-Related Accidents
How do fuel-related accidents occur, and what can be done to prevent them? Fuel-related accidents typically involve fuel contamination, fuel starvation, or fuel exhaustion. Fuel contamination occurs when substances other than fuel mix in the tank, such as water. Fuel starvation happens when fuel is on board but doesn’t reach the engine, often due to selecting the wrong fuel tank. Fuel exhaustion results from poor flight planning, leading to running out of fuel.
11. Pilot Error: The Dominant Factor in GA Accidents
Why is pilot error the leading cause of accidents in general aviation? Despite advancements in aviation safety, human factors continue to be a primary concern. In 2021, pilots were deemed at fault in 69% of GA accidents. The NTSB classifies these errors using “defining events,” with loss of control in-flight (LOC-I) being the most common and fatal.
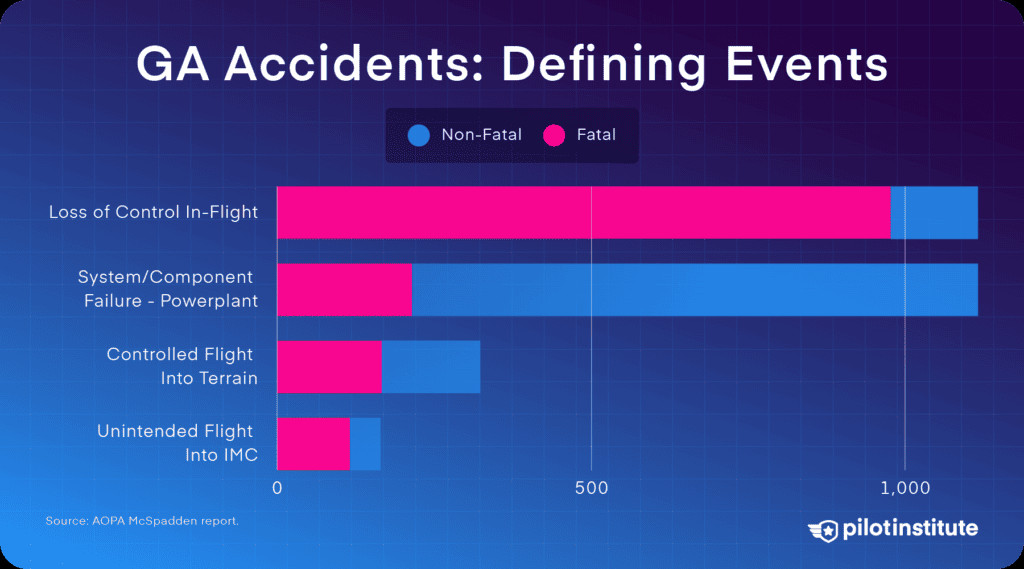 A selection of GA accident defining events
A selection of GA accident defining events
12. Loss of Control In-Flight (LOC-I): Understanding the Risks
What is loss of control in-flight (LOC-I), and why is it so dangerous? LOC-I occurs when the pilot loses control of the aircraft, often due to flying too slowly or making uncoordinated control inputs. Half of these accidents involve stalls and spins in the traffic pattern during maneuvering flight, which are seldom recoverable.
13. Common Accident Scenarios: Landings, Takeoffs, and Climbs
Where do many GA accidents happen during landings, but they are not typically the most fatal. The most common landing accident is loss of control.
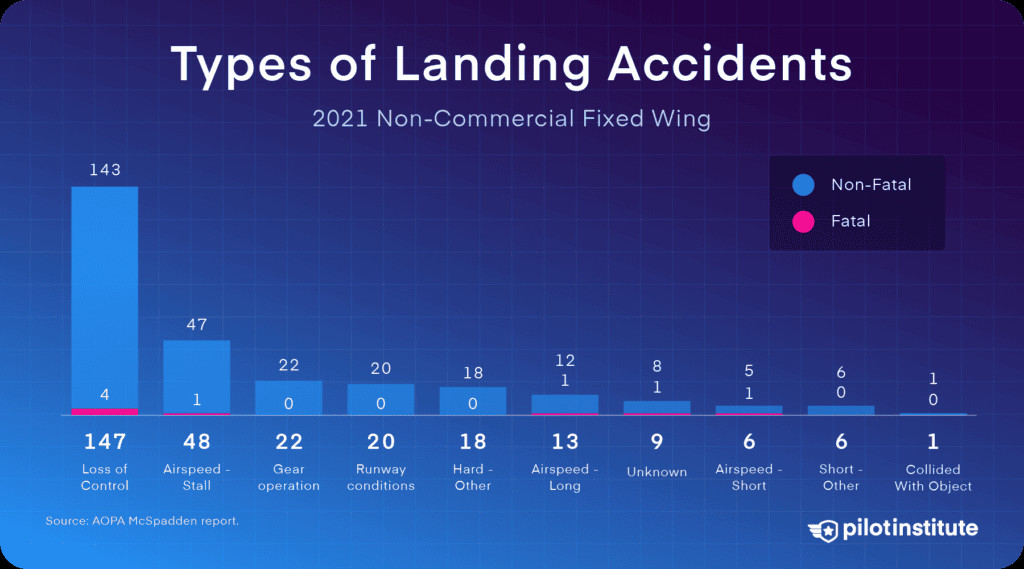 Types of GA landing accidents
Types of GA landing accidents
Takeoff and climb accidents have a higher fatality rate. The airplane is in a low-energy, low-altitude state with a high angle of attack, leaving little room for error in an emergency.
14. The Dangers of Controlled Flight Into Terrain (CFIT)
What is Controlled Flight Into Terrain (CFIT), and how can it be avoided? CFIT is an unintended collision with the ground or an obstacle, often resulting from a total loss of situational awareness or attempting to descend below minimums during instrument procedures.
 Controlled Flight into Terrain: a top cause of fatal accidents
Controlled Flight into Terrain: a top cause of fatal accidents
15. Unintended VFR Flight Into IMC: A Deadly Mistake
Why is flying into instrument meteorological conditions (IMC) under visual flight rules (VFR) so hazardous? Accidents caused by flying visually into clouds or low visibility had a 71% fatality rate in 2021. Poor instrument flight rules (IFR) technique and icing conditions can be deadly. Flying in IMC requires pilots to be highly skilled, and often, canceling the flight is the safest option.
16. Key Safety Measures and Best Practices in Aviation
What safety measures can reduce the risk in general aviation? Proficiency, going beyond legal minimums, is crucial. Instructional flights are safer due to supervised environments, structured operations, high maintenance standards, and more proficient instructors. Modeling a safety mindset can significantly enhance flight safety.
17. The Importance of Structured Flight Operations
Why are structured flight operations safer? Flight schools and airlines operate with structured, risk-averse practices. Flight schools maintain their aircraft to high standards, undergoing inspections every 100 hours, unlike many personal aircraft. Airlines have highly trained and proficient pilots who adhere to strict safety protocols.
18. How Can Pilots Enhance Their Proficiency?
What steps can pilots take to improve their proficiency? Regularly practicing maneuvers, staying updated on safety procedures, and seeking continuous training can significantly enhance a pilot’s skills. Additionally, participating in flight reviews and attending safety seminars can help pilots stay sharp and informed.
19. The Impact of Decision-Making on Flight Safety
How does decision-making affect flight safety? Sound decision-making is crucial for safe flying. Pilots must evaluate weather conditions, aircraft performance, and their own capabilities before each flight. Avoiding pressure to fly when conditions are unfavorable and making conservative choices can prevent many accidents.
20. Incorporating Advanced Technology for Enhanced Safety
How can advanced technology improve aviation safety? Advanced avionics, such as autopilot systems, electronic flight instrument systems (EFIS), and GPS navigation, enhance situational awareness and reduce pilot workload. These technologies provide pilots with better information and assistance, making flying safer and more efficient.
21. The Role of Regular Aircraft Maintenance in Safety
Why is regular aircraft maintenance vital for flight safety? Properly maintained aircraft are less likely to experience mechanical failures. Regular inspections, timely repairs, and adherence to maintenance schedules ensure that aircraft are in optimal condition. This proactive approach significantly reduces the risk of accidents caused by mechanical issues.
22. Understanding and Mitigating Weather-Related Risks
How can pilots mitigate weather-related risks? Weather plays a significant role in aviation safety. Pilots should thoroughly assess weather conditions before and during flights. Understanding weather patterns, receiving accurate weather briefings, and using onboard weather radar systems help pilots make informed decisions and avoid hazardous weather.
23. The Significance of Risk Management in Aviation
Why is risk management essential for pilots? Effective risk management involves identifying potential hazards and implementing strategies to mitigate them. Pilots should use tools like the FAA Risk Assessment Matrix to evaluate risks and make informed decisions. By systematically assessing risks, pilots can reduce the likelihood of accidents and enhance overall safety.
24. Emphasizing the Importance of Continuous Learning
How does continuous learning contribute to aviation safety? The aviation industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies and procedures emerging regularly. Continuous learning ensures that pilots stay updated on the latest advancements, best practices, and safety recommendations. This commitment to learning helps pilots maintain their proficiency and adapt to new challenges.
25. Promoting a Safety Culture in Aviation
How can a safety culture improve aviation practices? A strong safety culture encourages open communication, reporting of errors, and a proactive approach to safety. When pilots and other aviation professionals feel comfortable discussing safety concerns and sharing lessons learned, the entire industry benefits. A positive safety culture reduces accidents and enhances overall performance.
26. Exploring the Safety Benefits of Flight Simulators
How do flight simulators enhance pilot training and safety? Flight simulators provide a safe and controlled environment for pilots to practice various scenarios, including emergencies. Simulators allow pilots to refine their skills, improve their decision-making abilities, and become more comfortable handling challenging situations without the risks associated with real flight.
27. The Role of Aviation Organizations in Promoting Safety
How do aviation organizations contribute to safety? Organizations such as the AOPA and the FAA play a crucial role in promoting aviation safety. They provide resources, training programs, and regulatory guidance to help pilots and other aviation professionals stay informed and proficient. These organizations also conduct research and analyze accident data to identify trends and develop strategies for reducing accidents.
28. Debunking Common Myths About Aviation Safety
What are some common misconceptions about aviation safety? Many people believe that all aviation is inherently dangerous, but commercial aviation is statistically very safe. Another myth is that pilot error is unavoidable; in reality, proactive training and risk management can significantly reduce pilot-related accidents. By debunking these myths, we can promote a more accurate understanding of aviation safety.
29. Highlighting Success Stories in Aviation Safety
What examples demonstrate successful improvements in aviation safety? Over the years, advancements in technology, training, and regulation have led to significant improvements in aviation safety. The introduction of modern avionics, enhanced training programs, and stricter regulatory standards have all contributed to reducing accident rates. By highlighting these success stories, we can inspire continued efforts to improve safety.
30. Encouraging Proactive Safety Measures for All Pilots
How can pilots take a proactive approach to safety? Pilots should conduct thorough pre-flight inspections, meticulously plan their flights, and adhere to all safety regulations. They should also prioritize continuous learning, participate in safety seminars, and stay updated on the latest aviation news and recommendations. By taking these proactive steps, pilots can significantly reduce their risk and contribute to a safer aviation environment.
31. The Financial Impact of Aviation Accidents
What are the economic consequences of aviation accidents? Aviation accidents can result in significant financial losses, including aircraft damage, medical expenses, and liability claims. These costs can be substantial for pilots, aircraft owners, and insurance companies. Investing in safety measures and training can help reduce the likelihood of accidents and minimize these financial burdens.
32. The Emotional Toll of Aviation Accidents
How do aviation accidents affect those involved emotionally? Beyond the physical and financial consequences, aviation accidents can have a profound emotional impact on pilots, passengers, and their families. Dealing with the aftermath of an accident can be traumatic and may require professional support. Emphasizing safety and preventing accidents can help minimize this emotional toll.
33. Promoting Ethical Decision-Making in Aviation
Why is ethical decision-making essential for aviation safety? Ethical decision-making involves making choices that prioritize safety and integrity. Pilots should be committed to upholding the highest ethical standards in their decision-making process, even when faced with pressure or challenging circumstances. Promoting ethical decision-making helps ensure that safety remains the top priority in all aviation activities.
34. Staying Informed with Aviation News and Updates
How can pilots stay informed about the latest aviation news and updates? Staying updated on aviation news is crucial for pilots to remain aware of safety alerts, regulatory changes, and industry trends. Pilots can subscribe to aviation publications, follow aviation organizations on social media, and attend industry events to stay informed. This knowledge helps pilots make informed decisions and maintain their proficiency.
35. The Importance of Reporting Safety Concerns
Why is it important for pilots to report safety concerns? Reporting safety concerns helps identify potential hazards and prevent accidents. Pilots should feel comfortable reporting any issues or concerns they have, whether related to aircraft maintenance, air traffic control, or airport operations. A culture of open reporting promotes transparency and continuous improvement in aviation safety.
36. Leveraging Aviation Safety Resources and Tools
What resources and tools are available to enhance aviation safety? Numerous resources and tools can assist pilots in enhancing their safety practices. These include flight planning software, weather briefing services, safety checklists, and online training modules. Leveraging these resources can help pilots make more informed decisions and reduce their risk.
37. The Future of Aviation Safety Technologies
What innovations are on the horizon for aviation safety technologies? The future of aviation safety is being shaped by innovative technologies such as advanced sensor systems, artificial intelligence, and autonomous flight capabilities. These technologies have the potential to further reduce accident rates and enhance overall safety. As these technologies continue to develop, they will play an increasingly important role in the aviation industry.
38. Addressing Fatigue and Its Impact on Pilot Performance
How does fatigue affect pilot performance, and what can be done to mitigate it? Fatigue can significantly impair pilot performance, leading to errors in judgment, reduced reaction times, and decreased situational awareness. Pilots should prioritize getting adequate rest before flights and implement strategies for managing fatigue during long flights. Proper rest and fatigue management are crucial for maintaining safety.
39. The Role of Air Traffic Control in Ensuring Safety
How does air traffic control contribute to aviation safety? Air traffic control plays a vital role in ensuring the safe and efficient flow of air traffic. Air traffic controllers provide guidance and support to pilots, helping them navigate through the airspace and avoid potential conflicts. Effective communication and coordination between pilots and air traffic controllers are essential for maintaining safety.
40. Encouraging Community Involvement in Aviation Safety
How can the aviation community contribute to safety improvements? The aviation community, including pilots, mechanics, air traffic controllers, and other professionals, can contribute to safety improvements by sharing their knowledge, experiences, and best practices. Collaboration and open communication within the community promote a culture of safety and continuous improvement.
41. Is Flying Safer Than Driving? Drawing a Conclusion
So, is flying safer than driving? While commercial air travel remains incredibly safe, general aviation, particularly personal flights, carries a higher risk. By understanding the risk factors and adopting robust safety measures, pilots can significantly reduce the likelihood of accidents. Remember, proficiency, sound decision-making, and continuous learning are your best defenses in the sky.
Visit flyermedia.net to explore aviation training options, read the latest aviation news, and discover career opportunities in the field. Whether you’re an aspiring pilot or a seasoned aviator, flyermedia.net provides the resources you need to enhance your knowledge and pursue your passion for flight.
FAQ: Common Questions About Aviation Safety
1. Is it safer to fly or drive in bad weather?
Generally, it is safer to drive in bad weather, provided you adjust your driving to the conditions. Flying in bad weather significantly increases risk due to potential icing, turbulence, and reduced visibility.
2. What are the safest airlines to fly with?
Airlines with modern fleets, rigorous maintenance schedules, and comprehensive pilot training programs are generally considered the safest. Research airlines’ safety records to make informed choices.
3. How can I reduce my fear of flying?
Understanding the safety measures in place, learning about the technology behind air travel, and using relaxation techniques can help reduce fear of flying.
4. What is the role of the FAA in ensuring aviation safety?
The FAA sets and enforces regulations for aviation safety, including aircraft maintenance, pilot training, and air traffic control. They also investigate accidents and work to prevent future incidents.
5. What should I do in case of an emergency during a flight?
Listen carefully to the crew’s instructions and follow their guidance. Familiarize yourself with the location of emergency exits and safety equipment before takeoff.
6. Are smaller planes less safe than larger planes?
Smaller planes, typically used in general aviation, have a higher accident rate per flight hour than larger commercial airliners due to differences in pilot training, maintenance, and operational environments.
7. What are the main causes of airplane crashes?
The main causes of airplane crashes include pilot error, mechanical failures, weather-related issues, and air traffic control errors.
8. How often do planes undergo maintenance checks?
Commercial planes undergo regular maintenance checks, ranging from pre-flight inspections to more extensive checks every few hundred flight hours. General aviation aircraft maintenance schedules vary.
9. What are the chances of surviving a plane crash?
Survival rates in plane crashes vary widely depending on the severity of the crash, the location, and the response time of emergency services. However, modern aviation safety features significantly increase the chances of survival.
10. What can passengers do to improve their safety during a flight?
Passengers can improve their safety by listening to the pre-flight safety briefing, keeping their seatbelts fastened, and following the crew’s instructions during emergencies.
Address: 600 S Clyde Morris Blvd, Daytona Beach, FL 32114, United States.
Phone: +1 (386) 226-6000.
Website: flyermedia.net.
Remember to visit flyermedia.net for more information on aviation training, news, and career opportunities. Your dream of flying starts here!
